Old Shute House
Old Shute House (known as Shute Barton between about 1789 and the 20th century), located at Shute, near Colyton, Axminster, Devon, is the remnant of a mediaeval manor house with Tudor additions, under the ownership of the National Trust. It was given a Grade I listing on 14 December 1955.[1] It is one of the most important non-fortified manor houses of the Middle Ages still in existence. It was built about 1380 as a hall house and was greatly expanded in the late 16th century and partly demolished in 1785. The original 14th-century house survives, although much altered.
- See also: New Shute House

This article is based on the work of Bridie (1955), which has however been superseded as the standard work of reference on the architectural history of the building by the unpublished Exeter Archaeology Report of 2008 produced for the National Trust.[2] This report draws on new evidence gained from the recently discovered survey of 1559 made by Sir William Petre, which lists each main room of the then existing house together with its contents. From this evidence a conjectural ground plan of the house pre-1785 was recently produced by Roger Waterhouse.








Description
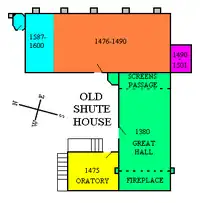
The original 1380 building was a simple parallelogram measuring externally 36 feet by 46 feet, containing a single large room, a great hall, extending up to the roof, lit by four 12 foot pointed-arched gothic windows, two on each of the long sides. The original entry door survives in the middle of the northern façade, but the two 12 foot flanking windows were later filled in, although their outlines are still visible in the stonework. The fireplace was at the western end and the dais on which was situated the lord's table was at the opposite eastern end, beyond which was the screens-passage leading to the domestic outbuildings.
A private chamber for the lord's private occupation was built over the screens-passage, but extended partially into the great hall as a gallery, leaving most of it still open to the roof. This new chamber was reached via an octagonal tower added at the NE corner of the rectangular building, accessible from the dias, containing a circular staircase. The stone door-frame of the screens-passage door in the east wall leading from the great hall into the original out-buildings serving as kitchen, buttery and pantry survives, but now as an internal door as the Tudor additional wing was built onto the east wall of the 1380 great hall.
At the west end of the great hall the great fireplace survives, spanning almost the whole width of the room, and containing a hearth 10 feet in depth. The external walls on either side of this huge hearth were strengthened by buttresses, still surviving, to counter the outward force exerted on the walls by the weight of the chimney breast. The fireplace is said to be the largest existing mediaeval one in Britain, with a span of 24 feet. The will dated 1407 of William Bonville, the original builder, mentions "ma salle (hall), ma chambre, panetrie (pantry for breadmaking), botellie (buttery for storage of wine) cusyne (kitchen) and pestrine (pastry room)"[6]
At a later period a ceiling was inserted over the whole of the great hall to provide upper floor chambers, and even later a second ceiling was added to provide a middle floor of accommodation. Additional small windows were then required to provide light to the top floors. Thus, the ancient arch-braced roof is no longer visible from the floor of the great hall. Modern horizontal pine tie-beams were later added to the arched roof timbers, which detract from the grandeur of the structure.[7] In the Tudor age the house was greatly extended and more than doubled in size, due to the alterations of Cicely Bonville, Baroness Harington and Marchioness of Dorset (1460–1529), the great heiress of the Bonville estates. The Pole family also made some additions in the late 16th century.
Descent of the manor
Bonville
The original hall-house was built in about 1380 by Sir William Bonville I (c.1332-1408), Sheriff of Somerset, Dorset and Devon. His Inquisition post mortem lists his vast land holdings in Cornwall, Wiltshire, Devon and Somerset, including Stapyldon and Sock Dennis (Somerset), West Kington (Wiltshire), Wiscombe and Southleigh and Meriet.
Sir William Bonville I (d. 1408) married as his first wife Margaret d'Aumarle, the heiress of Meriet. By her he had his eldest son Sir John Bonville, who pre-deceased his father when Sir John died 21 October 1396. He had, however, married Elizabeth FitzRoger, the daughter and sole heiress of John (or Henry) FitzRoger of Chewton Mendip, Somerset, by whom he left on his death a four-year-old son and heir William Bonville, K.G., first Lord Bonville (1392–1461), whose summons to Parliament on 10 March 1449 made him 1st Baron Bonville. He was born and baptized at Shute on 31 August 1392, as his Proof of age inquisition held at Honiton in 1413 attests. He was appointed by the king a Knight of the Garter on 8 February 1461.
During the Wars of the Roses, Lord Bonville formed a deep enmity with Thomas de Courtenay, 5th Earl of Devon (1414–1458), largely based on the wish of each man to be the pre-eminent power in Devon. Courtenay had as his secondary seat Colcombe Castle, only a few miles from Shute, and the proximity of their two estates served to fuel their enmity. They met decisively with their armed followers at the Battle of Clyst Heath, on 15 December 1455, at which Lord Bonville was defeated and after which the Earl sacked and pillaged Shute.[9] Lord Bonville witnessed the killing of both his son and grandson by Lancastrians on the same day at the Battle of Wakefield on 30 December 1460, and was himself beheaded on 18 February 1461 after the Second Battle of St Albans.
The sole survivor of the Bonville dynasty was his grandson's six-month-old infant daughter Cicely Bonville, Baroness Harington and Marchioness of Dorset (1460–1530). She was then heiress to one of the greatest estates in England and her valuable wardship was granted by King Edward IV to her mother and stepfather, Katherine Neville (sister of Richard Neville, 16th Earl of Warwick, The King-Maker, and Sir William Hastings, KG, but on the condition that she would at the age of sixteen become the wife of Thomas Grey, the son of the King's wife Elizabeth Woodville, by her first husband Sir John Grey of Groby. Thus the king could reward his wife by enriching her son by an advantageous marriage and ennobling him as 1st Marquess of Dorset.
Grey

Cecily survived the Wars of the Roses and in the peaceful reign of the first Tudor king she set about extending Shute House from a mediaeval hall house into a grand Tudor residence. She lived much of her later life at Astley Castle in Astley, Warwickshire, the ancestral seat of the Grey family, where she was buried. Her great-grand-daughter and ultimate heiress was Lady Jane Grey, executed in 1554, upon which all the Bonville inheritance escheated to the crown.
Petre
Following the attainder and executions of Sir Henry Grey, 3rd Marquess of Dorset and his daughter Lady Jane Grey, Queen Mary granted the Bonville estates to Sir William Petre, her principal Secretary of State.
Pole

In 1560 at Colyford, Sir William Petre sold the "house, materials and furniture of Shute House" to William Pole, Esquire (1515–1587), for £300. It was probably coincidental to the grant that the Poles were distant descendants of the brother of Sir William Bonville, the first builder of Shute.[12] Pole was Treasurer of the Inner Temple, a JP and was MP for Lyme Regis in 1545, Bridport in 1553 and for West Looe in 1559. He is buried in Colyton Church under a simple ledger-stone slab in the aisle with a much-worn inscription. In 1562 Pole acquired the lease for 1,200 years of a further eight score acres at Shute, for an annual rent of £16.[13] His son Sir William Pole (1561–1635), the antiquary, who had retired by 1618 to nearby Colcombe Castle, wrote sometime after that date: "My father had the howse (of Shute) and park from Sir William Petre and dwelled there during his leif and left it unto me, and my eldest son John holdeth it from mee".[14]
Descent of Shute in Pole family
The descent of Shute from Sir William Pole the antiquary was as follows:[15]
- Sir John Pole, 1st Baronet (died 1658), MP, son and heir of the antiquarian, who married his step-sister Elizabeth How, daughter and heiress of Roger How of Crediton. He lived at Shute and at Bromley St Leonards, Middlesex. He and his wife are depicted in life-size effigies under an ornate canopy supported on Corinthian columns in Colyton Church.
- Sir Courtenay Pole, 2nd Baronet (1618–1695), MP for Honiton, 2nd and eldest surviving son of the 1st baronet. His first name was in honour of the marriage of his father's sister to Francis Courtenay, de jure 4th Earl of Devon, of Powderham Castle. Two portraits of him exist at Antony House in Cornwall. Following the Restoration he purchased a painting of King Charles II by Lely now at Antony House. He married Urith Shapcote.
- Sir John Pole, 3rd Baronet (1649–1714), MP, son of the 2nd baronet. He married Anne Morice.
- Sir William Pole, 4th Baronet (1678–1741), Master of the Household to Queen Anne. His marble statue stands in Shute Church. He married Elizabeth Warry (died 1758). His younger brother was Rev. Carolus Pole (born 1686), Rector of St Breock,[16] who married Sarah Rashleigh, daughter of Jonathan Rashleigh (1642–1702) of Menabilly, Sheriff of Cornwall in 1686/7, and several times MP for Fowey, by his second wife Jane Carew, daughter of Sir John Carew, 3rd Baronet (1635–1692) of Antony in Cornwall. Sarah Rashleigh became the heiress of Antony and descendants of her marriage to Carolus Pole inherited Shute in 1926 on the death without progeny of Frederick Arundel de la Pole, 11th Baronet.
- Sir John Pole, 5th Baronet (1732–1760), who married Elizabeth Mills (died 1758).
- Sir John William de la Pole, 6th Baronet (1757–1799), MP, who married Anne Templer (1758–1832), daughter of James Templer (died 1782) of Stover House, Teigngrace, near Newton Abbot. In 1785 he demolished the most easterly Tudor additions to Old Shute House and built between 1787 and 1789 a new Palladian mansion known as New Shute House about half a mile to the east of the old house, which thenceforth became the family seat. Old Shute House then became a "barton", the Devonshire and West-Country term for a home farm to the estate. It was thus either let to a farmer or allowed as free accommodation to the Pole's farm manager.
- Sir William Templer-Pole, 7th Baronet (1782–1847), married twice, with issue from each marriage.
- John G. Reeve de la Pole, 8th Baronet (1808–1874), son of the 7th baronet by his first wife Sophia-Ann, died without issue.
- Sir William Edmund Pole, 9th Baronet (1816–1895), son of the 7th baronet by his second wife Charlotte Fraser. His wife was of the Talbot family.
- Edmund Reginald de la Pole, 10th Baronet (1844–1912), son of the 9th baronet, died without issue.
- Sir Frederick arundel de la Pole, 11th Baronet (1850–1926), died unmarried and without issue. He bequeathed Shute to his distant cousin:
- Sir John Gawen Pole-Carew (1902–1993) of Antony House, Cornwall, who on becoming the 12th Baronet changed his name to Carew-Pole. He transferred to Antony House the Pole furnishings, paintings and papers from New Shute House, which he let to a girls' school between 1933 and 1974 in which year he sold it. He also donated Old Shute House to the National Trust in 1959, on the condition that it would remain tenanted by his cousin Christopher Pole-Carew (born 1931, descended from Carolus Pole, younger brother of the 4th baronet) who remained, with his wife Gillian Burton, tenant there until 2008.[17]
National Trust
Although it is now managed by the National Trust, the Pole-Carew family, descendants of the Poles, have the right to live there. The former custodians, Christopher Pole-Carew and his wife Gillian, relinquished the role in 2008. The main part of the house opened as a holiday let in Spring 2011. The gatehouse is leased separately to the Landmark Trust who market it as a holiday let.[18]
Description by John Swete

The Devon topographer Rev. John Swete passed by Shute on his excursion of 29 January 1795, and recorded the following in his "Journal", having just left Colyton:[19] "I had now, by ascending somewhat of the hill, got in sight of the Old House of Shute, a good deal of which has been taken(-down). From the road it is seen as in the sketch (see at right), an embattled edifice of a castellated figure with projecting towers both in front and behind. A tower with pinnacles rear'd itself close at the back of the castle appearing as if it belonged to a church or chapel;" (i.e. St Michael's Church) "a fine relief was given to the whole of this pile by means of some noble trees that rose high behind it and over all was beheld (an) elevated hill." He continues to relate the story of the armed encounter of Bonville and Courtenay at Clyst Heath in 1455, which he understood to have been a battle of single combat, adding Risdon's story of the gallantry displayed toward his opponent by Courtenay when Bonville accidentally dropped his sword whereupon the former stood still and cast away his sword also, and to end the contest the two "lovingly embraced one another". Modern historians relate the incident without any such niceties, and indeed so bitter remained Courtenay's hatred of Bonville that he it was who successfully urged the unwilling King Henry VI to execute him after the Second Battle of St Albans in 1461. After having set-out the descent of Shute to the Poles, Swete noted that Old Shute was becoming neglected: "Thus the two rival families of Colcombe and Shute being no more, the two seats acknowledg'd one gentleman as their lord. But in process of time instead of the families, the seats themselves became rivals to one another and, Shute getting the superiority by the translation of the Pole family thither, Colcombe Castle became deserted and mouldered into a ruin and now in its turn, by another removal of the family to the new house, Shute is experiencing the same fate". He finishes his account of his visit to Shute by regretting due to lack of time his not having made a sketch of Shute Gateway "Which is by far too remarkable and picturesque to be omitted", and hopes to return again for the purpose.
References
- Historic England. "Old Shute House (1171033)". National Heritage List for England. Retrieved 3 July 2022.
- Cooper, Nicholas; Mannez, Pru; Blaylock, Stuart, Shute Barton, Devon: Historic Building Analysis and Archaeological Survey 2008, Exeter Archaeology Report no. 08.80, produced for the National Trust
- Per Bridie, M.F., Thye Story of Shute, Axminster, 1955
- Addendum to 1995 edition of Bridie, 1955
- Addendum to 1995 edition of Bridie, 1955
- Bridie, p.30
- Bridie, caption to image of roof timbers, p.31/31
- Source: Burke's General Armory 1884, p.99
- Orme, Nicholas, Representation & Rebellion in the Later Middle Ages, published in Kain, Roger & Ravenhill, William, (eds.) Historical Atlas of South-West England, Exeter, 1999, pp. 141, 144
- Robson, Thomas, The British Herald
- Pole, Sir William (d.1635), Collections Towards a Description of the County of Devon, Sir John-William de la Pole (ed.), London, 1791, p.497; Debrett's Peerage, 1968, p.645
- Bridie, p.79
- Bridie, p.80
- Bridie, p.81
- Bridie, p.ii, pedigree of Pole
- Vivian, p.143
- Bridie, Addendum to 1995 edition, by Christopher Pole-Carew
- "Holiday at Shute Gatehouse, Near Axminster, Devon | The Landmark Trust". www.landmarktrust.org.uk. Retrieved 3 July 2022.
- Travels in Georgian Devon, The Illustrated Journals of the Reverend John Swete, Vol.2, Gray, Todd (Ed.), Tiverton, 1998, pp.112-3
Sources
- Turner, Maureen A., The Building of New Shute House 1787–1790, MA dissertation, University of Exeter, Sept 1999
- Bridie, Marion Ferguson, The Story of Shute: The Bonvilles and the Poles, Axminster, 1955. (Published by Shute School Ltd.), reprinted 1995, Bridport.
- Pevsner N. & Cherry B., The Buildings of England: Devon, London, 2004, pp. 729–731. (Contains basic errors, e.g. will of William Bonville stated 1308, should be 1407)
Further reading
- Hussey, Christopher, two articles in Country Life Magazine on Old Shute House, vol.109, February 1951, pp 326, 398
