Pubic arch
The pubic arch, also referred to as the ischiopubic arch, is part of the pelvis. It is formed by the convergence of the inferior rami of the ischium and pubis on either side, below the pubic symphysis. The angle at which they converge is known as the subpubic angle.[1]
| Pubic arch | |
|---|---|
 Female pelvis (pubic arch labeled at bottom center) | |
 Male pelvis (pubic arch labeled at bottom center) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arcus pubicus |
| TA98 | A02.5.02.003 |
| TA2 | 1284 |
| FMA | 16951 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
Function
The pubic arch is one of three notches (the one in front) that separate the eminences of the lower circumference of the true pelvis.
Clinical significance
Subpubic angle
The subpubic angle (or pubic angle) is the angle in the human body as the apex of the pubic arch, formed by the convergence of the inferior rami of the ischium and pubis on either side. The subpubic angle is important in forensic anthropology, in determining the sex of someone from skeletal remains. A subpubic angle of 50–82 degrees indicates a male; an angle of 90 degrees indicates a female.[2] Other sources operate with 50–60 degrees for males and 70–90 degrees in females.[1] Women have wider hips, and thus a greater subpubic angle, in order to allow for child birth.
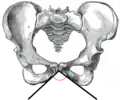 Female subpubic angle
Female subpubic angle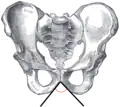 Male subpubic angle
Male subpubic angle
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 240 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 240 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- Bojsen-Møller, Finn; Simonsen, Erik B.; Tranum-Jensen, Jørgen (2001). Bevægeapparatets anatomi [Anatomy of the Locomotive Apparatus] (in Danish) (12th ed.). pp. 257–258. ISBN 978-87-628-0307-7.
- Anthony J. Bertino. Forensic Science - Fundamentals and Investigations. South-Western Cengage Learning, 2000. ISBN 978-0-538-44586-3. Page 368