Sumoto, Hyōgo
Sumoto (洲本市, Sumoto-shi) is a city located on Awaji Island, Hyōgo Prefecture, Japan. As of 1 June 2022, the city had an estimated population of 42,094 and a population density of 230 persons per km².[1] The total area of the city is 182.38 square kilometres (70.42 sq mi).
Sumoto
洲本市 | |
|---|---|
 | |
 Flag  Seal | |
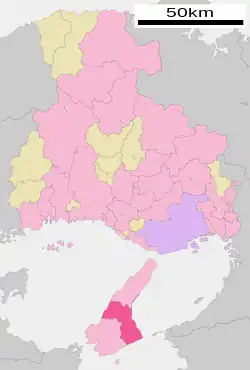 Location of Sumoto in Hyōgo Prefecture | |
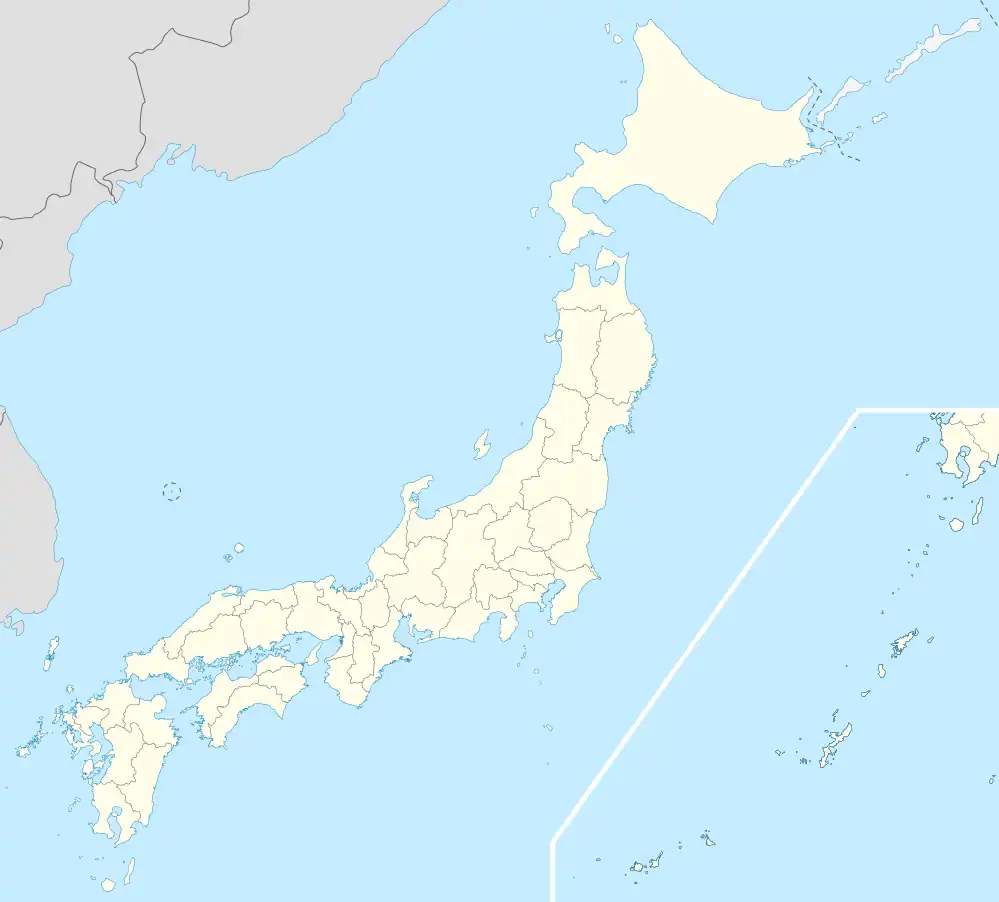 Sumoto Location in Japan | |
| Coordinates: 34°21′N 134°54′E | |
| Country | Japan |
| Region | Kansai |
| Prefecture | Hyōgo |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Michihiro Takeuchi |
| Area | |
| • Total | 182.38 km2 (70.42 sq mi) |
| Population (April 30, 2022) | |
| • Total | 42,094 |
| • Density | 230/km2 (600/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+09:00 (JST) |
| City hall address | 3-4-10 Honmachi, Sumoto-shi, Hyōgo-ken 656-8686 |
| Climate | Cfa |
| Website | Official website |
| Symbols | |
| Bird | Plover |
| Fish | Japanese Spanish mackerel (Scomberomorus niphonius) |
| Flower | Narcissus and Rapeseed |
| Tree | Pine |


Geography
The city of Sumoto occupies the middle of Awaji Island, sandwiched between Awaji and Minamiawaji. with the Gulf of Harima on the Seto Inland Sea to the west and Osaka Bay to the east. The Sumoto River flows into Osaka Bay in the center of the city area, part of which are within the borders of the Setonaikai National Park
Climate
Sumoto has a humid subtropical climate (Köppen climate classification Cfa) with hot summers and cool winters. Precipitation is significant throughout the year, but is somewhat lower in the winter.
| Climate data for Sumoto, Hyōgo (1991−2020 normals, extremes 1919−present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 19.5 (67.1) |
22.2 (72.0) |
24.4 (75.9) |
28.3 (82.9) |
32.2 (90.0) |
33.6 (92.5) |
37.3 (99.1) |
38.0 (100.4) |
36.2 (97.2) |
30.1 (86.2) |
26.0 (78.8) |
21.8 (71.2) |
38.0 (100.4) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 8.5 (47.3) |
9.2 (48.6) |
12.7 (54.9) |
18.2 (64.8) |
22.7 (72.9) |
25.5 (77.9) |
29.4 (84.9) |
31.0 (87.8) |
27.0 (80.6) |
21.5 (70.7) |
16.2 (61.2) |
11.1 (52.0) |
19.4 (66.9) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 5.4 (41.7) |
5.6 (42.1) |
8.6 (47.5) |
13.7 (56.7) |
18.3 (64.9) |
21.7 (71.1) |
25.6 (78.1) |
26.9 (80.4) |
23.5 (74.3) |
18.3 (64.9) |
13.1 (55.6) |
8.0 (46.4) |
15.7 (60.3) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 2.6 (36.7) |
2.5 (36.5) |
5.0 (41.0) |
9.8 (49.6) |
14.6 (58.3) |
18.8 (65.8) |
23.0 (73.4) |
24.1 (75.4) |
20.8 (69.4) |
15.6 (60.1) |
10.2 (50.4) |
5.2 (41.4) |
12.7 (54.9) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −5.2 (22.6) |
−6.1 (21.0) |
−4.0 (24.8) |
0.1 (32.2) |
5.5 (41.9) |
9.5 (49.1) |
15.5 (59.9) |
16.9 (62.4) |
12.1 (53.8) |
5.8 (42.4) |
0.7 (33.3) |
−3.0 (26.6) |
−6.1 (21.0) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 48.2 (1.90) |
67.1 (2.64) |
109.0 (4.29) |
117.5 (4.63) |
145.0 (5.71) |
198.2 (7.80) |
182.2 (7.17) |
117.0 (4.61) |
223.6 (8.80) |
185.6 (7.31) |
91.5 (3.60) |
75.1 (2.96) |
1,559.9 (61.41) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 1 (0.4) |
1 (0.4) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
2 (0.8) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.5 mm) | 7.5 | 7.8 | 10.7 | 10.5 | 10.4 | 12.7 | 10.8 | 7.3 | 10.9 | 9.8 | 7.7 | 7.9 | 114.1 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 1 cm) | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.8 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 68 | 68 | 68 | 69 | 72 | 80 | 82 | 78 | 78 | 75 | 72 | 69 | 73 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 138.9 | 146.4 | 183.1 | 201.4 | 208.9 | 158.5 | 197.1 | 232.1 | 165.7 | 163.8 | 139.9 | 133.9 | 2,069.8 |
| Source: JMA[2][3] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
Per Japanese census data,[4] the population of Sumoto has been declining steadily over the past 60 years.
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1960 | 62,632 | — |
| 1970 | 56,171 | −10.3% |
| 1980 | 54,826 | −2.4% |
| 1990 | 54,049 | −1.4% |
| 2000 | 52,248 | −3.3% |
| 2010 | 47,271 | −9.5% |
History
The city of Sumoto is situated in ancient Awaji Province, and developed as a castle town around the Muromachi period Sumoto Castle. It was ruled as part of Tokushima Domain during the Edo period. After the Meiji restoration, it became part of Tsuna District, Hyōgo. The town of Sumoto was established with the creation of the modern municipalities system April 1, 1889. It was raised to city status on February 11, 1940. On February 11, 2006, the town of Goshiki (from Tsuna District) was merged into Sumoto
Government
Sumoto has a mayor-council form of government with a directly elected mayor and a unicameral city council of 18 members. Sumoto contributes one member to the Hyogo Prefectural Assembly. In terms of national politics, the city is part of Hyōgo 9th district of the lower house of the Diet of Japan.
Economy
The local economy is largely rural, and is based on agriculture and commercial fishing. Sumoto has traditionally been famous for its production of Awaji onions, Naruto oranges and Kobe Beef.
Education
Sumoto has 13 public elementary schools and five public middle schools operated by the city government and two public high schools operated by the Hyōgo Prefectural Department of Education. The city also operates one combined elementary/middle school. There are also one private combined middle/high school.
Transportation
Railway
Sumoto does not have any passenger rail service.
Other
Jointly with Minami Awaji and Awaji, the city operates a low-cost electric bike rental scheme, designed to attract visitors to stay for more than one day in order to explore the island.[5]
Sister City relations
Local attractions
- Sumoto Castle - A castle ruin, one of the Continued Top 100 Japanese Castles.[6]
- Awajishima Historical Museum
- Yura Fortress
- Wellness Park Goshiki Takataya Kahei Park
Notable people from Sumoto
- Mao Daichi, actress
- Mao Miyaji, actress
References
- "Sumoto city official statistics" (in Japanese). Japan.
- 観測史上1~10位の値(年間を通じての値). JMA. Retrieved February 28, 2022.
- 気象庁 / 平年値(年・月ごとの値). JMA. Retrieved February 28, 2022.
- Hyōgo population statistics
- "Rental bicycles eyed to boost tourism". Yomiuri Shimbun. Japan. 19 July 2010. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- "続日本100名城" (in Japanese). 日本城郭協会. Retrieved 25 July 2019.
External links
- Sumoto City official website (in Japanese)