Alpha Herculis
Alpha Herculis (α Herculis, abbreviated Alpha Her, α Her), also designated 64 Herculis, is a multiple star system in the constellation of Hercules. Appearing as a single point of light to the naked eye, it is resolvable into a number of components through a telescope. It has a combined apparent magnitude of 3.08, although the brightest component is variable in brightness. Based on parallax measurements obtained during the Hipparcos mission, it is approximately 360 light-years (110 parsecs) distant from the Sun.
 | |
| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Hercules |
| A | |
| Right ascension | 17h 14m 38.853s[1] |
| Declination | +14° 23′ 25.34″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 3.350[1] (2.7–4.0[2]) |
| B | |
| Right ascension | 17h 14m 39.181s[1] |
| Declination | +14° 23′ 23.98″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 5.322[1] |
| Characteristics | |
| A | |
| Evolutionary stage | AGB[3] |
| Spectral type | M5 Ib-II[3] |
| U−B color index | +1.01[4] |
| B−V color index | +1.45[4] |
| Variable type | SRc[2] |
| B | |
| Spectral type | G8III + A9IV-V[3] |
| Astrometry | |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −7.32[5] mas/yr Dec.: 36.07[5] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 9.07 ± 1.32 mas[5] |
| Distance | approx. 360 ly (approx. 110 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −2.3[6] + 1.8 + 2.8[7] |
| Details | |
| A | |
| Mass | 2.5+1.6 −1.1[8] M☉ |
| Radius | 284 ± 60, 264–303[3] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 7,244–9,333[3] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | −0.41±0.19[9] cgs |
| Temperature | 3,155–3,365[3] K |
| Ba | |
| Mass | ~2.5[3] M☉ |
| Luminosity | 126[3] L☉ |
| Temperature | 4,900[3] K |
| Bb | |
| Mass | ~2[3] M☉ |
| Luminosity | 26[3] L☉ |
| Temperature | 7,350[3] K |
| Age | 0.41–1.25[3] Gyr |
| Other designations | |
| A: HD 156014, HR 6406, SAO 102680 | |
| B: HD 156015, HR 6407, SAO 102681 | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | α Her |
| A | |
| B | |
System

Alpha Herculis is a triple star system. The primary (brightest) of the three stars, designated α1 Herculis or α Herculis A, is a pulsating variable star on the asymptotic giant branch (AGB), and is the second nearest AGB star after Mira. The primary star forms a visual binary pair with a second star, which is itself a spectroscopic binary.[3]
Alpha Herculis also forms the A and B components of a wider system designated WDS J17146+1423, with two additional faint visual companions designated WDS J17146+1423C and D.[11] The two fainter stars are far more distant than the triple system.[12]
Nomenclature
α Herculis (Latinised to Alpha Herculis) is the system's Bayer designation; α1 and α2 Herculis, those of its two visible components. 64 Herculis is the system's Flamsteed designation. WDS J17146+1423 is the wider system's designation in the Washington Double Star Catalog. The designations of Alpha Herculis' main components as Alpha Herculis A and B and the wider system's four components as WDS J17146+1423A, B, C and D, together with the spectroscopic pair - Alpha Herculis Ba and Bb - derive from the convention used by the Washington Multiplicity Catalog (WMC) for multiple star systems, and adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU).[13]
Alpha Herculis bore the traditional name Rasalgethi or Ras Algethi (Arabic: رأس الجاثي ra‘is al-jāthī 'Head of the Kneeler').[14] 'Head' comes from the fact that in antiquity Hercules was depicted upside down on maps of the constellation. In 2016, the IAU organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN)[15] to catalog and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN approved the name Rasalgethi for the component Alpha Herculis A (α1) on 30 June 2016 and it is now so included in the List of IAU-approved Star Names.[15]
The term ra's al-jaθiyy or Ras al Djathi appeared in the catalogue of stars in the Calendarium of Al Achsasi al Mouakket, which was translated into Latin as Caput Ingeniculi.[16]
In Chinese astronomy, Alpha Herculis is called 帝座, Pinyin: Dìzuò, meaning 'Emperor's Seat'. The star is seen as marking itself, and stands alone in the center of the Emperor's Seat asterism, Heavenly Market enclosure (see: Chinese constellations).[17] 帝座 (Dìzuò) was westernized into Ti Tso by R.H. Allen, with the same meaning [18]
Properties
Alpha Herculis A and B are more than 500 AU apart, with an estimated orbital period of approximately 3600 years. A presents as a relatively massive red bright giant, but radial velocity measurements suggest a companion with a period of the order of a decade.[11] B's two components are a primary yellow giant star and a secondary, yellow-white dwarf star in a 51.578 day orbit.[20]
Alpha Herculis A is an asymptotic giant branch (AGB) star, a luminous red giant that has both hydrogen and helium shells around a degenerate carbon-oxygen core. It is the second nearest AGB star to the Sun.[3] The angular diameter of the star has been measured with an interferometer as 34 ± 0.8 mas, or 0.034 arcseconds.[21] At its estimated distance of 110 parsecs this corresponds to a radius of about 280 million kilometers (or 170 million miles), which is roughly 400 R☉ or 1.87 AU.[lower-alpha 1] If Alpha Herculis were at the center of the Solar System its radius would extend past the orbit of Mars at 1.5 AU but not quite as far as the asteroid belt. The red giant is estimated to have started its life with about 2.175-3.250 M☉.[3]
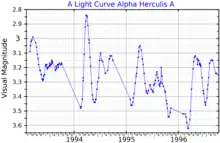
Alpha Herculis A has been specified as a standard star for the spectral class M5 Ib-II.[3] Like most type M stars near the end of their lives, Alpha Herculis is experiencing a high degree of stellar mass loss creating a sparse, gaseous envelope that extends at least 930 AU.[20] It is a semiregular variable with complex changes in brightness with periods ranging from a few weeks to many years. The most noticeable variations occur at timescales of 80–140 days and at 1,000 - 3,000 days. The strongest detectable period is 128 days.[22] The full range in brightness is from magnitude 2.7 to 4.0,[2] but it usually varies over a much smaller range of around 0.6 magnitudes.[22]
Notes
- To determine Rasalgethi's radius in terms of solar units, the calculations begin with the formula for angular diameter as follows:
- .
- .
- (rounded).
References
- Høg, E.; Fabricius, C.; Makarov, V. V.; Urban, S.; Corbin, T.; Wycoff, G.; Bastian, U.; Schwekendiek, P.; Wicenec, A. (2000). "The Tycho-2 catalogue of the 2.5 million brightest stars". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 355: L27. Bibcode:2000A&A...355L..27H. doi:10.1888/0333750888/2862. ISBN 0333750888.
- Samus, N. N.; Durlevich, O. V.; et al. (2009). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: General Catalogue of Variable Stars (Samus+ 2007-2013)". VizieR On-line Data Catalog: B/GCVS. Originally Published in: 2009yCat....102025S. 1. Bibcode:2009yCat....102025S.
- Moravveji, Ehsan; Guinan, Edward F.; Khosroshahi, Habib; Wasatonic, Rick (2013). "The Age and Mass of the α Herculis Triple-star System from a MESA Grid of Rotating Stars with 1.3 <= M/M ⊙ <= 8.0". The Astronomical Journal. 146 (6): 148. arXiv:1308.1632. Bibcode:2013AJ....146..148M. doi:10.1088/0004-6256/146/6/148. S2CID 117872505.
- Ducati, J. R. (2002). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: Catalogue of Stellar Photometry in Johnson's 11-color system". CDS/ADC Collection of Electronic Catalogues. 2237. Bibcode:2002yCat.2237....0D.
- van Leeuwen, F (November 2007). "Hipparcos, the New Reduction". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 474 (2): 653–664. arXiv:0708.1752. Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357. S2CID 18759600.
- Huang, W.; Wallerstein, G.; Stone, M. (2012). "A catalogue of Paschen-line profiles in standard stars". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 547: A62. arXiv:1210.7893. Bibcode:2012A&A...547A..62H. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201219804. S2CID 119286159.
- Reimers, D. (1977). "On the absolute scale of mass-loss in red giants. I - Circumstellar absorption lines in the spectrum of the visual companion of Alpha-1 HER". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 61: 217. Bibcode:1977A&A....61..217R.
- Moravveji, E.; Guinan, E. F.; Sobouti, Y. (2011). "On the Mass and Evolutionary Status of the Bright Red AGB Supergiant α1 Herculis". Why Galaxies Care About Agb Stars Ii: Shining Examples and Common Inhabitants. 445: 163. Bibcode:2011ASPC..445..163M.
- Schröder, K.-P.; Cuntz, M. (April 2007), "A critical test of empirical mass loss formulas applied to individual giants and supergiants", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 465 (2): 593–601, arXiv:astro-ph/0702172, Bibcode:2007A&A...465..593S, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20066633, S2CID 55901104
- "alf Her". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Retrieved 2010-09-26.
- "Washington Double Star Catalog". United States Naval Observatory. Archived from the original on 2011-02-14. Retrieved 2018-07-10.
- Brown, A. G. A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 616. A1. arXiv:1804.09365. Bibcode:2018A&A...616A...1G. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051.
- Hessman, F. V.; Dhillon, V. S.; Winget, D. E.; Schreiber, M. R.; Horne, K.; Marsh, T. R.; Guenther, E.; Schwope, A.; Heber, U. (2010). "On the naming convention used for multiple star systems and extrasolar planets". arXiv:1012.0707 [astro-ph.SR].
- Kurt Vonnegut. "Constellations: Hercules 'the Strongman'". The BBC (British Broadcasting Corporation). Retrieved 2010-11-14.
- "IAU Working Group on Star Names (WGSN)". Retrieved 22 May 2016.
- Knobel, E. B. (June 1895). "Al Achsasi Al Mouakket, on a catalogue of stars in the Calendarium of Mohammad Al Achsasi Al Mouakket". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 55 (8): 429. Bibcode:1895MNRAS..55..429K. doi:10.1093/mnras/55.8.429.
- (in Chinese) AEEA (Activities of Exhibition and Education in Astronomy) 天文教育資訊網 2006 年 6 月 25 日
- Richard Hinckley Allen: Star Names — Their Lore and Meaning: Hercules
- Wasatonic, Richard P. (January 1997). "Photoelectric Photometry of TX Psc, Alpha Her A, Omicron Cet, and RT Cyg". The Journal of the American Association of Variable Star Observers. 26 (1): 1–13. Bibcode:1997JAVSO..26....1W. Retrieved 18 December 2022.
- Deutsch, Armin J. (March 1956). "The Circumstellar Envelope of Alpha Herculis". Astrophysical Journal. 123: 210–227. Bibcode:1956ApJ...123..210D. doi:10.1086/146152.
- Benson, J. A.; Dyck, H. M.; Mason, W. L.; Howell, R. R.; Ridgway, S. T.; et al. (December 1991). "The infrared angular diameter of Alpha Herculis measured with a Michelson interferometer". Astronomical Journal. 102: 2091–2097. Bibcode:1991AJ....102.2091B. doi:10.1086/116033.
- Percy, John R; Wilson, Joseph B; Henry, Gregory W (2001). "Long‐TermVRIPhotometry of Small‐Amplitude Red Variables. I. Light Curves and Periods". Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific. 113 (786): 983. Bibcode:2001PASP..113..983P. doi:10.1086/322153.
External links
- An Atlas of the Universe: Multiple Star Orbits
- Upside down Hercules showing Alpha Herculisethi as the head: Hercules