Rhyl
Rhyl (/rɪl/; Welsh: Y Rhyl, pronounced [ə ˈr̥ɨl]) is a seaside town and community in Denbighshire, Wales. The town lies within the historic boundaries of Denbighshire, on the north-east coast of Wales at the mouth of the River Clwyd.
Rhyl
| |
|---|---|
 Rhyl Location within Denbighshire | |
| Population | 26,149 (2011) |
| OS grid reference | SJ015815 |
| Community |
|
| Principal area | |
| Preserved county | |
| Country | Wales |
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom |
| Post town | RHYL |
| Postcode district | LL18 |
| Dialling code | 01745 |
| Police | North Wales |
| Fire | North Wales |
| Ambulance | Welsh |
| UK Parliament | |
| Senedd Cymru – Welsh Parliament | |
To the west is Kinmel Bay and Towyn, to the east Prestatyn, and to the southeast Rhuddlan and St Asaph. At the 2011 Census, Rhyl had a population of 25,149, with Rhyl–Kinmel Bay having 31,229.[2] Rhyl forms a conurbation with Prestatyn and its two outlying villages, the Rhyl/Prestatyn Built-up area, whose 2011 population of 46,267 makes it North Wales's most populous non-city. Rhyl was once an elegant Victorian resort town but suffered rapid decline around the 1990s and 2000s but has since been improved by major regeneration around and in the town.
Etymology
Early documents refer to a dwelling in the area named Ty'n Rhyl ("Rhyl croft"), and a manor house with that name still exists in the oldest part of the town.[3] Its Welsh orthography has proved difficult for English writers to transliterate as Rhyl's opening voiceless alveolar trill is uncommon in the English language (represented in modern Welsh by the digraph 'Rh'). As such the name has appeared in English texts as Hulle (1292), Hul (1296), Ryhull (1301), Hyll (1506), Hull (1508), yr Hyll (1597), Rhil (1706), Rhûl (1749), Rhul (1773) Rhyll (1830) and Rhyl (1840).[4]
The etymonic origin of the word Rhyl has been the subject of debate for more than a century.[5] It has been suggested that it derives from a contraction of Yr Heol ("The Road"). However, this derivation is problematic as it is thought that no road of significance passed through the area before the name was already extant.[3] Another suggested etymology, that the name is a hybrid of an unfamiliar English word ("hill") within Welsh syntax (Yr Hyl becoming Yr Rhyl) is considered highly unlikely as the town is situated on coastal marshland, with no hills in the vicinity.[4] One etymology that gained popularity in the twentieth century suggests that the original dwelling of Ty'n Rhyl derived from Tŷ'n yr haul (House in the Sun/House of Sunshine). This may be an example of folk etymology, as Rhyl gained popularity as a summer destination for Welsh-speaking tourists and was advertised in English and Welsh as "Sunny Rhyl".[3][4][5]
Buildings, landmarks and attractions

Rhyl has a number of Grade II listed buildings and landmarks. These include the Parish Church of St Thomas in Bath Street, which is listed as Grade II*.[6] Others are the Midland Bank building, the railway station along with two signal boxes and the public telephone box on the up platform, the Royal Alexandra Hospital, the Sussex Street Baptist Church, Rhyl Town Hall, the Swan public house in Russell Road, the war memorial, and the Welsh Presbyterian Church in Clwyd Street.[7]
.jpg.webp)
Also notable is the Grade II listed Foryd Harbour Bridge, a blue bridge with distinctive bowstring girders built in 1932. Situated over the River Clwyd, it links Rhyl with Kinmel Bay.
Another landmark is the Church of St Margaret of Antioch. The Marble Church was built by Lady Margaret in memory of her late husband, Sir Henry Peyto Willoughby de Broke. It was completed within four years and consecrated on 23 August 1860, becoming the parish church of a new parish of Bodelwyddan, covering an area formerly in that of St Asaph. The church opens daily from 9:30 to 16:30, except between 25 December and 6 January.
A previous Rhyl landmark was the ornate Pavilion Theatre with five domes, which was demolished in 1974. Half a mile further down the promenade stood Rhyl Pier, opened in 1867 at 2,355 feet (718 m) long. The structure was damaged by ships in 1883 and again in 1891. It was further damaged in 1901 by fire. Storms were responsible for further damage in 1909 in 1913 was closed as unsafe. Although it reopened with a much-reduced length in 1930, it closed again in 1966 and was demolished in 1973.[8]
Rhyl's top attractions on the West Parade are Rhyl Children's Village theme park, and the 250-foot (76 m) Sky Tower (formerly the Clydesdale Bank tower, brought to Rhyl from the 1988 Glasgow Garden Festival). The Sky Tower opened in 1989,[9] but it was closed to the public in 2010 and transformed into an illuminated beacon in 2017.[10][11][12] A VUE Cinema is also located there.
On the East Parade is the SeaQuarium. Up until 2014, Rhyl Suncentre was also an attraction on the East Parade; an indoor water leisure centre which opened in 1980 at a cost of £4.25 million and featured a heated swimming pool, water chutes and slides, and Europe's first indoor surfing pool.[13] The local council closed the centre in early 2014 and it was demolished in 2016. A new Travelodge hotel was built next to the site, which opened in early 2019.[14] A new indoor/outdoor water park, the SC2, opened further along the promenade in 2019, and includes various pools with water chutes and slides, as well as a separate "Ninja Tag" assault course game complex. Also on the East Parade is the New Pavilion Theatre, opened in 1991. It has over 1,000 seats and is managed by Denbighshire County Council.[15] Redevelopment of the Pavilion theatre in 2017 provided for a new façade, entrance foyer and restaurant, and refurbished bar areas.[16]
Marine Lake
The Marine Lake, an artificial excavation in the west of the town, used to be a tourist destination, with fairground rides and a zoo. The lake is a 12-hectare man-made reservoir and it was officially opened in 1895. Rhyl Miniature Railway is the only original attraction remaining on the site, a narrow gauge railway that travels around the lake and is now based at the new museum and railway centre. There is also a playground and numerous watersports clubs based around the lake.[17]

The Marine Lake Funfair was demolished in the late 1960s, having been replaced by the nearby Ocean Beach Funfair. Ocean Beach finally closed on 2 September 2007 and was demolished to make way for a planned new development initially called Ocean Plaza. This was to include apartments, a hotel and various retail outlets.[18] However, work on Ocean Plaza never went ahead as scheduled and the land lay vacant for several years after the original developers, Modus Properties, went bankrupt in 2009. The site was sold to a new company, Scarborough Development Group (SDG), in 2010, but again no work commenced on the site for several years. In 2014, SDG submitted revised plans to develop the land on a much smaller scale than the original plans.[19] Now called Marina Quay, the plans no longer include the building of new apartments on the land as Natural Resources Wales' flood regulations now prohibit this.[20] The plans were approved by the local authority in November 2014. In August 2015, The Range retail chain signed a 20-year lease and opened a new outlet on the site in March 2018.[21] Aldi also opened a branch on the site in 2019.
Governance
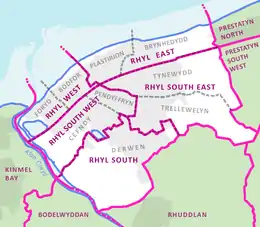
For elections to Denbighshire County Council, Rhyl divides into five electoral wards: Rhyl East, Rhyl South, Rhyl South East, Rhyl South West and Rhyl West. After the 2017 elections, all but two of the eleven councillors belonged to the Welsh Labour Party.[22] In 2008 Rhyl West appeared as the most deprived ward in Wales in the Welsh Index of Multiple Deprivation.[23]
The 22 councillors on Rhyl Town Council are divided among nine community wards: Brynhedydd and Plastirion (in Rhyl East); Cefndy, Derwen, Pendyffryn, Trellewellyn and Tynewydd (Rhyl South, South East and South West); Bodfor and Foryd (in Rhyl West).[24]
Sport
Association Football Rhyl F.C., commonly known as the Lilywhites, is a football club that played historically in English non-league football, but has competed since 1992 in the Welsh football pyramid. In the 2003–2004 season it won the Welsh Premier League, the Welsh Cup and the Welsh League Cup, and was losing finalist in the FAW Premier Cup. In the 2008–2009 season it again won the Welsh Premier League.[25] On 17 May 2010, it was announced that Rhyl's Welsh Premier licence had been revoked. Its appeal was unsuccessful and it was relegated to the Cymru Alliance,[26] returning to the Welsh Premier League in 2013 after winning the Cymru Alliance title, becoming the first club in the history of the competition to complete the season unbeaten.[25] Rhyl has played in Europe on a few occasions. On 21 April 2020, the club announced it was going to cease trading and be formally wound up.[27] In May 2020, a phoenix club was set up under the name of C.P.D. Y Rhyl 1879.[28]
Rugby Union Rhyl and District RFC is the town's rugby union club. It completed a move from its old ground on the Waen in Rhuddlan, when a new ground and clubhouse opened at Tynewydd Fields in 2018.
Hockey Rhyl is home to the oldest field hockey club in Wales, formed in 1890. Its first international game was also played at Rhyl, between Ireland and Wales in 1895.
Climate
The climate is cool and temperate in Rhyl. The climate here is classified as Cfb by the Köppen climate classification. The average temperature in Rhyl is 9.3 °C (48.7 °F). Annual precipitation averages 794 mm (31.3 in).
| Climate data for Rhyl No 2 (77 m elevation) 1981–2010 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 7.8 (46.0) |
7.9 (46.2) |
9.9 (49.8) |
12.2 (54.0) |
15.4 (59.7) |
17.8 (64.0) |
19.8 (67.6) |
19.5 (67.1) |
17.2 (63.0) |
14.0 (57.2) |
10.6 (51.1) |
8.2 (46.8) |
13.4 (56.1) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 2.6 (36.7) |
2.5 (36.5) |
3.9 (39.0) |
5.1 (41.2) |
7.5 (45.5) |
10.2 (50.4) |
12.4 (54.3) |
12.1 (53.8) |
10.5 (50.9) |
7.9 (46.2) |
5.2 (41.4) |
2.8 (37.0) |
6.9 (44.4) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 75.4 (2.97) |
54.1 (2.13) |
56.4 (2.22) |
49.1 (1.93) |
55.8 (2.20) |
56.3 (2.22) |
55.5 (2.19) |
68.6 (2.70) |
74.8 (2.94) |
92.3 (3.63) |
87.1 (3.43) |
88.9 (3.50) |
814.1 (32.05) |
| Average rainy days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 14.5 | 11.7 | 12.9 | 10.2 | 9.9 | 9.3 | 10.3 | 11.7 | 11.1 | 14.3 | 15.3 | 14.7 | 145.7 |
| Source: Met Office[29] | |||||||||||||
Transport
Rhyl railway station on the North Wales Coast Line is served by through trains of Avanti West Coast between Holyhead and London Euston, and by Transport for Wales Rail services: to Cardiff Central via Newport and Crewe, and to Manchester Piccadilly. Other stations nearby include Abergele & Pensarn, Prestatyn, Flint, Colwyn Bay and Llandudno Junction.[30] The direct Transport for Wales and Avanti West Coast services to Holyhead give connections by Stena Line or Irish Ferries to Dublin Port.
The A548 road through the town links with the A55 Holyhead to Chester road at Abergele. The A525 road runs south from the town to Rhuddlan, St Asaph and Ruthin.[31] Several Arriva Buses Wales bus services are run along the main coast road between Chester and Holyhead, linking the resorts. Another route runs between Rhyl and Denbigh.[32]
Notable people
In birth order:
Music
- Wayne Bickerton (1941–2015), record producer and musician
- Kim Simmonds (1947–2022), lead singer, guitarist and founding member of Savoy Brown, was born in Newbridge, Caerphilly.
- Michael Leslie Peters (born 1959), lead singer and founding member of The Alarm, was born in Prestatyn, grew up in Rhyl and attended Rhyl High School.
- Steve Strange (1959–2015), lead singer of the band Visage, was born in Newbridge, Caerphilly, but lived in Rhyl as a child.
- Lisa Scott-Lee (born 1975), singer and dancer founding member of Steps.
- The Alarm (1981–1991), rock band[33]
Politics
- Isaac Jenks (1816–1888), ironmaster and Mayor of Wolverhampton, died at Rhyl.
- Mungo Lewis (1894–1969), Manitoba politician
- Ann Jones (born 1953), Welsh Labour and Co-operative Party MS
- Gareth Davies (born 1988), Welsh Conservative MS
The arts
- Patrick Garnett (1932–2006), Swinging Sixties architect[34]
- Nathan Penlington (living), poet and magician
Scholarship and literature
- Thomas Aubrey (1808–1867), Methodist minister of religion and preacher
- Edward Ross Wharton (1844–1896), classical scholar, etymologist and lexicographer[35]
- Vernon R. Young (1937–2004), research scientist specializing in protein and amino acid requirements
- Bob Griffiths (born 1953), born in Rhyl, Church in Wales priest, British Armed Forces chaplain, then Archdeacon of Wrexham
Sport
- William Roberts (born 1863, fl. 1880s – 1890s), international footballer
- Don Oakes (1928–1977), professional footballer (Arsenal F.C.)
- Elliott Hewitt (born 1944), professional footballer (Notts County F.C.)
- David Harrison (born 1972), jockey, winner of 1992 Royal Hunt Cup at Royal Ascot
- Ched Evans (born 1988), footballer (Sheffield United F.C.)
- James Chester (born 1989), international footballer (Aston Villa F.C.)
Stage and broadcasting
- Ruth Ellis (1926–1955), nightclub hostess and murderer, was the last woman hanged in the UK.
- Nerys Hughes (born 1941), actress
- Carol Vorderman (born 1960), TV broadcaster and game-show host, attended Rhyl's Blessed Edward Jones High School.
- Sara Sugarman (born 1962), actress and film director
- Alexa Davies (born 1995), actress best known for Young Rosie in Mamma Mia! Here We Go Again
References
- "Rhyl Town Council Website". Rhyl Town Council. Retrieved 20 January 2022.
- UK Census (2011). "Local Area Report – Rhyl Parish (1170221471)". Nomis. Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 18 March 2018.
- Turner, Robin (7 May 2016). "This is how the Welsh place you live got its name". Cardiff: WalesOnli.
- Owen, Hywel Wyn; Morgan, Richard (2007). Dictionary of the Place-Names of Wales. p. 422. ISBN 978-1-84323-901-7.
- Hughes, T (16 September 1905). "Etymology of Rhyl" (in Welsh). Rhyl Journal. National Library of Wales. p. 1.
- "Parish Church of St Thomas, Rhyl". British Listed Buildings. Retrieved 30 April 2016.
- "Listed Buildings in Rhyl, Wales". British Listed Buildings. Retrieved 30 April 2016.
- "History of Rhyl Pier". National Piers Society. Retrieved 30 April 2016.
- Tourism in Peripheral Areas: Case Studies. Channel View Publications Ltd. 2000. p. 31. ISBN 978-1-8731502-3-8.
- "Work to turn Rhyl Sky Tower into 'landmark' light beacon begins". Daily Post. 11 March 2017. Retrieved 21 May 2019.
- "Sky Tower stays shut". Rhyl Journal. 11 April 2012. Retrieved 28 November 2013.
- "Rhyl Sky Tower may still have a future but not as a ride". BBC News. 12 September 2012. Retrieved 28 November 2013.
- "The Sun Centre, Rhyl". BBC: Domesday Reloaded. 1989. Retrieved 1 May 2016.
- "Rhyl Sun Centre will not re-open as "wet attraction"". BBC News. 25 March 2014. Retrieved 1 May 2016.
- "Pavilion Theatre, Rhyl". Retrieved 1 May 2016.
- Williams, Kelly (9 November 2017). "Take a peek inside Rhyl Pavilion's new 1891 restaurant ahead of its opening". North Wales Live. Retrieved 3 November 2020.
- Howe, Marjorie (2000). Old Rhyl: From 1850s – 1910. Gwasg Helygain Ltd. p. 60. ISBN 978-0-9522755-4-1.
- "End of an era for Rhyl's funfair". BBC News. 2 September 2007. Retrieved 1 May 2016.
- "Plans for Ocean Plaza development go on display". News North Wales. 7 February 2014. Retrieved 1 May 2016.
- Williams, Kelly (6 February 2014). "Rhyl Ocean Plaza: Backlash over downsized plans for derelict funfair". Daily Post. Retrieved 1 May 2016.
- Hughes, Owen (4 August 2015). "Rhyl funfair site secures The Range as anchor tenant". Daily Post. Retrieved 1 May 2016.
- Gareth Joy (5 May 2017) Election 2017: Denbighshire Council results, Point FM. Retrieved 30 March 2018.
- "MP paints out town's tainted past". BBC News. 10 October 2008. Retrieved 30 March 2018.
- Councillors, Rhyl Town Council website. Retrieved 30 March 2018.
- "Club history". Rhyl F.C. Retrieved 1 May 2016.
- "Rhyl FC's Welsh Premier appeal fails FAW test". BBC Sport. 17 May 2010. Retrieved 1 May 2016.
- "Rhyl FC set to close after 141 years". BBC Sport. Retrieved 13 June 2021.
- Accessed 13 June 2021.
- "Rhyl (Denbighshire) UK climate averages".
- "Crewe to Holyhead". North Wales Coast Railway. 2012. Retrieved 1 May 2016.
- Concise Road Atlas: Britain. AA Publishing. 2015. pp. 47–55. ISBN 978-0-7495-7743-8.
- "Discover the towns of Wales". Arriva Wales. Arriva Buses Wales. Retrieved 1 May 2016.
- "The Alarm Biography, Songs, & Albums". AllMusic.
- Jonathan Glancey, "Patrick Garnett, Architect whose designs caught the mood of swinging London", The Guardian, 8 June 2006, accessed 3 October 2023
- Bibliography backing description: Retrieved 7 February 2017.




