Selenomonad
Members of the genus Selenomonas (motile crescent-shaped bacteria in general) are referred to trivially as selenomonads. The genus Selenomonas constitutes a group of motile crescent-shaped bacteria and includes species living in the gastrointestinal tracts of animals, in particular the ruminants. A number of smaller forms discovered with the light microscope are now in culture but many, especially the large selenomonads are not, owing to their fastidious and incompletely known growth requirements.
| Selenomonad | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Bacteria |
| Phylum: | Bacillota |
| Class: | Negativicutes |
| Order: | Selenomonadales |
| Family: | Selenomonadaceae |
| Genus: | Selenomonas von Prowazek 1913[1] |
| Type species | |
| Selenomonas sputigena (Flügge 1886) Boskamp 1922 | |
| Species[2] | |
|
See text | |
Gram stain
The family Veillonellaceae was transferred from the order Eubacteriales to the new order Selenomonadales in the new class Negativicutes.[3] Despite most of the members of the Bacillota staining positive for the Gram stain and being trivially called "low-GC Gram-positives" (c.f. Bacterial phyla), members of the Negativicutes stain Gram-negative and possess a double bilayer.[3]
This transfer now appears to have been mistaken.[4] On further examination the Selenomonads appear to be members of the Clostridia.
Etymology
The etymology of the name Selenomonas comes from the Ancient Greek noun selênê (σελήνη), meaning the moon, a linking -o- and the noun monas (μόνας) which in microbiology has come to mean bacterium.[2] The name Selenomonas simply refers to the crescent moon-shaped profile of this organism and not in any way to the chemical element selenium. The unique cell morphology of certain large selenomonads (with its in-folding of the cell membrane behind the flagella) would indicate bilateral symmetry along the long axis—an unusual property for prokaryotes.
History and description
The literature on Selenomonas has roots dating back to the 19th century—and beyond—since the features and movements of living (then unclassified) crescent-shaped microorganisms from the human mouth were first described by Antonie van Leeuwenhoek in 1683.[5] During more recent years the crescent-shaped organism observed in ruminant stomachs has been variously described as:
- Ancyromonas ruminantium,[6]
- Selenomastix ruminantium,[7]
- Spirillum ruminantium,[8]
- Selenomonas ruminantium.[9]
As can be ascertained from the above nomenclature, the genus Selenomonas provides a fascinating history of scientific discovery, involving placement then re-placement in the classification systematics, oscillating between animal and bacterial kingdoms. In early descriptions it was thought to be a protozoan and hence for a while received the name Selenomastix.
The most morphologically interesting members of the selenomonads are undoubtedly the large motile crescents found in the warm anaerobic nutrient-rich microecosystem provided by ruminant rumen, guinea-pig caecum (S. palpitans) and even pockets in the human gingiva (S. sputigena). In the illustrated atlas of sheep rumen organisms of Moir and Masson their organisms nos. 4 and 5 represent two forms of the large Selenomonads.[10] These crescents live only a short time under the light microscope but during that time display a remarkable "tumbling" motion produced by one (or two—during cell division) flagella emanating from a refractile basal body on the concave side, which was first described by Woodcock & LaPage, studied later by Lessel & Breed (with photomicrographic addendum from C. F. Robinow),[11] then by Jeynes, who (mistakenly) interpreted it as a "blepharoplast".[12][13]
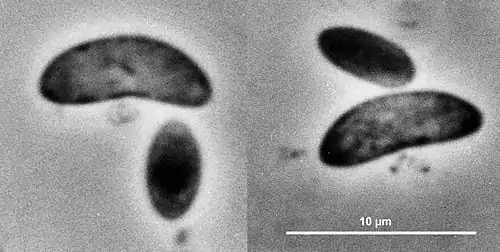
Years later, preparations of native rumen contents were examined for the first time by transmission electron microscopy of thin sections, negative stains and freeze-fracture replicas.[14][15] and many of the reasons for previous confusion were clarified. The "flagellum" was found to be quite unrelated to the flagellum of ciliate protozoa, instead consisting of a "fascicle" of numerous bacterial-type flagella (each displaying 11-fold subunit symmetry), twisted just outside the cell body into helical bundles to form strong organs of propulsion. The large crescents (which are better described as "bean-shaped") have flagella which are quite differently inserted into the concave side of the cell from those of the smaller species of Selenomonas. The small selenomonads have a rather low number of individual flagella inserted in a longitudinal row along the concave side whereas the large selenomonads have a much larger number, inserted into a circular patch of the cell membrane in the concave side in a close-packed (hexagonal) pattern, each flagellum inserted into a bullet-shaped structure at the cell membrane. Another interesting feature is the refractile body located beneath the massive flagella bundle characterizing the large crescents. It is not related morphologically to the ciliate blepharoplast (a "9+2" centriole-related structure found in cryptogams such as cycads, Ginkgo biloba and algae e.g. Euglena and Chlamydomonas). This flagella-associated structure observed in the large selenomonad can perhaps best be described as a "basal sac" formed by an invagination (in-folding) of the "polar organelle" region of the bacterial cell membrane in the middle of the concave side of the organism so that it lies directly behind the flagella. It appears to be unique in prokaryotes so far examined since in other bacteria possessing polar organelles, the structure is situated beside and around the flagella insertion bases in the cell membrane, but never lying behind them in the cytoplasm as in the case of the large selenomonad. The large crescents, with their unique morphology, still present many puzzles in their systematics. It is already clear from ultrastructural features that the genus Selenomonas is most probably an artificial classification, bringing together possibly unrelated organisms, simply because of their common possession of crescent morphology and peculiar flagellar insertion location. Successful attempts to maintain the large crescents in continuous culture over short terms have been reported by Prins [16] but long term culturing has not been possible so far. Genetic sequencing of the large crescents should provide the essential information required to better understand and classify these organisms.

With regard to the small selenomonads, research on obesity suggests that S. noxia may be an indicator of change in oral microbial ecology and might be directly or indirectly involved in obesity.[17]
Phylogeny
The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN)[2] and National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI)[18]
| 16S rRNA based LTP_01_2022[19][20][21] | 120 marker proteins based GTDB 07-RS207[22][23][24] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Unassigned species:
- "S. palpitans" Simons 1922
References
- Von Prowazek, S. (1913). "Zur Parasitologie von Westafrika" [Parasitology of West Africa]. Zentralblatt für Bakteriologie, Parasitenkunde, Infektionskrankheiten und Hygiene, Abteilung I. 7 (1/2): 32–36.
- J.P. Euzéby. "Selenomonas". List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN). Retrieved 9 September 2022.
- Marchandin, H.; Teyssier, C.; Campos, J.; Jean-Pierre, H.; Roger, F.; Gay, B.; Carlier, J. -P.; Jumas-Bilak, E. (2009). "Negativicoccus succinicivorans gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from human clinical samples, emended description of the family Veillonellaceae and description of Negativicutes classis nov., Selenomonadales ord. nov. and Acidaminococcaceae fam. nov. in the bacterial phylum Firmicutes". International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology. 60 (6): 1271–1279. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.013102-0. PMID 19667386.
- Yutin N, Galperin MY (2013). "A genomic update on Clostridial phylogeny: Gram-negative spore formers and other misplaced Clostridia". Environ Microbiol. 15: 2631–41. doi:10.1111/1462-2920.12173. PMC 4056668. PMID 23834245.
- Dobell, C. (1932). Antony van Leeuwenhoek and his "little animals". New York, Harcourt, Brace and company.
- Certes, A. (1889). "Note sur les micro-organismes de la panse des ruminants". Bull. Soc. Zool. France. 14: 70–73.
- Woodcock, H. M. & G. Lapage (1914). "On a remarkable type of protistan parasite". Quarterly Journal of Microscopical Science. 59: 431–458.
- MacDonald, J. B. Madlener, E. M. & Socransky, S. S. (1959). "Observations on Spirillum sputigenum and its relationship to Selenomonas species with special reference to flagellation". J. Bacteriol. 77 (5): 559–565. doi:10.1128/JB.77.5.559-565.1959. PMC 290421. PMID 13654218.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Wenyon, C.M. (1926). Protozoology, Vol. 1.
- Moir, R.J. & Masson, M.J. (1952). "An illustrated scheme for the microscopic identification of the rumen micro-organisms of sheep". J. Pathol. Bacteriol. 64 (2): 343–350. doi:10.1002/path.1700640210. PMID 14946656.
- Lessel, E.F. Jr. & Breed, R.S. (1954). "Selenomonas Boskamp, 1922. A genus that includes species showing an unusual type of flagellation". Bacteriol. Rev. 18 (3): 165–169. doi:10.1128/MMBR.18.3.165-169.1954. PMC 180798. PMID 13189856.
- Jeynes, M.H. (1955). "Taxonomic position of the Genus Selenomonas (von Prowazek". Nature. 176 (December): 1077. Bibcode:1955Natur.176.1077J. doi:10.1038/1761077a0. S2CID 4165067.
- Jeynes, M.H. (1956). "Analysis of the Genus Selenomonas with respect to its transfer to the Protozoa". International Bulletin of Bacteriological Nomenclature and Taxonomy. 6 (2): 53–59. doi:10.1099/0096266X-6-2-53.
- Chalcroft J.P; Bullivant S & Howard B.H. (1973). "Ultrastructural studies on Selenomonas ruminantium from the sheep rumen". Journal of General Microbiology. 79 (1): 135–146. doi:10.1099/00221287-79-1-135. PMID 4773919.
- Kingsley V V & Hoeniger J F M (1 December 1973). "Growth, structure, and classification of Selenomonas". Bacteriological Reviews. 37 (4): 479–521. doi:10.1128/MMBR.37.4.479-521.1973. PMC 413832. PMID 4129090.
- Prins, R.A. (1971). "Isolation, Culture and Fermentation Characteristics of Selenomonas ruminantium var. bryanti var. n. from the Rumen of Sheep". J. Bacteriol. 105 (3): 820–825. doi:10.1128/JB.105.3.820-825.1971. PMC 248505. PMID 4323298.
- J.M. Goodson, D. Groppo, S. Halem1, and E. Carpino (2009). "Is Obesity an Oral Bacterial Disease?". Journal of Dental Research. 88 (6): 519–523. doi:10.1177/0022034509338353. PMC 2744897. PMID 19587155. NIHMSID NIHMS131569.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Sayers; et al. "Selenomonas". National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) taxonomy database. Retrieved 9 September 2022.
- "The LTP". Retrieved 23 February 2022.
- "LTP_all tree in newick format". Retrieved 23 February 2022.
- "LTP_01_2022 Release Notes" (PDF). Retrieved 23 February 2022.
- "GTDB release 07-RS207". Genome Taxonomy Database. Retrieved 20 June 2022.
- "bac120_r207.sp_labels". Genome Taxonomy Database. Retrieved 20 June 2022.
- "Taxon History". Genome Taxonomy Database. Retrieved 20 June 2022.