Ansa cervicalis
The ansa cervicalis (or ansa hypoglossi in older literature) is a loop formed by muscular branches of the cervical plexus formed by branches of cervical spinal nerves C1-C3. The ansa cervicalis has two roots - a superior root (formed by branch of C1) and an inferior root (formed by union of branches of C2 and C3) - that unite distally, forming a loop. It is situated within the carotid sheath.[1]: 334
| Ansa cervicalis | |
|---|---|
 Ansa cervicalis. Superior root labeled as "descending hypoglossal," Inferior root labeled as "descending cervical." | |
| Details | |
| Innervates | sternohyoid muscle, sternothyroid muscle, omohyoid muscle |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | ansa cervicalis, ansa hypoglossi |
| TA98 | A14.2.02.013 |
| TA2 | 6376 |
| FMA | 55142 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
Branches of the ansa cervicalis innervate three of the four infrahyoid muscles: the sternothyroid, sternohyoid, and omohyoid muscles (note that the thyrohyoid muscle is the one infrahyoid muscle not innervated by the ansa cervicalis - it is instead innervated by cervical spinal nerve 1 via a separate thyrohyoid branch[2]: 582, 600 ).
Its name means "handle of the neck" in Latin.
Anatomy
The ansa cervicalis is typically embedded within the anterior wall of the carotid sheath anterior to the internal jugular vein.[1]: 344
Superior root
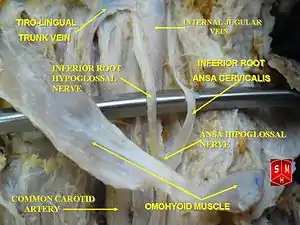
The superior root of the ansa cervicalis (formerly known as descendens hypoglossi[1]: 500 ) is by fibres of the cervical spinal nerve 1 [1]: 344 [3] (and, according to some sources, of cervical spinal nerve 2 as well[3]) that have joined and run with the hypoglossal nerve (CN XII) for some distance before[1]: 344 progressively[1]: 369 branching off the CN XII in the carotid triangle to form the superior root.[1]: 344
The superior root is situated within the carotid triangle.[1]: 344 It passes anterior-ward between the internal carotid artery and the common carotid artery.[1]: 500 It curves around the occipital artery before descending upon the anterior aspect of the internal carotid artery and the common carotid artery.[1]: 344 on the carotid sheath. It issues a branch to the superior belly of the omohyoid muscle,[1]: 344 and the upper parts of the sternothyroid and sternohyoid muscles before uniting with the inferior root.
Inferior root
The inferior root of the ansa cervicalis (formerly known as descendens cervicalis[1]: 500 ) is formed by the union of fibers of the anterior rami spinal cervical nerves C2-C3 that unite as part of the cervical plexus.[1]: 344
The inferior root curves posteroanteriorly around[1]: 344 the lateral side of the internal jugular vein[1]: 343 before descending to unite with the superior root upon the (inferior portion of) the internal jugular vein. It may occasionally pass anterior in between the internal jugular vein and the internal carotid artery.[1]: 344
Branches
Branches to the sternothyroid muscle, sternohyoid muscle, and inferior belly of the omohyoid muscle issue from the loop of the ansa cervicalis, whereas the branch for the superior belly of the omohyoid muscle arises from the superior root.[1]: 344
Additional images
 Cervical plexus shown in purple
Cervical plexus shown in purple Plan of the cervical plexus.
Plan of the cervical plexus. The right brachial plexus with its short branches, viewed from in front.
The right brachial plexus with its short branches, viewed from in front.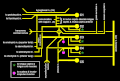 Cervical plexus
Cervical plexus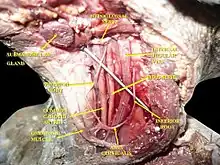 Muscles, arteries and nerves of neck.Newborn dissection.
Muscles, arteries and nerves of neck.Newborn dissection.
References
- Sinnatamby, Chummy S. (2011). Last's Anatomy (12th ed.). Elsevier Australia. ISBN 978-0-7295-3752-0.
- Standring, Susan (2020). Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice (42th ed.). New York. ISBN 978-0-7020-7707-4. OCLC 1201341621.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Moore, Keith L.; Dalley, Arthur F.; Agur, Anne M. R. (2018). Clinically Oriented Anatomy (8th ed.). Wolters Kluwer. p. 1005. ISBN 978-1-4963-4721-3.
External links
- Anatomy figure: 25:03-08 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- Photo and description at Tufts University
- MedicalMnemonics.com: 1042
- https://web.archive.org/web/20080304085514/http://www.med.mun.ca/anatomyts/nerve/cerplex.htm