Halland County
Halland County (Swedish: Hallands län, [ˈhǎlːan(d)s ˈlɛːn]) is a county (län) on the western coast of Sweden. It corresponds roughly to the cultural and historical province of Halland. The capital is Halmstad. Prince Julian, the son of Prince Carl Philip, is Duke of Halland.
Halland County
| |
|---|---|
 Flag  Coat of arms | |
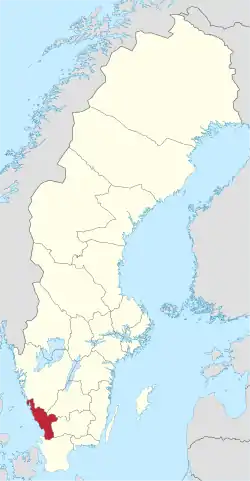 Halland County in Sweden | |
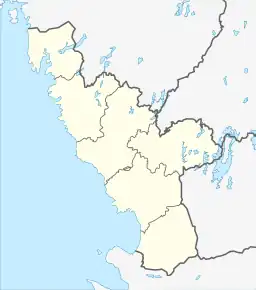 Location map of Halland County in Sweden | |
| Coordinates: 56°43′00″N 12°49′16″E | |
| Country | |
| Founded | 1719 |
| Capital | Halmstad |
| Municipalities | |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Lena Sommestad |
| • Council | Region Halland |
| Area | |
| • Total | 5,454 km2 (2,106 sq mi) |
| Population (30 September 2017)[1] | |
| • Total | 323,729 |
| • Density | 59/km2 (150/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| ISO 3166 code | SE-N |
| GDP/ Nominal | SEK 61,339 million (2004) |
| GDP per capita | SEK 221,000 |
| NUTS Region | SE231 |
| Website | www |
It borders the counties of Västra Götaland, Jönköping, Kronoberg, Scania and the sea of the Kattegat.
Heraldry
The County of Halland inherited its coat of arms from the province of Halland. When it is shown with a royal crown it represents the County Administrative Board.
Province
Counties mainly serve administrative purposes in Sweden. The culture and history of the area is to be found in its provincial counterpart Halland. The county was designed with virtually the same boundaries as the province. The major exception is a part of Hylte Municipality, which belongs to the province of Småland.
Geography
- Genevadsån river
Administration
The main aim of the County Administrative Board is to fulfil the goals set in national politics by the Riksdag and the Government, to coordinate the interests and promote the development of the county, to establish regional goals and safeguard the due process of law in the handling of each case. The County Administrative Board is a Government Agency headed by a governor. See List of Halland Governors.
Politics
Region Halland is the local government for Halland County, and is controlled by the regional council and regional board of Halland. The regional council is elected directly by the residents in regional elections held every four years at the same time as municipal and Riksdag elections.
Among the main responsibilities of the Halland Regional Council (Region Halland) are health care and public transit. The right-wing 'bourgeoisie' parties have held a majority in every election from 1912 until 2014, regaining it in 2018 and losing it again in 2022. However, even when only able to form a minority, the right-wing have controlled the regional board.
Governors
Riksdag elections
The table details all Riksdag election results of Halland County since the unicameral era began in 1970. The blocs denote which party would support the Prime Minister or the lead opposition party towards the end of the elected parliament.
| Year | Turnout | Votes | V | S | MP | C | L | KD | M | SD | NyD | Left | Right |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1970[2] | 89.9 | 119,972 | 2.4 | 37.7 | 33.5 | 13.1 | 1.8 | 11.8 | 40.0 | 58.4 | |||
| 1973[3] | 91.9 | 134,086 | 2.6 | 36.6 | 37.4 | 7.6 | 0.9 | 14.5 | 39.3 | 59.5 | |||
| 1976[4] | 92.8 | 146,371 | 2.4 | 35.4 | 35.1 | 10.3 | 0.7 | 15.9 | 37.7 | 61.4 | |||
| 1979[5] | 91.8 | 150,322 | 3.0 | 35.8 | 27.6 | 10.3 | 0.8 | 22.2 | 38.8 | 60.1 | |||
| 1982[6] | 92.5 | 155,884 | 3.2 | 37.8 | 1.7 | 23.9 | 5.9 | 1.3 | 26.1 | 41.0 | 55.8 | ||
| 1985[7] | 90.9 | 159,494 | 2.9 | 38.4 | 1.7 | 18.5 | 15.6 | 22.7 | 41.3 | 56.8 | |||
| 1988[8] | 87.3 | 157,729 | 3.4 | 38.0 | 5.7 | 17.9 | 13.1 | 2.1 | 19.5 | 47.1 | 50.5 | ||
| 1991[9] | 88.2 | 164,719 | 2.6 | 32.1 | 3.2 | 13.7 | 9.1 | 7.0 | 24.3 | 7.4 | 34.7 | 54.1 | |
| 1994[10] | 88.0 | 170,741 | 4.2 | 40.4 | 4.7 | 12.6 | 6.7 | 3.7 | 25.4 | 1.5 | 49.3 | 48.4 | |
| 1998[11] | 82.8 | 164,049 | 8.6 | 31.8 | 3.9 | 8.4 | 4.3 | 12.8 | 24.7 | 44.3 | 50.2 | ||
| 2002[12] | 81.5 | 168,247 | 5.9 | 35.8 | 3.9 | 9.5 | 13.9 | 9.9 | 17.4 | 1.0 | 45.7 | 50.7 | |
| 2006[13] | 83.5 | 179,470 | 4.0 | 31.6 | 4.0 | 10.4 | 7.7 | 6.7 | 29.7 | 2.9 | 39.6 | 54.4 | |
| 2010[14] | 86.2 | 195,565 | 3.5 | 26.8 | 5.9 | 8.8 | 7.8 | 5.6 | 34.7 | 5.4 | 36.2 | 56.9 | |
| 2014[15] | 87.5 | 206,559 | 3.8 | 28.4 | 5.9 | 8.4 | 5.7 | 4.4 | 27.7 | 12.9 | 38.0 | 46.2 | |
| 2018[16] | 89.0 | 216,982 | 4.8 | 25.8 | 3.5 | 10.1 | 5.7 | 7.1 | 22.9 | 18.6 | 44.3 | 54.3 | |
| 2022[17] | 86.6 | 224,183 | 4.0 | 28.3 | 3.6 | 7.0 | 4.8 | 6.0 | 22.5 | 22.6 | 42.9 | 55.9 |
Municipalities
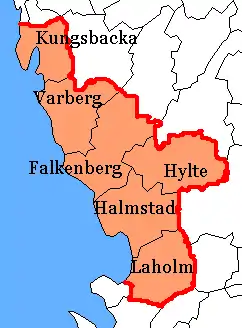
Sweden's counties are entities for Sweden's municipalities, responsible for such things as child care, education, street planning, etc. Municipalities in Halland County are, from north to south, with the numbers of inhabitants::
In Halland Province: (2021)
- Falkenberg: 46,773
- Halmstad: 104,573
- Hylte: 10,619
- Kungsbacka: 85,301
- Laholm: 26,319
- Varberg: 66,658
Culture
Music groups
- Gyllene Tider
- Roxette
- Isildurs Bane
- Sonic Syndicate
- Sabel
Localities in order of size
The five most populous localities of Halland County in 2020:[18]
| # | Locality | Population |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Halmstad | 71,422 |
| 2 | Varberg | 36,327 |
| 3 | Falkenberg | 28,747 |
| 4 | Kungsbacka | 24,071 |
| 5 | Onsala | 12,415 |
Demographics
Foreign background
SCB have collected statistics on backgrounds of residents since 2002. These tables consist of all who have two foreign-born parents or are born abroad themselves.[19] The chart lists election years and the last year on record alone.
| Location | 2002 | 2006 | 2010 | 2014 | 2018 | 2019 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Falkenberg | 10.8 | 12.1 | 13.6 | 15.5 | 18.6 | 19.2 |
| Halmstad | 15.7 | 17.0 | 18.8 | 20.1 | 24.5 | 25.2 |
| Hylte | 14.0 | 16.5 | 19.5 | 24.3 | 31.8 | 32.1 |
| Kungsbacka | 7.0 | 7.3 | 7.8 | 8.6 | 10.7 | 11.1 |
| Laholm | 8.5 | 9.7 | 11.6 | 13.5 | 18.0 | 18.7 |
| Varberg | 9.0 | 9.6 | 10.7 | 11.8 | 13.7 | 14.2 |
| Total | 11.0 | 11.9 | 13.2 | 14.8 | 17.8 | 18.4 |
| Source: SCB [19] | ||||||
References
- "Folkmängd i riket, län och kommuner 30 september 2017 och befolkningsförändringar 1 juli–30 september 2017. Totalt". Statistics Sweden. 8 November 2017. Retrieved 19 November 2017.
- "Riksdagsvalet 1970" (PDF). SCB. Retrieved 21 September 2021.
- "Riksdagsvalet 1973" (PDF) (in Swedish). SCB. Retrieved 14 September 2021.
- "Riksdagsvalet 1976" (PDF) (in Swedish). SCB. Retrieved 14 September 2021.
- "Riksdagsvalet 1979" (PDF) (in Swedish). SCB. Retrieved 14 September 2021.
- "Riksdagsvalet 1982)" (PDF) (in Swedish). SCB. Retrieved 14 September 2021.
- "Riksdagsvalet 1985" (PDF) (in Swedish). SCB. Retrieved 14 September 2021.
- "Riksdagsvalet 1988)" (PDF) (in Swedish). SCB. Retrieved 14 September 2021.
- "Riksdagsvalet 1991" (PDF) (in Swedish). SCB. Retrieved 14 September 2021.
- "Riksdagsvalet 1994" (PDF) (in Swedish). SCB. Retrieved 14 September 2021.
- "Riksdagsvalet 1998" (PDF) (in Swedish). SCB. Retrieved 14 September 2021.
- "Valresultat Riksdag 2002" (in Swedish). Valmyndigheten. Archived from the original on 7 September 2021. Retrieved 14 September 2021.
- "Allmänna val 17 september 2006" (in Swedish). Valmyndigheten. Archived from the original on 28 September 2021. Retrieved 14 September 2021.
- "Röster - Val 2010" (in Swedish). Valmyndigheten. Archived from the original on 17 December 2018. Retrieved 14 September 2021.
- "Röster - Val 2014" (in Swedish). Valmyndigheten. Archived from the original on 11 November 2020. Retrieved 14 September 2021.
- "Röster - Val 2018" (in Swedish). Valmyndigheten. Archived from the original on 17 December 2018. Retrieved 14 September 2021.
- "Valpresentation". resultat.val.se (in Swedish). Retrieved 2023-01-26.
- "Tätorter 2010 (Localities 2010)". Statistics Sweden (in Swedish). 2010. Retrieved 9 February 2014.
- "PxWeb - välj variabler och värden" (in Swedish). SCB. Retrieved 11 August 2020.
External links
- Halland County Administrative Board
- Halland County Council Archived 2009-06-18 at the Wayback Machine
- Regional Association of Local Authorities in Halland
- Hotels in Halland Archived 2020-01-09 at the Wayback Machine