Smart bookmark
Smart bookmarks are an extended kind of Internet bookmark used in web browsers.[1][2][3] By accepting an argument, they directly give access to functions of web sites, as opposed to filling web forms at the respective web site for accessing these functions. Smart bookmarks can be used for web searches, or access to data on web sites with uniformly structured web addresses (e.g., user profiles in a web forum).
History
Smart bookmarks first were introduced in OmniWeb on the NEXTSTEP platform in 1997/1998, where they were called shortcuts.[4] The feature was subsequently taken up by Opera, Galeon and Internet Explorer for Mac, so they can now be used in many web browsers, most of which are Mozilla based, like Kazehakase and Mozilla Firefox.
In Web, smart bookmarks appear in a dropdown menu when entering text in the address bar. By selecting a smart bookmark the respective web site is accessed using the text as argument. Smart bookmarks can also be added to the toolbar, together with their own textbox.[5] The same applies to Galeon, which also allows the user to collapse and expand the textboxes within the toolbar. Smart bookmarks can also be shared, and there is a collection of them at the web site of the Galeon project.
Usage
There are two ways to employ smart bookmarks: either through the assignment of keywords or without. E.g., Mozilla derivatives and also Konqueror requires the assigning of keywords that can then be typed directly into the address bar followed by the term. Epiphany does not allow assigning keywords. Instead, the term is typed directly into the address bar, then all smart bookmarks appear on the address bar, can be dropped down the list, and selected.
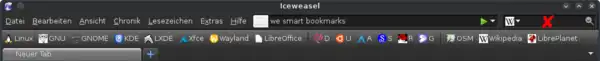 Smart bookmarks usage: Entering a keyword and search a term separated by a blank space into the address bar.
Smart bookmarks usage: Entering a keyword and search a term separated by a blank space into the address bar.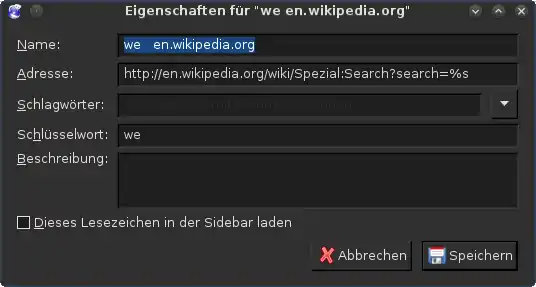 Smart bookmark creation in Iceweasel
Smart bookmark creation in Iceweasel
See also
- Bookmarklets, making it possible to use javascript with smart bookmarks
- iMacros for Firefox, embeds web browser macros in bookmarks or links
References
- "How to Set Keyword Bookmarks in Google Chrome". 22 February 2010.
- "In Firefox, what are smart keywords and how do I use them?".
- "Accelerators". 5 November 2020.
- Shaw, David Andrew (2004-03-22), "OmniWeb 3.0/3.1", Rhapsody Resource Page, retrieved 2012-03-22
- "Smart Bookmarks", The GNOME Project, retrieved 2011-12-14
External links
- Smart Bookmarksat the Galeon site Archived 2005-09-08 at the Wayback Machine
- Smart Bookmarks And Bookmarklets