Siege of Léva
This page is partially a translation of the French version
| Battle of Léva/Levice | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Austro-Turkish War (1663-1664) | |||||||
.JPG.webp) Battle of Léva | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
| Jean-Louis Raduit de Souches | Ali Pasha † | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 12,000 | 20,000 | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| 100-200 | 1,000-2,000 | ||||||
The siege of Léva was fought on 19 July 1664 as part of the Austro-Turkish War (1663–1664), between a Habsburg army led by Jean-Louis Raduit de Souches and an Ottoman army under the command of Ali Pasha. The battle took place near Léva, Kingdom of Hungary (present-day Slovakia) and was a Habsburg victory.
The battle
At the beginning of 1664, the Imperial Army was divided into three corps: In the south 17.000 Hungarian-Croatian troops under command of Miklós Zrínyi. In the center the main army of Raimondo Montecuccoli of 28,500 men, which had to stop the 100,000-man-strong army of Grand vizier Köprülü Fazıl Ahmed. The third corps were the 8,500 men under general Louis Raduit de Souches in the North. Souches' army first conquered Nyitra on 3 May and then defeated the Ottomans under Mehmet Küçük on 16 May near Zsarnóca (Scharnowitz).
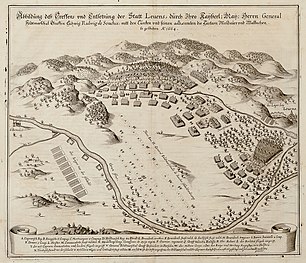
An Ottoman relief army under Ali Pasha was sent from Buda to halt the imperial army near Léva. But this Ottoman army, composed mainly of irregular troops, was no match for the well-organized imperial battalions of musketeers, protected by their phalanx of pikemen. At first, de Souches hid a part of his troops to provoke an Ottoman attack. When they walked into the trap and then discovered the rest of the enemy's army, the irregular Ottoman troops panicked and fled, leaving many dead and a rich booty of carts and weaponry on the battlefield, including eleven large artillery pieces. The commander, Ali Pacha, was killed during the rout.
This victory was strategically important, especially with possibility of burning the bridge over the Danube at Párkány (Gockern), thus isolating Upper Hungary from any further Turkish incursions. But eventually nothing came of it when, after even greater victory in the Battle of Saint Gotthard, Emperor Leopold I - to the outrage of Hungarian nobility - signed the unfavorable Peace of Vasvár.
Citations
References
- Tóth, Ferenc (2007). Saint Gotthard 1664, une Bataille Européenne [Saint Gotthard 1664, a European Battle] (in French). Lavauzelle. ISBN 978-2-7025-1064-3.