List of states and union territories of India by population
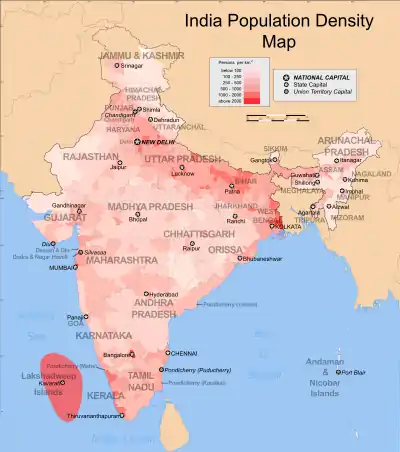
India is a union consisting of 28 states and 8 union territories.[1] As of 2022, with an estimated population of 1.4 billion, India is the world's most populous country. India occupies 2.4% of the world's area and is home to 17.5% of the world's population.[2] The Indo-Gangetic Plain has one of the world's biggest stretches of fertile flat-deep alluvium and are among the most densely populated areas of the world. The eastern and western coastal regions of Deccan Plateau are also densely populated regions of India. The Thar Desert in western Rajasthan is one of the most densely populated deserts in the world.[3] The northern and north-eastern states along the Himalayas contain cold arid deserts with fertile valleys. These states have relatively less population density due to indomitable physical barriers.[4]
Census of India
The first population census in British India was conducted in 1872. Since India's independence in 1947, a census has been conducted every 10 years, the first occurring in 1951.[5] The census in India is conducted by the Office of the Registrar General and Census Commissioner under the Ministry of Home Affairs, and is one of the largest administrative tasks conducted by a federal government.[6]
The latest population figures are based on data from the 2011 census of India.[7] During the decade of 2001–2011, India's annual population growth rate has slowed down from 2.15 percent to 1.76 percent.[7] Based on decennial census data, Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu has the fastest growth rate of 55.1 percent, followed by Meghalaya (27.8 percent) and Arunachal Pradesh (25.9 percent). Nagaland recorded the lowest growth rate of -0.5 percent.[8]
India has 641,000 inhabited villages and 72.2 percent of the total population reside in these rural areas.[8] Of them 145,000 villages have population size of 500–999 persons; 130,000 villages have population size of 1000–1999 and 128,000 villages have population size of 200–499. There are 3,961 villages that have a population of 10,000 persons or more.[9] India's 27.8 percent urban population lives in more than 5,100 towns and over 380 urban agglomerations.[10] In the decade of 1991–2001, migration to major cities caused rapid increase in urban population.[11][12] On the basis of net migrants by last residence during the past decade, Maharashtra had most immigration with 2.3 million, followed by National Capital Territory of Delhi (1.7 million), Gujarat (0.68 million) and Haryana (0.67 million). Uttar Pradesh (−2.6 million) and Bihar (−1.7 million) topped the list for interstate emigration.[13] The five states of Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, Bihar, West Bengal and Madhya Pradesh account for almost half (47.90 percent) of the total Indian population.[7]
While the national average for the sex ratio shows an increase from 933 in 2001 to 940 in 2011,[7] the 2011 census shows a sharp decline in the child sex ratio, the number of females per thousand males in a population between age group 0–6 years.[7] States such as Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Mizoram and Andaman and Nicobar Islands recorded an increase in India's child sex ratio.[7] The national child sex ratio has declined from 927 in 2001 to 914 in 2011.[7] Telangana census was separated from Andhra Pradesh state census figures, after Telangana was officially formed on 2 June 2014.[14]
List
Data from Census 2011 as published by the Registrar General & Census Commissioner,[15] Government of Telangana,[16] and then Planning Commission.[17]
(Population density is rounded to the nearest integer)
| List of states and union territories of India by population (2011 Census of India) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | State or Union Territory | Population[18][19] | National Share (%) | Decadal growth (2001–2012) |
Rural population | Percent rural | Urban population | Percent urban | Population Density[lower-alpha 1] | Sex ratio | Lok Sabha seats | Rajya Sabha seats |
| 1 (S1) | Uttar Pradesh | 199,812,341 | 16.51% | 20.2% | 155,317,278 | 77.73% | 44,495,063 | 22.27% | 828/km2 (2,140/sq mi) | 912 | 80 | 31 |
| 2 (S2) | Bihar | 104,099,452 | 8.6% | 25.4% | 92,341,436 | 88.71% | 11,758,016 | 11.29% | 1,102/km2 (2,850/sq mi) | 918 | 40 | 16 |
| 3 (S3) | Maharashtra | 112,374,333 | 9.28% | 16% | 61,556,074 | 54.78% | 50,818,259 | 45.22% | 365/km2 (950/sq mi) | 929 | 48 | 19 |
| 4 (S4) | West Bengal | 91,276,115 | 7.54% | 13.8% | 62,183,113 | 68.13% | 29,093,002 | 31.87% | 1,029/km2 (2,670/sq mi) | 953 | 42 | 16 |
| 5 (S5) | Madhya Pradesh | 72,626,809 | 6% | 20.3% | 52,557,404 | 72.37% | 20,069,405 | 27.63% | 236/km2 (610/sq mi) | 931 | 29 | 11 |
| 6 (S6) | Tamil Nadu | 72,147,030 | 5.96% | 15.6% | 37,229,590 | 51.6% | 34,917,440 | 48.4% | 555/km2 (1,440/sq mi) | 996 | 39 | 18 |
| 7 (S7) | Rajasthan | 68,548,437 | 5.66% | 21.3% | 51,500,352 | 75.13% | 17,048,085 | 24.87% | 201/km2 (520/sq mi) | 928 | 25 | 10 |
| 8 (S8) | Karnataka | 61,095,297 | 5.05% | 15.6% | 37,469,335 | 61.33% | 23,625,962 | 38.67% | 319/km2 (830/sq mi) | 973 | 28 | 12 |
| 9 (S9) | Gujarat | 60,439,692 | 4.99% | 19.3% | 34,694,609 | 57.4% | 25,745,083 | 42.6% | 308/km2 (800/sq mi) | 919 | 26 | 11 |
| 10 (S10) | Andhra Pradesh | 49,577,103[lower-alpha 2] | 4.1% | 11.0% | 34,966,693 | 70.53% | 14,610,410 | 29.47% | 303/km2 (780/sq mi) | 993 | 25 | 11 |
| 11 (S11) | Odisha | 41,974,219 | 3.47% | 14.0% | 34,970,562 | 83.31% | 7,003,656 | 16.69% | 269/km2 (700/sq mi) | 979 | 21 | 10 |
| 12 (S12) | Telangana | 35,003,674 | 2.89% | 13.58% | 21,395,009 | 61.12% | 13,608,665 | 38.88% | 312/km2 (810/sq mi) | 988 | 17 | 7 |
| 13 (S13) | Kerala | 33,406,061 | 2.76% | 4.9% | 17,471,135 | 52.3% | 15,934,926 | 47.7% | 859/km2 (2,220/sq mi) | 1,084 | 20 | 9 |
| 14 (S14) | Jharkhand | 32,988,134 | 2.73% | 22.4% | 25,055,073 | 75.95% | 7,933,061 | 24.05% | 414/km2 (1,070/sq mi) | 948 | 14 | 6 |
| 15 (S15) | Assam | 31,205,576 | 2.58% | 17.1% | 26,807,034 | 85.9% | 4,398,542 | 14.1% | 398/km2 (1,030/sq mi) | 958 | 14 | 7 |
| 16 (S16) | Punjab | 27,743,338 | 2.29% | 13.89% | 17,344,192 | 62.52% | 10,399,146 | 37.48% | 551/km2 (1,430/sq mi) | 895 | 13 | 7 |
| 17 (S17) | Chhattisgarh | 25,545,198 | 2.11% | 22.6% | 19,607,961 | 76.76% | 5,937,237 | 23.24% | 189/km2 (490/sq mi) | 991 | 11 | 5 |
| 18 (S18) | Haryana | 25,351,462 | 2.09% | 19.9% | 16,509,359 | 65.12% | 8,842,103 | 34.88% | 573/km2 (1,480/sq mi) | 879 | 10 | 5 |
| 19 (UT1) | NCT of Delhi | 16,787,941 | 1.39% | 21.2% | 419,042 | 2.5% | 16,368,899 | 97.5% | 11,297/km2 (29,260/sq mi) | 868 | 7 | 3 |
| 20 (UT2) | Jammu and Kashmir | 12,267,032 | 1.01% | 23.6% | 9,064,220 | 73.89% | 3,202,812 | 26.11% | 297/km2 (770/sq mi) | 890 | 5 | 4 |
| 21 (S19) | Uttarakhand | 10,086,292 | 0.83% | 18.8% | 7,036,954 | 69.77% | 3,049,338 | 30.23% | 189/km2 (490/sq mi) | 963 | 5 | 3 |
| 22 (S20) | Himachal Pradesh | 6,864,602 | 0.57% | 12.9% | 6,176,050 | 89.97% | 688,552 | 10.03% | 123/km2 (320/sq mi) | 972 | 4 | 3 |
| 23 (S21) | Tripura | 3,673,917 | 0.3% | 14.8% | 2,712,464 | 73.83% | 961,453 | 26.17% | 350/km2 (910/sq mi) | 960 | 2 | 1 |
| 24 (S22) | Meghalaya | 2,966,889 | 0.25% | 27.9% | 2,371,439 | 79.93% | 595,450 | 20.07% | 132/km2 (340/sq mi) | 989 | 2 | 1 |
| 25 (S23) | Manipur[lower-alpha 3] | 2,570,390 | 0.21% | 24.5% | 1,793,875 | 69.79% | 776,515 | 30.21% | 122/km2 (320/sq mi) | 992 | 2 | 1 |
| 26 (S24) | Nagaland | 1,978,502 | 0.16% | −0.6% | 1,407,536 | 71.14% | 570,966 | 28.86% | 119/km2 (310/sq mi) | 931 | 1 | 1 |
| 27 (S25) | Goa | 1,458,545 | 0.12% | 8.2% | 551,731 | 37.83% | 906,814 | 62.17% | 394/km2 (1,020/sq mi) | 973 | 2 | 1 |
| 28 (S26) | Arunachal Pradesh | 1,383,727 | 0.11% | 26.0% | 1,066,358 | 77.06% | 317,369 | 22.94% | 17/km2 (44/sq mi) | 938 | 2 | 1 |
| 29 (UT3) | Puducherry | 1,247,953 | 0.1% | 28.1% | 395,200 | 31.67% | 852,753 | 68.33% | 2,598/km2 (6,730/sq mi) | 1,037 | 1 | 1 |
| 30 (S27) | Mizoram | 1,097,206 | 0.09% | 23.5% | 525,435 | 47.89% | 571,771 | 52.11% | 52/km2 (130/sq mi) | 976 | 1 | 1 |
| 31 (UT4) | Chandigarh | 1,055,450 | 0.09% | 17.2% | 28,991 | 2.75% | 1,026,459 | 97.25% | 9,252/km2 (23,960/sq mi) | 818 | 1 | – [lower-alpha 4] |
| 32 (S28) | Sikkim | 610,577 | 0.05% | 12.9% | 456,999 | 74.85% | 153,578 | 25.15% | 86/km2 (220/sq mi) | 890 | 1 | 1 |
| 33 (UT5) | Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu | 585,764 | 0.05% | 55.1% | 243,510 | 41.57% | 342,254 | 58.43% | 970/km2 (2,500/sq mi) | 711 | 2 | – [lower-alpha 5] |
| 34 (UT6) | Andaman and Nicobar Islands | 380,581 | 0.03% | 6.9% | 237,093 | 62.3% | 143,488 | 37.7% | 46/km2 (120/sq mi) | 876 | 1 | – [lower-alpha 6] |
| 35 (UT7) | Ladakh | 274,000 | 0.02% | 17.8% | 43,840 | 16% | 230,160 | 84% | 2.8/km2 (7.3/sq mi) | 853 | 1 | – [lower-alpha 7] |
| 36 (UT8) | Lakshadweep | 64,473 | 0.01% | 6.3% | 14,141 | 21.93% | 50,332 | 78.07% | 2,013/km2 (5,210/sq mi) | 946 | 1 | – [lower-alpha 8] |
| Total | India | 1,210,569,573 | 100% | 17.7% | 833,463,448 | 68.84% | 377,106,125 | 31.16% | 382/km2 (990/sq mi) | 940 | 543 | 245 (233+12)[lower-alpha 9] |
Notes
- For determining population density of India and the State of Jammu and Kashmir, the data excludes areas claimed by India but controlled by Pakistan (78,114 km2) and China (5,180 km2 in Shaksgam Valley and 37,555 km2 under Aksai Chin and other areas).[20][21]
- Calculated by subtracting the population of Telangana from Andhra Pradesh's Census 2011 figures.
- Excludes Mao-Maram, Paomata, and Purul sub-divisions of Senapati district of Manipur.
- No state legislature
- No state legislature
- No state legislature
- No state legislature
- No state legislature
- Includes 12 Presidential nominations
See also
References
- "National Portal of India". www.india.gov.in. Retrieved 2022-08-08.
- "Census and you - Area And Population". 2007-12-26. Archived from the original on 26 December 2007. Retrieved 2022-08-08.
- "Report of the Task Force on Grasslands and Deserts" (PDF). 2011-12-10. Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 December 2011. Retrieved 2022-08-08.
- "India - General Profile, Land Use Classification and Land Use Pattern" (PDF). 2006-05-14. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 May 2006. Retrieved 2022-08-08.
- "Census Organisation of India". Government of India (2001). Census of India. Archived from the original on December 1, 2008. Retrieved 2008-12-04.
- "Brief history of census". Government of India (2001). Census of India. Archived from the original on 2013-11-13. Retrieved 2008-10-26.
- "India Census 2011, Provisional Population Totals". The Hindu. Chennai, India.
- "Archived copy" (PDF). The Hindu. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-11-03.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - "Area and Population". Government of India (2001). Census of India. Archived from the original on 2007-12-26. Retrieved 2008-10-26.
- "Urban Agglomerations (UAs) & towns". Government of India (2001). Census of India. Archived from the original on 2013-11-13. Retrieved 2008-12-04.
- Shinde, Swati (13 Sep 2008). "Migration rate to city will dip". The Times of India. Archived from the original on 5 November 2012. Retrieved 2008-12-08.
- "Develop towns to stop migration to urban areas: economist". The Hindu. Chennai, India. Dec 3, 2005. Archived from the original on December 5, 2005. Retrieved 2008-12-08.
- "Migration". Government of India (2001). Census of India. Archived from the original on 2013-11-13. Retrieved 2008-10-26.
- "T-party today: India's 29th state Telangana is born - Times of India ►". The Times of India. 2 June 2014. Archived from the original on 17 September 2018. Retrieved 15 September 2018.
- "Population and decadal change by residence : 2011 (PERSONS)" (PDF). Office of the Registrar General & Census Commissioner, India. p. 2. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2016-06-24. Retrieved 2019-01-15.
- "Statistical Year Book 2015" (PDF). telangana.gov.in. Directorate of Economics and Statistics, Government of Telangana. Archived (PDF) from the original on 19 October 2019. Retrieved 4 March 2019.
- "Census 2011 (Final Data) - Demographic details, Literate Population (Total, Rural & Urban)" (PDF). planningcommission.gov.in. Planning Commission, Government of India. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 January 2018. Retrieved 15 January 2019.
- "List of states with Population, Sex Ratio and Literacy Census 2011". www.census2011.co.in. Retrieved 2023-04-30.
- "Census 2011: Population in States and Union Territories of India". Jagranjosh.com. 2016-10-14. Retrieved 2023-04-30.
- "J&K 2011 Population density census" (PDF). Archived from the original on 2018-12-25. Retrieved 2022-01-06.
- "Religion PCA 2011 J&K census". Archived from the original on 2016-02-09. Retrieved 2016-01-14.