SF3B1
Splicing factor 3B subunit 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SF3B1 gene.[5][6]
| SF3B1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | SF3B1, Hsh155, MDS, PRP10, PRPF10, SAP155, SF3b155, splicing factor 3b subunit 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 605590 MGI: 1932339 HomoloGene: 6696 GeneCards: SF3B1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Function
This gene encodes subunit 1 of the splicing factor 3b protein complex. Splicing factor 3b, together with splicing factor 3a and a 12S RNA unit, forms the U2 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins complex (U2 snRNP). The splicing factor 3b/3a complex binds pre-mRNA upstream of the intron's branch site in a sequence independent manner and may anchor the U2 snRNP to the pre-mRNA. Splicing factor 3b is also a component of the minor U12-type spliceosome. The carboxy-terminal two-thirds of subunit 1 have 22 non-identical, tandem HEAT repeats that form rod-like, helical structures. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms.[6]
Interactions
SF3B1 has been shown to interact with:
Clinical relevance
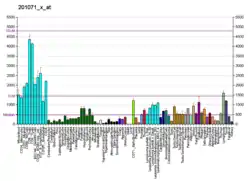
Mutations in this gene have been recurrently seen in cases of advanced chronic lymphocytic leukemia,[12] myelodysplastic syndromes[13] and breast cancer.[14] SF3B1 mutations are found in 60%-80% of patients with refractory anemia with ring sideroblasts (RARS; which is a myelodysplastic syndrome) or RARS with thrombocytosis (RARS-T; which is a myelodysplastic syndrome/myeloproliferative neoplasm). There is also an emerging body of evidence to suggest implications of SF3B1 mutations being involved in orbital melanoma.
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000115524 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000025982 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Wang C, Chua K, Seghezzi W, Lees E, Gozani O, Reed R (May 1998). "Phosphorylation of spliceosomal protein SAP 155 coupled with splicing catalysis". Genes & Development. 12 (10): 1409–14. doi:10.1101/gad.12.10.1409. PMC 316838. PMID 9585501.
- "Entrez Gene: SF3B1 splicing factor 3b, subunit 1, 155kDa".
- Ajuh P, Kuster B, Panov K, Zomerdijk JC, Mann M, Lamond AI (December 2000). "Functional analysis of the human CDC5L complex and identification of its components by mass spectrometry". The EMBO Journal. 19 (23): 6569–81. doi:10.1093/emboj/19.23.6569. PMC 305846. PMID 11101529.
- Will CL, Urlaub H, Achsel T, Gentzel M, Wilm M, Lührmann R (September 2002). "Characterization of novel SF3b and 17S U2 snRNP proteins, including a human Prp5p homologue and an SF3b DEAD-box protein". The EMBO Journal. 21 (18): 4978–88. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdf480. PMC 126279. PMID 12234937.
- Boudrez A, Beullens M, Waelkens E, Stalmans W, Bollen M (August 2002). "Phosphorylation-dependent interaction between the splicing factors SAP155 and NIPP1". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 277 (35): 31834–41. doi:10.1074/jbc.M204427200. PMID 12105215.
- Das BK, Xia L, Palandjian L, Gozani O, Chyung Y, Reed R (October 1999). "Characterization of a protein complex containing spliceosomal proteins SAPs 49, 130, 145, and 155". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 19 (10): 6796–802. doi:10.1128/mcb.19.10.6796. PMC 84676. PMID 10490618.
- Will CL, Schneider C, MacMillan AM, Katopodis NF, Neubauer G, Wilm M, Lührmann R, Query CC (August 2001). "A novel U2 and U11/U12 snRNP protein that associates with the pre-mRNA branch site". The EMBO Journal. 20 (16): 4536–46. doi:10.1093/emboj/20.16.4536. PMC 125580. PMID 11500380.
- Quesada V, Conde L, Villamor N, Ordóñez GR, Jares P, Bassaganyas L, Ramsay AJ, Beà S, Pinyol M, Martínez-Trillos A, López-Guerra M, Colomer D, Navarro A, Baumann T, Aymerich M, Rozman M, Delgado J, Giné E, Hernández JM, González-Díaz M, Puente DA, Velasco G, Freije JM, Tubío JM, Royo R, Gelpí JL, Orozco M, Pisano DG, Zamora J, Vázquez M, Valencia A, Himmelbauer H, Bayés M, Heath S, Gut M, Gut I, Estivill X, López-Guillermo A, Puente XS, Campo E, López-Otín C (January 2012). "Exome sequencing identifies recurrent mutations of the splicing factor SF3B1 gene in chronic lymphocytic leukemia". Nature Genetics. 44 (1): 47–52. doi:10.1038/ng.1032. PMID 22158541. S2CID 205343043.
- Malcovati L, Papaemmanuil E, Bowen DT, Boultwood J, Della Porta MG, Pascutto C, Travaglino E, Groves MJ, Godfrey AL, Ambaglio I, Gallì A, Da Vià MC, Conte S, Tauro S, Keenan N, Hyslop A, Hinton J, Mudie LJ, Wainscoat JS, Futreal PA, Stratton MR, Campbell PJ, Hellström-Lindberg E, Cazzola M (December 2011). "Clinical significance of SF3B1 mutations in myelodysplastic syndromes and myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative neoplasms". Blood. 118 (24): 6239–46. doi:10.1182/blood-2011-09-377275. PMC 3236114. PMID 21998214.
- Koboldt, Daniel C.; Fulton, Robert S.; McLellan, Michael D.; Schmidt, Heather; Kalicki-Veizer, Joelle; McMichael, Joshua F.; Fulton, Lucinda L.; Dooling, David J.; Ding, Li; Mardis, Elaine R.; Wilson, Richard K.; Ally, Adrian; Balasundaram, Miruna; Butterfield, Yaron S. N.; Carlsen, Rebecca; Carter, Candace; Chu, Andy; Chuah, Eric; Chun, Hye-Jung E.; Coope, Robin J. N.; Dhalla, Noreen; Guin, Ranabir; Hirst, Carrie; Hirst, Martin; Holt, Robert A.; Lee, Darlene; Li, Haiyan I.; Mayo, Michael; Moore, Richard A.; et al. (October 2012). "Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours". Nature. 490 (7418): 61–70. Bibcode:2012Natur.490...61T. doi:10.1038/nature11412. PMC 3465532. PMID 23000897.
Further reading
- Andersson B, Wentland MA, Ricafrente JY, Liu W, Gibbs RA (April 1996). "A "double adaptor" method for improved shotgun library construction". Analytical Biochemistry. 236 (1): 107–13. doi:10.1006/abio.1996.0138. PMID 8619474.
- Yu W, Andersson B, Worley KC, Muzny DM, Ding Y, Liu W, Ricafrente JY, Wentland MA, Lennon G, Gibbs RA (April 1997). "Large-scale concatenation cDNA sequencing". Genome Research. 7 (4): 353–8. doi:10.1101/gr.7.4.353. PMC 139146. PMID 9110174.
- Gozani O, Potashkin J, Reed R (August 1998). "A potential role for U2AF-SAP 155 interactions in recruiting U2 snRNP to the branch site". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 18 (8): 4752–60. doi:10.1128/mcb.18.8.4752. PMC 109061. PMID 9671485.
- Das BK, Xia L, Palandjian L, Gozani O, Chyung Y, Reed R (October 1999). "Characterization of a protein complex containing spliceosomal proteins SAPs 49, 130, 145, and 155". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 19 (10): 6796–802. doi:10.1128/mcb.19.10.6796. PMC 84676. PMID 10490618.
- Pauling MH, McPheeters DS, Ares M (March 2000). "Functional Cus1p is found with Hsh155p in a multiprotein splicing factor associated with U2 snRNA". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 20 (6): 2176–85. doi:10.1128/MCB.20.6.2176-2185.2000. PMC 110834. PMID 10688664.
- Dias Neto E, Correa RG, Verjovski-Almeida S, Briones MR, Nagai MA, da Silva W, Zago MA, Bordin S, Costa FF, Goldman GH, Carvalho AF, Matsukuma A, Baia GS, Simpson DH, Brunstein A, de Oliveira PS, Bucher P, Jongeneel CV, O'Hare MJ, Soares F, Brentani RR, Reis LF, de Souza SJ, Simpson AJ (March 2000). "Shotgun sequencing of the human transcriptome with ORF expressed sequence tags". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 97 (7): 3491–6. Bibcode:2000PNAS...97.3491D. doi:10.1073/pnas.97.7.3491. PMC 16267. PMID 10737800.
- Das R, Zhou Z, Reed R (May 2000). "Functional association of U2 snRNP with the ATP-independent spliceosomal complex E". Molecular Cell. 5 (5): 779–87. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80318-4. PMID 10882114.
- Brand M, Moggs JG, Oulad-Abdelghani M, Lejeune F, Dilworth FJ, Stevenin J, Almouzni G, Tora L (June 2001). "UV-damaged DNA-binding protein in the TFTC complex links DNA damage recognition to nucleosome acetylation". The EMBO Journal. 20 (12): 3187–96. doi:10.1093/emboj/20.12.3187. PMC 150203. PMID 11406595.
- Will CL, Schneider C, MacMillan AM, Katopodis NF, Neubauer G, Wilm M, Lührmann R, Query CC (August 2001). "A novel U2 and U11/U12 snRNP protein that associates with the pre-mRNA branch site". The EMBO Journal. 20 (16): 4536–46. doi:10.1093/emboj/20.16.4536. PMC 125580. PMID 11500380.
- Jurica MS, Licklider LJ, Gygi SR, Grigorieff N, Moore MJ (April 2002). "Purification and characterization of native spliceosomes suitable for three-dimensional structural analysis". RNA. 8 (4): 426–39. doi:10.1017/S1355838202021088. PMC 1370266. PMID 11991638.
- Boudrez A, Beullens M, Waelkens E, Stalmans W, Bollen M (August 2002). "Phosphorylation-dependent interaction between the splicing factors SAP155 and NIPP1". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 277 (35): 31834–41. doi:10.1074/jbc.M204427200. PMID 12105215.
- Will CL, Urlaub H, Achsel T, Gentzel M, Wilm M, Lührmann R (September 2002). "Characterization of novel SF3b and 17S U2 snRNP proteins, including a human Prp5p homologue and an SF3b DEAD-box protein". The EMBO Journal. 21 (18): 4978–88. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdf480. PMC 126279. PMID 12234937.
- Golas MM, Sander B, Will CL, Lührmann R, Stark H (May 2003). "Molecular architecture of the multiprotein splicing factor SF3b". Science. 300 (5621): 980–4. Bibcode:2003Sci...300..980G. doi:10.1126/science.1084155. PMID 12738865. S2CID 31046270.
- Banerjee H, Rahn A, Gawande B, Guth S, Valcarcel J, Singh R (February 2004). "The conserved RNA recognition motif 3 of U2 snRNA auxiliary factor (U2AF 65) is essential in vivo but dispensable for activity in vitro". RNA. 10 (2): 240–53. doi:10.1261/rna.5153204. PMC 1370536. PMID 14730023.
- Will CL, Schneider C, Hossbach M, Urlaub H, Rauhut R, Elbashir S, Tuschl T, Lührmann R (June 2004). "The human 18S U11/U12 snRNP contains a set of novel proteins not found in the U2-dependent spliceosome". RNA. 10 (6): 929–41. doi:10.1261/rna.7320604. PMC 1370585. PMID 15146077.
- Beausoleil SA, Jedrychowski M, Schwartz D, Elias JE, Villén J, Li J, Cohn MA, Cantley LC, Gygi SP (August 2004). "Large-scale characterization of HeLa cell nuclear phosphoproteins". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 101 (33): 12130–5. Bibcode:2004PNAS..10112130B. doi:10.1073/pnas.0404720101. PMC 514446. PMID 15302935.
- Lin KT, Lu RM, Tarn WY (October 2004). "The WW domain-containing proteins interact with the early spliceosome and participate in pre-mRNA splicing in vivo". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 24 (20): 9176–85. doi:10.1128/MCB.24.20.9176-9185.2004. PMC 517884. PMID 15456888.