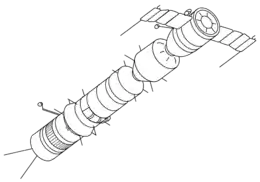
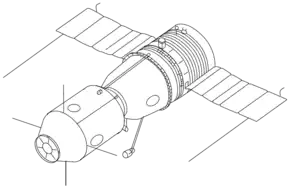
Soyuz-A
Sergei Korolev initially promoted the Soyuz A-B-V circumlunar complex (7K-9K-11K) concept (also known as L1) in which a two-man craft Soyuz 7K would rendezvous with other components (9K and 11K) in Earth orbit to assemble a lunar excursion vehicle, the components being delivered by the proven R-7 rocket. [1][2]
 | |
| Manufacturer | OKB-1 |
|---|---|
| Country of origin | Soviet Union |
| Applications | Carry up to three cosmonauts to lunar orbit. |
| Specifications | |
| Regime | Low Earth Medium Earth Circumlunar |
| Production | |
| Status | Cancelled |
| Launched | None |
| Related spacecraft | |
| Derivatives | Soyuz 7K-OK (first Soyuz generation to fly crewed) |
Besides the Soyuz 7K spacecraft, the complex would feature a Soyuz 9K booster and a Soyuz 11K tanker with twin whip antennas.
The 7K would have been equipped with cameras and sensors to study the lunar surface during the flyby, at a distance of 1,000 to 20,000 km from the Moon's surface. Total flight time would have been 7 to 8 days.
Relation with other Soyuz versions
Soyuz A is the base concept for the entire Soyuz spacecraft family. The 7K series is a direct descendant of this original proposal. The list below shows proposed, flown (in bold) and military (in italic) Soyuz versions.
- Soyuz-A (1963)
- Soyuz P (1962)
- Soyuz PPK (1964)
- Soyuz R (1962)
- Soyuz 7K-TK (1966)
- Soyuz 7K-VI Zvezda (1964)
- Soyuz OIS (1967)
- Soyuz OB-VI (1967)
- Soyuz 7K-S (1974)
- Soyuz 7K-ST (1974)
- Soyuz T (1976-86)
- Soyuz TM (1986-02)
- Soyuz TMA (2002-12)
- Soyuz TMA-M (2010-16)
- Soyuz MS (2016-...)
- Progress M (1989-09)
- Progress M1 (2000-14)
- Progress MS (2015)
- Soyuz T (1976-86)
- Soyuz 7K-LOK (1967)
- Soyuz 7K-L1 (1967-70)
- Soyuz 7K-L1E (1970-71)
- Soyuz 7K-L1 (1967-70)
- Soyuz 7K-OK (1967-71)
- Soyuz 7K-OKS (1971)
- Soyuz 7K-T (1973-81)
- Progress 7K-TG (1978-90)
- Soyuz 7K-TM (1975)
- Soyuz 7K-T (1973-81)
- Soyuz 7K-OKS (1971)
- Soyuz P (1962)
References
- "Soyuz A". astronautix.com. Mark Wade. 2001-10-31. Retrieved 2010-07-16.
- Pike, John. "L-1 Lunar Circumnavigation Mission". GlobalSecurity.org. Retrieved 2009-06-30.

