Siege of Pelium
The siege of Pelium was undertaken by Alexander the Great against the Illyrian tribes of what is modern-day Albania. It was critical for Alexander to take this pass as it provided easy access to Illyria and Macedonia, which was urgently needed in order to quell the unrest in Greece at this time in Athens and Thebes. This was an important point of demarcation in Alexander's early reign, as it established him among the Danubian tribes to the north as a serious monarch to be reckoned with, just as he would later establish this precedent for the Greek city states under his hegemony. Taking this place allowed Alexander to march his army to southern Greece quickly, which would eventually result in the total destruction of Thebes.
| Siege of Pelium | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of Alexander's Balkan campaign | |||||||
 The Plain of Pelium | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
| Macedon | Illyrians | ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
Alexander the Great Hephaestion |
Cleitus Glaukias | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
|
23,000 total
| 7,000 | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| 2,000 | 5,000 | ||||||
| Alexanders' first attempt to siege Pelion failed and the Macedonians were forced by Illyrians to retreat on the other side of the river, which thus far could have been interpreted as a sort of Illyrian victory. But after three days Alexander undertook a night attack defeating by surprise the defenseless Illyrians. Without support from the outside, Cleitus and his Illyrians burned the stronghold and fled to Glaukias' realm.[1] | |||||||
Background
News of the Illyrian revolt under the chieftain Cleitus and Glaukias of the Taulantii first reached the ears of Alexander while he was campaigning on the Danube against some of the northern tribes that his father, Philip II of Macedon had previously reduced to a satisfactory level of subjection, although not outright submission. As this area had been far from the Greek theatre of operations, Phillip had been satisfied with the level of subjection he had reduced them to.
Alexander was immediately concerned about the news of this revolt, as the fortified settlement of Pelium itself occupied one of the most important passes between Illyria and Macedonia. As a result of this, Alexander would have to make a long march around a mountain range to the south, and then into Illyria. In addition to this, without access to this crucial pass, Alexander could be cut off from Greece, which had freshly revolted, and would eventually do so again, with aid of the Great King. The loss of this pass, and the resultant long march would give the Greek city states to the south ample time to prepare for Alexander's arrival while he was reducing the Illyrians.
An ally of Alexander offered aid to him by protecting his flank from Illyrian tribes while he marched towards Pelium. Langarus, of the Agrianians, made frequent incursions into the country of the Autariatae, and managed to put them on guard sufficiently to allow Alexander to march by in relative peace. Having successfully made this march, Alexander arrived to find Cleitus in control of Pelium and awaiting the arrival of King Glaukias with reinforcements.[2] When Alexander arrived, Cleitus reportedly sacrificed three boys, three girls, and three black rams before meeting the Macedonians.[2]
Opening
Alexander arrived with 23,000 soldiers and determined to attack Pelium at once, as he hoped to take the place out of hand before King Glaukias could arrive and reinforce Cleitus. The first thing Alexander did upon arriving was set up the Macedonian camp.[2]
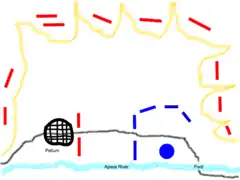
The Macedonians found that not only was Pelium itself held, which commanded the plateau, but the heights surrounding the Plain of Pelium was held in force. Upon completing the camp, Alexander resolved to attack the troops of Cleitus that were surrounding the heights. This he did with some effect, and as a result of this assault the Illyrians retreated within the walls of Pelium.[2]
Alexander then attempted to take the town by assault, but failing in this,[2] he started to erect circumvallation and contravallation around Pelium. This, however, was interrupted by the arrival of Glaukias and his reinforcements the next day, which compelled Alexander to retreat from the heights that he had captured the day before.
Battle and siege

Having been forced back into the plain itself by King Glaukias, Alexander was in now a perilous situation. He was outnumbered by the Illyrians, who were free to gather supplies. Not only that, but Alexander was anxious to take Pelium quickly before Thebes and Athens could seriously consider imperiling Macedonian hegemony.[3] Therefore, not only did Alexander have pressing issues elsewhere, but the Illyrian forces were determined to annihilate Alexander's forces, and could afford to wait.
Being short of supplies, Alexander sent Philotas, one of his lieutenants, out to forage for materials. King Glaukias witnessed this force leaving, and pursued and attacked the foragers. However, Alexander was - with some difficulty - able to fend off the attackers and extricate his hypaspists, Agrianians, and bowmen.
Seeking to seize his line of retreat before putting his shoulder to the siege, Alexander desired to attack the heights that commanded the defile through which he had come. This defile was small, and only four men could march through it abreast.[4] He drew up some of his infantry and cavalry in front of the settlement of Pelium itself to defend this maneuver from being attacked by a sortie from Cleitus.[5] He then drew up his phalanx, one hundred and twenty men deep,[5] with 200 cavalry on either flank, and arranged his soldiers to perform close-order drills down on the plain, in full view of the Illyrians, in complete silence. As Peter Green describes:
At given signals the great forest of sarissas would rise to the vertical 'salute' position, and then dip horizontally as for battle-order. The bristling spear-line swung now right, now left, in perfect unison. The phalanx advanced, wheeled into column and line, moved through various intricate formations as though on the parade-ground - all without a word being uttered. The barbarians had never seen anything like it. From their positions in the surrounding hills they stared down at this weird ritual, scarcely able to believe their eyes. Then, little by little, one straggling group after another began to edge closer, half-terrified, half-enthralled. Alexander watched them, waiting for the psychological moment. Then, at last, he gave his final pre-arranged signal. The left wing of the cavalry swung into wedge formation, and charged. At the same moment, every man of the phalanx beat his spear on his shield, and from thousands of throats there went up the terrible ululating Macedonian war-cry - 'Alalalalai!' - echoing and reverberating from the mountains. This sudden, shattering explosion of sound, especially after the dead stillness which had preceded it, completely unnerved Glaucias' tribesmen, who fled back in wild confusion from the foothills to the safety of their fortress.
— Peter Green, Alexander of Macedon, 356-323 B.C. (1991)[6]
The Macedonian forces took the heights overlooking Pelium. During this engagement, not a single Macedonian armored soldier was killed.[7] However, deaths among light troops were usually not reported, and it is unknown whether any were killed in this instance.[7]
There were still some Illyrian light infantry on the heights that commanded the ford, and it was critical for Alexander to seize these heights in order to gain control of the entire plain. Before engaging in battle, Alexander decided to re-establish his camp on the far side of the river near the ford in order to ensure the security of both his operations and his camp. However, in the process of doing so he ran the danger of being engaged in the rear while his troops were crossing the river. The Illyrians indeed attacked him, perceiving his army to be retreating. So he ordered his troops to turn around to simulate an advance, while initiating a charge with his companion cavalry. Meanwhile, he also ordered his archers to turn around and fire their arrows from mid-stream.[8] Having gained a place of relative security on the far side of the river, Alexander was able to freely supply his army and await reinforcements.[7] After three days,[1] before reinforcements arrived, however, Macedonian scouts reported that they observed the Illyrians becoming careless in protecting the settlement, as they thought Alexander was in retreat.[7]
Acting on this intelligence, Alexander awaited the arrival of night, and then rushed ahead without awaiting the crossing of his complete force, leading his archers, his shield-bearing guards, the Agrianians, and the brigade of Coenus as the leading unit. He then rushed down upon the defenders with his Agrianians and archers, who were formed in phalanx formation. Many of the Illyrians were still asleep, and were taken completely by surprise. A great slaughter followed; many of the Illyrians were also captured.[9]
- Pelium Maneuver
 1
1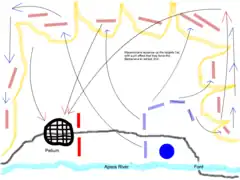 2
2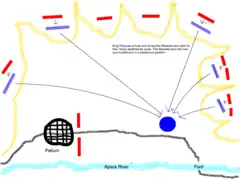 3
3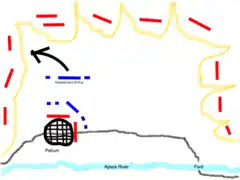 4
4
Result
As a result of this siege, Alexander gained Pelium, and built a fresh outpost there, as the Illyrians had burnt the settlement that had previously been situated there.[9] The Illyrians asked for terms, and Alexander was happy to accept their terms and allow them to swear loyalty to him for a time. Having completed his conquest, Alexander had established himself as a new monarch to be revered, and was now free to march south to Boeotia and deal with the threat from Thebes and Athens.
Notes
- Vujčić 2021, pp. 524–525.
- Dodge, 201
- Dodge, 198
- Dodge, 202
- Dodge, 204
- Green, p.132-133
- Dodge, 206
- Dodge, 205
- Dodge, 208
References
- Dodge, Theodore (1890). Alexander. New York, NY: Da Capo. ISBN 0-306-80690-8.
- Hammond, N. G. L.; Walbank, Frank William (2001). A History of Macedonia: 336-167 B.C. Vol. III. Oxford: Clarendon Press. ISBN 0-19-814815-1.
- Green, Peter (1991). Alexander of Macedon, 356-323 B.C.. University of California Press. ISBN 0520071662.
- Vujčić, Nemanja (2021). "The City of Pelion and the Illyrian War of Alexander". Greek, Roman, and Byzantine Studies. 61.
External links
- Livius Archived 2016-09-09 at the Wayback Machine
- T.A.Dodge. Alexander
- Plutarch