Carbon price
Carbon pricing (or CO2 pricing) is a method for nations to address climate change. The cost is applied to greenhouse gas emissions in order to encourage polluters to reduce the combustion of coal, oil and gas – the main driver of climate change. The method is widely agreed[1] and considered to be efficient. Carbon pricing seeks to address the economic problem that emissions of CO2 and other greenhouse gases (GHG) are a negative externality – a detrimental product that is not charged for by any market.
| Part of a series on |
| Climate change and society |
|---|
A carbon price usually takes the form of a carbon tax or a Cap and Trade system (generally via an emissions trading scheme (ETS)), a requirement to purchase allowances to emit.[2][3]
21.7% of global GHG emissions are covered by carbon pricing in 2021, a major increase due to the introduction of the Chinese national carbon trading scheme.[4][5] Regions with carbon pricing include most European countries and Canada. On the other hand, top emitters like India, Russia, the Gulf states and many US states have not yet introduced carbon pricing.[6] Australia had a carbon pricing scheme from 2012 to 2014. In 2020, carbon pricing generated $53bn in revenue.[7]
According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, a price level of $135–5500 in 2030 and $245–13,000 per ton CO2 in 2050 would be needed to drive carbon emissions to stay below the 1.5°C limit.[8]
Latest models of the social cost of carbon calculate a damage of more than $3000/tCO2 as a result of economy feedbacks and falling global GDP growth rates, while policy recommendations range from about $50 to $200.[9] Many carbon pricing schemes including the ETS in China remain below $10/tCO2.[5] One exception is the European Union Emissions Trading System (EU-ETS) which exceeded 100€/tCO2 ($118) in February 2023.[10]
A carbon tax is generally favoured on economic grounds for its simplicity and stability, while cap-and-trade theoretically offers the possibility to limit allowances to the remaining carbon budget. Current implementations are only designed to meet certain reduction targets.
Purposes
Carbon pricing is considered by many economists to be the most efficient way to reduce emissions.[2] This means that it reduces emissions for the least possible cost, where these costs include the cost of efficiency measures as well as the cost of the inconvenience of making do with less of the goods and services provided by fossil fuels. This efficiency comes about by eliminating a market failure (the un-priced external costs of carbon emissions) at its source – by pricing these costs.[11]
Economics points out that since regulators would have an extremely hard time finding out the value that each emitter receives from emitting,[lower-alpha 1] this efficient outcome is extremely unlikely if the regulator chooses who can emit and who cannot. This is why economics teaches that command and control regulation will not be efficient, and will be less efficient than a market mechanism, such as carbon pricing. In the words of the IPCC, "[renewable energy subsidies] are less efficient alternatives to carbon taxes and emissions trading for inducing mitigation" (section 3.8.1.2).[12]
Concepts
| Part of a series on |
| Climate change and society |
|---|
Emissions Trading

In a cap-and-trade design, the market for permits automatically adjusts the carbon price to a level that insures that the cap is met.[13][14] The government establishes an emissions cap, for example 1000 tCO2 per year. Then it either gives the allowances to stakeholders, or auctions them off to the highest bidder. After the permits have been distributed, they can be traded privately. Emitters without the required allowances face a penalty that would cost more than buying permits. If the cap is low, permits will be in short supply (scarcity) and the price of permits will be high.
The EU ETS uses this method. In practice it resulted in a fairly strong carbon price from 2005 to 2009, but that was later undermined by an oversupply as well as by the Great Recession. Recent policy changes have led to a steep increase of the carbon price since 2018, exceeding 100€/tCO2 ($118) in February 2023.[10]
Carbon tax

| Part of a series on |
| Climate change and society |
|---|
A carbon tax is a tax levied on the carbon emissions required to produce goods and services. Carbon taxes are intended to make visible the "hidden" social costs of carbon emissions, which are otherwise felt only in indirect ways like more severe weather events. In this way, they are designed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by increasing prices of the fossil fuels that emit them when burned. This both decreases demand for goods and services that produce high emissions and incentivizes making them less carbon-intensive.[15] In its simplest form, a carbon tax covers only CO2 emissions; however, it could also cover other greenhouse gases, such as methane or nitrous oxide, by taxing such emissions based on their CO2-equivalent global warming potential.[16] When a hydrocarbon fuel such as coal, petroleum, or natural gas is burned, most or all of its carbon is converted to CO
2. Greenhouse gas emissions cause climate change, which damages the environment and human health. This negative externality can be reduced by taxing carbon content at any point in the product cycle.[17][18][19][20] Carbon taxes are thus a type of Pigovian tax.[21]
Hybrid designs
Cap-and-trade systems can include price stability provisions with floor and ceiling limits.[31] Such designs are often referred to as hybrid designs.[12]: 47 To the extent the price is controlled by these limits, it can be considered a tax.
Carbon tax versus emissions trade
Carbon emissions trading works by setting a quantitative limit on the emissions produced by emitters. As a result, the price automatically adjusts to this target. This is the main advantage compared to a fixed carbon tax. A carbon tax is considered easier to enforce on a broad-base scale than cap-and-trade programs. The simplicity and immediacy of a carbon tax has been proven effective in British Columbia, Canada – enacted and implemented in five months.[32] A hybrid cap-and-trade program puts a limit on price increases and, in some cases, sets a floor price as well. The upper limit is set by adding more allowances to the market at a set price while the floor price is maintained by not allowing sales into the market at a price below the floor.[33] The Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative, for example, sets an upper limit on allowance prices through its cost containment provision.
However, industries may successfully lobby to exempt themselves from a carbon tax. It is therefore argued that with emissions trading, polluters have an incentive to cut emissions, but if they are exempted from a carbon tax, they have no incentive to cut emissions.[34] On the other hand, freely distributing emission permits could potentially lead to corrupt behaviour.[35]
Most cap and trade programs have a descending cap, usually a fixed percentage every year, which gives certainty to the market and guarantees that emissions will decline over time. With a tax, there can be estimates of reduction in carbon emissions, which may not be sufficient to change the course of climate change. A declining cap gives allowance for firm reduction targets and a system for measuring when targets are met. It also allows for flexibility, unlike rigid taxes.[32] Providing emission permits (also called allowances) under emissions trading is preferred in situations where a more accurate target level of emissions certainty is needed.[36]
Revenue policies
Standard proposals for using carbon revenues include
- a return to the public on a per-capita basis[37] This can compensate the risk of rising energy prices reaching high levels as long as cheap wind and solar power is not available yet. Rich people who tend to have a larger carbon footprint would pay more while poorer people can even benefit from such a regulation.
- subsidies accelerating the transition to renewable energy
- research, public transport, car sharing and other policies that promote carbon neutrality
- subsidies for negative emissions: Depending on the technology, such as PyCCS or BECCS, the cost for generating negative emissions is about $150–165 per ton of CO2.[38] The removal past emissions – 1,700 Gt in total[39] – can theoretically be addressed by auctioning allowances starting with a price that exceeds the removal costs of the proposed emissions.
Social cost of carbon
The exact monetary damage caused by a tonne of CO2 depends on climate and economic feedback effects and remains to some degree uncertain. Latest calculations show an increasing trend. Dynamic models include discount rates. This results in lower costs in the current state and higher costs once that carbon budgets are used up.
| Source | Year | carbon price per tCO2 | remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Interagency Working Group (US government)[40] | 2013 / 2016 | $42 | Central estimate for 3% discount rate in 2020 |
| $212 | high impact value for 2050 / 3% discount / 95th percentile | ||
| German Environmental Agency[41] | 2019 | $213 (180 €) | with 1% time preference |
| $757 (640 €) | without time preference | ||
| Kikstra et al.[9] | 2021 | $3372 | including economic feedbacks |
Price levels
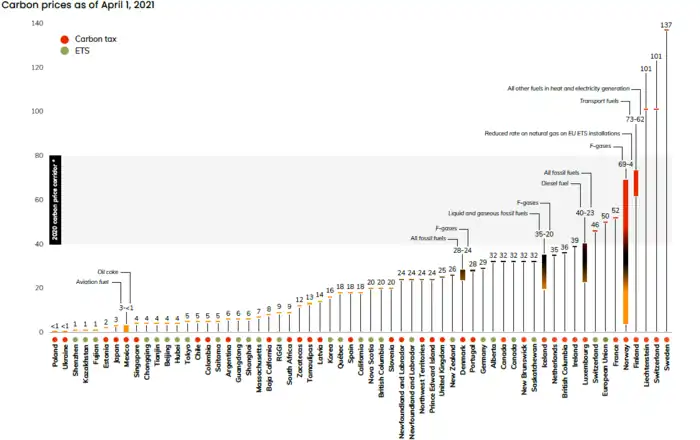
About one third of the systems stays below $10/tCO2, the majority is below $40. One exception is the steep incline in the EU-ETS reaching $60 in September 2021. Sweden and Switzerland are the only countries with more than $100/tCO2.
Market price surge in fossil fuels
Unexpected spikes in natural gas prices and commodities such as oil and coal in 2021 caused a debate whether a carbon price increase should be postponed to avoid additional social burden. On the other hand, a redistribution on a per-capita-basis would even release poorer households which tend to consume less energy compared to wealthier parts of the population. The higher the high carbon price the greater the relief. Looking at individual situations though, the compensation would not apply to commuters in rural areas or people living in houses with poor insulation. They neither have liquidity to invest into solutions using less fossil fuels and would be dependent on credits or subsidies. If the fossil price surge persists, the necessity for an additional carbon price to gain competitiveness for renewable energies comes into question. On the other hand, a carbon price still helps to provide an incentive to use more effective fossil fuel technologies such as CCGT gas turbines in contrast to high-emission coal.[43]
Scope and coverage
In the relevant countries with ETS and taxes, about 40% to 80% of emissions are covered.[44] The schemes differ much in detail. They include or exclude fuels, transport, heating, agriculture or other greenhouse gases apart from CO2 like methane or fluorinated gases.[45] In many EU member states like France or Germany, there is a coexistence of two systems: The EU-ETS covers power generation and large industry emissions while national ETS or taxes put a different price on petrol, natural gas and oil for private consumption.
| country / region | type | share[44] | coverage / remarks[46] | revenue 2020[44] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EU | ETS | 39% | industry, electricity, intra-EU aviation | $22.5 bn |
| China | ETS | 40% | electricity, district heating | launched 2021 |
| Canada | tax | 22% | National pricing in Canada, additional taxes and ETS in provinces | $3.4 bn |
| France | tax | 35% | non EU-ETS | $9.6 bn |
| Germany | ETS | 40% | non EU-ETS: transport, heating | $ 8.75 bn (€7.4 bn) expected, launch 2021[47] |
| Japan | tax | 75% | $2.4 bn | |
| Sweden | tax | 40% | transport, buildings, industry, agriculture[48] | $2.3 bn |
Other taxes and price components
The final consumer price for fuels and electric energy depends on individual tax regulations and conditions in each country. Though carbon pricing is playing an increasing role, energy taxes, VAT, utility expenses and other components are still the main cause for completely different price levels between countries.
Impact on retail prices
The table gives examples for a carbon price of $100 or 100 units of any other currency accordingly. Food calculation is all based on CO2 equivalents including the high impact of methane emissions.
| FUEL[49] | impact |
|---|---|
| 1 L petrol | $0.24 |
| 1 L diesel | $0.27 |
| TRANSPORT[49] | impact | remarks |
|---|---|---|
| 500 km car travel, 1 passenger | $8.40 | 7 L petrol per 100 km |
| 500 km jet aircraft per seat | $6.70 | 0.134 kgCO2/km, Domestic flight NZ, A320, 173 seats, all occupied, with radiative forcing multiplier[50] |
| 500 km small aircraft per seat | $32.95 | 0.659 kgCO2/km, Domestic flight NZ, less than 50 seats, all occupied[50] |
| 5000 km jet aircraft, economy class, per seat | $76.50 | 0.153 kgCO2/km, >3700 km[51] |
| 5000 km jet aircraft, first class, per seat | $292.50 | 0.585 kgCO2/km, >3700 km[51] |
| ELECTRICITY[52] | impact |
|---|---|
| 1 kWh lignite | $0.11 |
| 1 kWh hard coal | $0.10 |
| 1 kWh natural gas | $0.06 |
| 1 kWh natural gas (CCGT) | $0.04 |
| HEAT[53] | impact |
|---|---|
| 1 KWh from natural gas | $0.02 |
| 1 KWh from light fuel oil | $0.03 |
| 1 L light fuel oil | $0.29 |
| FOOD | at farm gate | life cycle assessment | source / remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 kg lamb | $2.04 | $3.92 | [54] |
| 1 kg beef | $1.52 | $2.70 | $33.50 with land-use in tropical rain forests[54] |
| 1 kg butter | $1.47 | [55] | |
| 1 kg cheese | $0.98 | $1.35 | [54] |
| 1 kg pork | $0.46 | $1.21 | [54] |
| 1 kg rice | $0.24 | $0.27 | white rice[56] |
| 1 kg chicken | $0.23 | $0.69 | [54] |
| 1 kg fish | $0.41 | $0.61 | salmon / canned tuna[54] |
| 1 kg eggs | $0.20 | $0.41 | 100 g per egg[54] |
| 1 kg nuts | $0.13 | $0.23 | [56] |
| 1 L milk | $0.11 | $0.19 | 2% fat[54] |
| 1 kg tofu | $0.07 | $0.20 | [56] |
| 1 kg potatoes | $0.03 | $0.29 | Eastern Idaho[57] |
Economics
| Part of a series about |
| Environmental economics |
|---|
 |
Many economic properties of carbon pricing hold regardless of whether carbon is priced with a cap or a tax. However, there are a few important differences. Cap-based prices are more volatile and so they are riskier for investors, consumers and for governments that auction permits. Also, caps tend to short-out the effect of non-price policies such as renewables subsidies, while carbon taxes do not.
Carbon leakage
Carbon leakage is the effect that regulation of emissions in one country/sector has on the emissions in other countries/sectors that are not subject to the same regulation.[58] There is no consensus over the magnitude of long-term carbon leakage.[59]
The leakage rate is defined as the increase in CO2 emissions outside the countries taking domestic mitigation action, divided by the reduction in emissions of countries taking domestic mitigation action. Accordingly, a leakage rate greater than 100% means that actions to reduce emissions within countries had the effect of increasing emissions in other countries to a greater extent, i.e., domestic mitigation action had actually led to an increase in global emissions.
Estimates of leakage rates for action under the Kyoto Protocol ranged from 5% to 20% as a result of a loss in price competitiveness, but these leakage rates were considered very uncertain.[58] For energy-intensive industries, the beneficial effects of Annex I actions through technological development were considered possibly substantial. However, this beneficial effect had not been reliably quantified. On the empirical evidence they assessed, Barker et al. (2007) concluded that the competitive losses of then-current mitigation actions, e.g., the EU-ETS, were not significant.
Under the EU ETS rules Carbon Leakage Exposure Factor is used to determine the volumes of free allocation of emission permits to industrial installations.
A general perception among developing countries is that discussion of climate change in trade negotiations could lead to green protectionism by high-income countries[60] Eco-tariffs on imports ("virtual carbon") consistent with a carbon price of $50 per ton of CO2 could be significant for developing countries. In 2010, World Bank commented that introducing border tariffs could lead to a proliferation of trade measures where the competitive playing field is viewed as being uneven. Tariffs could also be a burden on low-income countries that have contributed very little to the problem of climate change.
Interactions with renewable energy policies
Cap-and-trade and carbon taxes interact differently with non-price policies such as renewable energy subsidies. The IPCC explains this as follows:
A carbon tax can have an additive environmental effect to policies such as subsidies for the supply of RE. By contrast, if a cap-and-trade system has a binding cap (sufficiently stringent to affect emission-related decisions), then other policies such as RE subsidies have no further impact on reducing emissions within the time period that the cap applies [emphasis added].[61]: 29
Carbon pricing and economic growth
According to a 2020 study carbon prices have not harmed economic growth in wealthy industrialized democracies.[62]
In order for such a business model to become attractive, the subsidies would therefore have to exceed this value. Here, a technology openness could be the best choice, as a reduction in costs due to technical progress can be expected. Already today, these costs of generating negative emissions are below the costs of CO2 of $220 per ton,[63] which means that a state-subsidized business model for creating negative emissions already makes economic sense today. In sum, while a carbon price has the potential to reduce future emissions, a carbon subsidy has the potential to reduce past emissions.
Advantages and disadvantages
In late 2013, William Nordhaus, president of the American Economic Association, published The Climate Casino,[64] which culminates in a description of an international "carbon price regime". Such a regime would require national commitments to a carbon price, but not to a specific policy. Carbon taxes, caps, and hybrid schemes could all be used to satisfy such a commitment. At the same time Martin Weitzman, a leading climate economist at Harvard, published a theoretical study arguing that such a regime would make it far easier to reach an international agreement, while a focus on national targets would continue to make it nearly impossible.[65] Nordhaus also makes this argument, but less formally.
Similar views have previously been discussed by Joseph Stiglitz[66] and have previously appeared in a number of papers.[67] The price-commitment view appears to have gained major support from independent positions taken by the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund (IMF).[68]
The "Economists' Statement on Climate Change"[69] was signed by over 2500 economists including nine Nobel Laureates in 1997. This statement summarizes the economic case for carbon pricing as follows:
The most efficient approach to slowing climate change is through market-based policies. In order for the world to achieve its climatic objectives at minimum cost, a cooperative approach among nations is required – such as an international emissions trading agreement. The United States and other nations can most efficiently implement their climate policies through market mechanisms, such as carbon taxes or the auction of emissions permits.
This statement argues that carbon pricing is a "market mechanism" in contrast to renewable subsidies or direct regulation of individual sources of carbon emissions and hence is the way that the "United States and other nations can most efficiently implement their climate policies."
Carbon offsets for individuals[70] and businesses[71] may also be purchased through carbon offset retailers[72] like Carbonfund.org Foundation.
A new quantity commitment approach, suggested by Mutsuyoshi Nishimura, is for all countries to commit to the same global emission target.[73] The "assembly of governments" would issue permits in the amount of the global target and all upstream fossil-fuel providers would be forced to buy these permits.
In 2019 the UN Secretary General asked governments to tax carbon.[74]
The economics of carbon pricing is much the same for taxes and cap-and-trade. Both prices are efficient;[lower-alpha 2] they have the same social cost and the same effect on profits if permits are auctioned. However, some economists argue that caps prevent non-price policies, such as renewable energy subsidies, from reducing carbon emissions, while carbon taxes do not. Others argue that an enforced cap is the only way to guarantee that carbon emissions will actually be reduced; a carbon tax will not prevent those who can afford to do so from continuing to generate emissions.
Besides cap and trade, emission trading can refer to project-based programs, also referred to as a credit or offset programs. Such programs can sell credits for emission reductions provided by approved projects. Generally there is an additionality[75] requirement that states that they must reduce emissions more than is required by pre-existing regulation. An example of such a program is the Clean Development Mechanism under the Kyoto Protocol. These credits can be traded to other facilities where they can be used for compliance with a cap-and-trade program.[76] Unfortunately the concept of additionality is difficult to define and monitor, with the result that some companies purposefully increased emissions in order to get paid to eliminate them.[77]
Cap-and-trade programs often allow "banking" of permits. This means that permits can be saved and can be used in the future. This allows an entity to over-comply in early periods in anticipation of higher carbon prices in subsequent years.[78] This helps to stabilize the price of permits.[13]
Notes
- Emitters would all tend to claim I high value if asked by the regulator
- ignoring the riskiness of prices under caps
References
- Hagman, David; Ho, Emily; Loewenstein, George (June 2019). "Nudging out support for a carbon tax". Nature Climate Change. 9 (6): 484–489. Bibcode:2019NatCC...9..484H. doi:10.1038/s41558-019-0474-0. S2CID 182663891. Archived from the original on January 28, 2020. Retrieved September 3, 2019.
- "What is a carbon price and why do we need one?". London School of Economics. Archived from the original on May 15, 2019. Retrieved May 15, 2019.
- "What is Carbon Pricing? | Carbon Pricing Dashboard". carbonpricingdashboard.worldbank.org. Archived from the original on March 11, 2021. Retrieved March 14, 2021.
- World Bank 2021, p. 23
- Davies, Paul A.; Westgate, R. Andrew. "China's National ETS Launches Trading". Latham & Watkins. Retrieved September 7, 2021.
- "State and Trends of Carbon Pricing 2023" (PDF). World Bank Group. Retrieved June 2, 2023.
- World Bank 2021, p. 14
- IPCC SR15 Ch4 2018, p. 374
- Kikstra 2021, p. 22
- "Carbon Price Viewer". EMBER. Archived from the original on September 15, 2021. Retrieved September 7, 2021.
- N. Gregory Mankiw (2009). "Smart Taxes: An Open Invitation to Join the Pigou Club" (PDF). Eastern Economic Journal. Archived (PDF) from the original on August 16, 2014. Retrieved August 3, 2014.
- IPCC (2014). "Social, Economic and Ethical Concepts and Methods" (PDF). UN. Archived from the original (PDF) on June 29, 2014. Retrieved August 3, 2014.
- Robert N. Stavins (2007). "A U.S. Cap-and-Trade System to Address Global Climate Change" (PDF). The Hamilton Project. Retrieved March 31, 2019.
- EPA (2009). "Cap and Trade: Frequent Questions". Archived from the original on November 13, 2014. Retrieved August 3, 2014.
- Akkaya, Sahin; Bakkal, Ufuk (June 1, 2020). "Carbon Leakage Along with the Green Paradox Against Carbon Abatement? A Review Based on Carbon Tax". Folia Oeconomica Stetinensia. 20 (1): 25–44. doi:10.2478/foli-2020-0002. ISSN 1898-0198. S2CID 221372046. Archived from the original on August 29, 2020. Retrieved October 6, 2020.
- "Costs and Benefits to Agriculture from Climate Change Policy". www.card.iastate.edu. Archived from the original on July 27, 2020. Retrieved August 19, 2019.
- Bashmakov, I.; et al. (2001). "6.2.2.2.1 Collection Point and Tax Base". In B. Metz; et al. (eds.). Policies, Measures, and Instruments. Climate Change 2001: Mitigation. Contribution of Working Group III to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Print version: Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, and New York, N.Y., U.S.A.. This version: GRID-Arendal website. Archived from the original on December 28, 2013. Retrieved April 8, 2011.
- "Effects of a Carbon Tax on the Economy and the Environment". Congressional Budget Office. May 22, 2013. Archived from the original on September 29, 2017. Retrieved September 29, 2017.
- Kalkuhl, Matthias (September 2013). "Renewable energy subsidies: Second-best policy or fatal aberration for mitigation?" (PDF). Resource and Energy Economics. 35 (3): 217–234. doi:10.1016/j.reseneeco.2013.01.002. hdl:10419/53216. Archived (PDF) from the original on August 20, 2018. Retrieved August 20, 2018.
- Bashmakov, I.; et al. (2001). "Policies, Measures, and Instruments". In B. Metz; et al. (eds.). Climate Change 2001: Mitigation. Contribution of Working Group III to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, and New York, N.Y., U.S.A. Archived from the original on October 5, 2018. Retrieved May 20, 2009.
- Helm, D. (2005). "Economic Instruments and Environmental Policy". The Economic and Social Review. 36 (3): 4–5. Archived from the original on May 1, 2011. Retrieved April 8, 2011.
- "Carbon Taxes: What Can We Learn From International Experience?". Econofact. May 3, 2019. Archived from the original on May 7, 2019. Retrieved May 7, 2019.
- Gupta, S.; et al. (2007). "13.2.1.2 Taxes and charges". Policies, instruments, and co-operative arrangements. Climate Change 2007: Mitigation. Contribution of Working Group III to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (B. Metz et al. Eds.). Print version: Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, U.K., and New York, N.Y., U.S.A.. This version: IPCC website. Archived from the original on October 29, 2010. Retrieved March 18, 2010.
- "Carbon Taxes II". igmchicago.org. Archived from the original on November 26, 2016. Retrieved July 6, 2019.
- "Carbon Tax | IGM Forum". Archived from the original on November 26, 2016. Retrieved July 6, 2019.
- "Climate Change Policies". igmchicago.org. Archived from the original on November 18, 2018. Retrieved July 6, 2019.
- "ECONOMISTS' STATEMENT ON CARBON DIVIDENDS". clcouncil.org. 2019. Archived from the original on January 18, 2019. Retrieved February 18, 2019.
- "77 Countries, 100+ Cities Commit to Net Zero Carbon Emissions by 2050 at Climate Summit". Archived from the original on September 28, 2019. Retrieved September 24, 2019.
- World Bank Group (June 6, 2019). State and Trends of Carbon Pricing 2019 (Report). hdl:10986/31755. p. 24, Fig. 6
- World Bank Group (June 6, 2019). State and Trends of Carbon Pricing 2019 (Report). hdl:10986/31755. p. 21
- IMF (2014). "Factsheet: Climate, Environment, and the IMF" (PDF). International Monetary Fund. Archived (PDF) from the original on August 8, 2014. Retrieved August 2, 2014.
- Beinecke, Frances; Sachs, Jeffrey D.; Krupp, Fred; Pielke Jr., Roger A.; Stavins, Robert N.; Komanoff, Charles; Claussen, Eileen; Fischhoff, Baruch (May 7, 2009). "Putting a Price on Carbon: An Emissions Cap or a Tax? by". Yale Environment 360. Archived from the original on August 2, 2010. Retrieved August 6, 2010.
- "Carbon Pricing 101". Union of Concerned Scientists. Archived from the original on September 24, 2019. Retrieved October 11, 2019.
- Smith, S. (June 11, 2008). "Environmentally Related Taxes and Tradable Permit Systems in Practice" (PDF). OECD, Environment Directorate, Centre for Tax Policy and Administration. Retrieved April 26, 2010.
- World Bank (2010). "World Development Report 2010: Development and Climate Change" (PDF). The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development / The World Bank, 1818 H Street NW, Washington DC 20433. Archived (PDF) from the original on January 24, 2019. Retrieved November 12, 2014.
- Trade and climate change: WTO-UNEP Report. Geneve: WTO. 2009.
- Held, Benjamin (2019). "Carbon Dividend – An Instrument for a Socially Just Environmental and Climate Policy?". Wirtschaftsdienst (in German and English). 1: 53–60. doi:10.1007/s10273-019-2395-y. hdl:10419/213707. S2CID 159287863. Archived from the original on May 12, 2021. Retrieved May 11, 2021.
- Werner, C.; Schmidt, H-P; Gerten, D.; Lucht, W.; Kammann, C. (2018). "Biogeochemical potential of biomass pyrolysis systems for limiting global warming to 1.5 °C". Environmental Research Letters. 13 (4): 044036. Bibcode:2018ERL....13d4036W. doi:10.1088/1748-9326/aabb0e.
- Stainforth, Thorfinn (April 29, 2020). "More than half of all CO2 emissions since 1751 emitted in the last 30 years". IEEE.
- IWG 2016, p. 4
- Matthey, Astrid; Bünger, Björn (February 11, 2019). Methodological Convention 3.0 for the Assessment of Environmental Costs (PDF) (Report). German Environment Agency. p. 8. Archived (PDF) from the original on November 10, 2021. Retrieved September 13, 2021.
- World Bank 2021, p. 13
- Elkerbout, Milan (October 7, 2021). "Don't let high gas prices stop the EU ETS from doing its real job". Energy Post.
- World Bank 2021, pp. 29–30
- Asen, Elke. "Carbon Taxes in Europe 2020". Tax Foundation. Archived from the original on September 13, 2021. Retrieved September 13, 2021.
- "ICAP ETS-Map". ICAP. Archived from the original on August 31, 2021. Retrieved September 13, 2021.
- "Bund erwartet Rekorderlöse aus CO2-Rechten". Tagesschau (in German). ARD. August 2, 2021. Archived from the original on August 17, 2021.
- Ackva, Johannes; Hoppe, Janna. "The carbon tax in Sweden" (PDF). German Federal Ministry for the Environment, Nature Conservation and Nuclear Safety (BMU) / adelphi. Archived (PDF) from the original on April 13, 2021. Retrieved September 13, 2021.
- NZ Govt 2020, p. 22
- NZ Govt 2020, p. 60
- NZ Govt 2020, p. 64
- Quaschning 2021
- NZ Govt 2020, p. 20
- EWG 2011, p. 19,23
- WWF 2012
- EWG 2011, p. 45
- EWG 2011, p. 46
- Barker, T.; et al. (2007). "Mitigation from a cross-sectoral perspective". In B. Metz; et al. (eds.). Climate Change 2007: Mitigation. Contribution of Working Group III to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. IPCC. Archived from the original on June 8, 2011. Retrieved April 5, 2010.
- Goldemberg, J.; et al. (1996). "Introduction: scope of the assessment" (PDF). In J.P. Bruce; et al. (eds.). Climate Change 1995: Economic and Social Dimensions of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group III to the Second Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. IPCC. p. 31. ISBN 978-0-521-56854-8.
- "World Development Report 2010: Development and Climate Change" (PDF). World Bank. 2010. p. 251. Archived (PDF) from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved April 6, 2010.
- IPCC (2014). "IPCC 2014: Summary for Policymakers: Mitigation of Climate Change" (PDF). UN. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 2, 2014. Retrieved August 3, 2014.
- Driscoll, Daniel (January 2020). "Do Carbon Prices Limit Economic Growth?". Socius: Sociological Research for a Dynamic World. 6: 237802311989832. doi:10.1177/2378023119898326. ISSN 2378-0231.
- "Estimated social cost of climate change not accurate, Stanford scientists say". January 12, 2015. Archived from the original on June 24, 2019. Retrieved June 24, 2019.
- William D. Nordhaus (2013). The Climate Casino. Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0300189773.
- Martin Weitzman (2013). "Can Negotiating a Uniform Carbon Price Help to Internalize the Global Warming Externality?". World Bank. Archived from the original on October 20, 2014. Retrieved August 1, 2014.
- Joseph Stiglitz (2010). "Overcoming the Copenhagen Failure". Project Syndicate. Archived from the original on August 12, 2014. Retrieved July 26, 2014.
- "A Compete Collection of Carbon-Price-Commitment Papers". Archived from the original on August 11, 2014. Retrieved August 4, 2014.
- Davenport, Coral (April 23, 2016). "Carbon Pricing Becomes a Cause for the World Bank and I.M.F." The New York Times. Archived from the original on April 24, 2016. Retrieved April 25, 2016.
- Nine Nobel Laureates (1997). "Economists' Statement on Climate Change". Redefining Progress. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved February 25, 2014.
- "For Individuals - Offset Your Carbon Footprint". Carbonfund.org. Archived from the original on July 16, 2021. Retrieved July 21, 2021.
- "For Businesses - Offset Your Corporate Footprint". Carbonfund.org. Archived from the original on July 21, 2021. Retrieved July 21, 2021.
- "Carbon Offset Retailer". Carbonfund.org. Archived from the original on July 21, 2021. Retrieved July 21, 2021.
- Mutsuyoshi Nishimura (2014). "A new market-based solution achieving 2C and equity". Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Energy and Environment. 4: 133–138. doi:10.1002/wene.131.
- "Tax carbon, not people: UN chief issues climate plea from Pacific 'frontline'". The Guardian. May 15, 2019. Archived from the original on May 15, 2019. Retrieved May 15, 2019.
- Benito Müller (2009). "Additionality in the Clean Development Mechanism" (PDF). Oxford Institute for Energy Studies. Archived (PDF) from the original on August 10, 2014. Retrieved July 26, 2014.
- Types of Trading Archived October 25, 2012, at the Wayback Machine. Clean Air Market Programs. Retrieved July 8, 2012.
- Szabo, Michael (June 14, 2010). "Firms abusing Kyoto carbon trading scheme: watchdog". Reuters. Retrieved August 5, 2010.
- Cap and trade programs for greenhouse gas. iasplus.com
Sources
- IPCC (2018). Masson-Delmotte, V.; Zhai, P.; Pörtner, H.-O.; Roberts, D.; et al. (eds.). Global Warming of 1.5°C. An IPCC Special Report on the impacts of global warming of 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels and related global greenhouse gas emission pathways, in the context of strengthening the global response to the threat of climate change, sustainable development, and efforts to eradicate poverty (PDF). Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Global Warming of 1.5 °C —.
- de Coninck, H.; Revi, A.; Babiker, M.; Bertoldi, P.; et al. (2018). "Chapter 4: Strengthening and Implementing the Global Response" (PDF). IPCC SR15 2018. pp. 313–443.
- Kikstra, Jarmo S; Waidelich, Paul; Rising, James; Yumashev, Dmitry; Hope, Chris; Brierley, Chris M (September 6, 2021). "The social cost of carbon dioxide under climate-economy feedbacks and temperature variability". Environmental Research Letters. 16 (9): 094037. Bibcode:2021ERL....16i4037K. doi:10.1088/1748-9326/ac1d0b. S2CID 237427400.
- Bank, World (2021). State and Trends of Carbon Pricing 2021. The World Bank. doi:10.1596/978-1-4648-1728-1. ISBN 978-1-4648-1728-1. S2CID 242987579.
- "Technical Update of the Social Cost of Carbon for Regulatory Impact Analysis Under Executive Order 12866" (PDF). Interagency Working Group on Social Cost of Greenhouse Gases (US govt.). 2016. Retrieved September 12, 2021.
- "Measuring Emissions: A Guide for Organisations" (PDF). Ministry for the environment, New Zealand. 2020.
- Quaschning, Volker. "Specific Carbon Dioxide Emissions of Various Fuels". Retrieved September 23, 2021.
- "Meat Eater's Guide" (PDF). Environmental Working Group. 2011.
- Noleppa, Steffen (2012). "Klimawandel auf dem Teller" (PDF) (in German). WWF Germany. Archived from the original (PDF) on November 1, 2020.
External links
- Our Climate Put A Price On It campaign
- CDM Rulebook — Defines Kyoto commitments
- UN Climate Change Framework — Lists national commitments for 2020
- Pricing Carbon Initiative — US focused effort for carbon-pricing commitments