Svartholm fortress
The Svartholm fortress (Finnish: Svartholman merilinnoitus; Swedish: Svartholms fästning) was built between 1749 and 1764 outside Loviisa in Southern Finland by Augustin Ehrensvärd. The fortress, which lies at the mouth of the Bay of Loviisa, along with the planned land fortress at Loviisa, would have prevented invading Russian forces from entering what was then Swedish territory in present-day Finland.

Construction
After Swedish defeats in the Great Northern War as well as in the Russo-Swedish War of 1741-1743, there was a pressing need to construct fortifications to guard both the border as well as the coast of Finland. By 1745 Degerby (later Lovisa - Finnish: Loviisa) was deemed to be a suitable location for a border fortification and to protect it from hostile naval forces a seafortress at Svartholm was required to be built. Main base of operations and a base for Swedish naval forces would be built to Sveaborg (Finnish: Viapori).[1]
Plans for the fortifications were prepared by Lieutenant-Colonel Augustin Ehrensvärd, who was also tasked with constructing the fortresses in 1747. Construction started in 1748 and continued with increasing tempo as the external political situation deteriorated in 1749 and 1750. Over half of the Swedish army in Finland was tasked with the construction and in 1750 more than 6,000 men were working on the fortifications at Svartholm and Sveaborg. Ehrensvärd had tasked first Captain O. R. Clansenstierna and later (1751-1757) Lieutenant-Colonel Fabian Casimir Wrede with the construction efforts at Degerby and Svartholm who had in 1751 around 2 000 workers at their disposal. While the plans for the fortifications around the town had to be cut short it did not hinder the construction of Svartholm. King Adolf Frederick visited the site in 1751 which was renamed from Degerby to Lovisa (Finnish: Loviisa) after his wife Louisa Ulrika during his reign. Like at Sveaborg the Swedish participation to the Seven Years' War brought construction effort to a standstill.[2]
Work on the fortifications continued in the 1770s and after Ehrensvärd died were led in 1773-1774 by Jacob Magnus Sprengtporten but after his break with the King Gustav III works slowed down again. In 1775 works at fortifications around Lovisa were stopped when of the six planned bastions, only two were ready and efforts at Svartholm slowed further down and in 1778 only some minor construction took place. In 1788 when new war against Russia started the main fort of Svartholm was completed but the breastworks were not.[3]
Swedish service
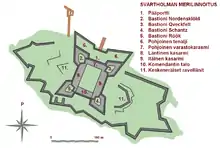
- Main Gate
- Bastion Nordenskiöld
- Bastion Qveckfelt
- Bastion Schantz
- Bastion Röök
- Northern tenaille
- Northern storage casemate
- Western casemate
- Easter casemate
- The house of the commander
- Non-completed ravelins
While Svartholm had been constructed as a seafortress it had never been designed to act as a naval base and had only its guns to offer as a support for the naval forces. Order to prepare the fort was issued already on 22 May 1788. While Svartholm did not really see any action in the Russo-Swedish War of 1788–1790 it did act as important staging ground and rallying point during several stages of the war.[4]
The fortress at Svartholm was still not ready in 1808, when the Finnish War erupted, and two-thirds of the guns and mortars were available. It had however been noted already in the 1760s, that it was not possible to place as many guns on the fortress as would be required to repulse a big attack from the sea. It had also been noted that the southern part left much to wish for. It was armed with 86 guns and 8 mortars and gad garrison of 700 men. However the fort had fallen into neglect with most of gun carriages having rotted away while others had not even had any carriages to begin with. Small arms were in similar condition and fort lacked both food and ammunition which had not been stocked in sufficient quantities.[5]
Commander of Svartholm before the war had been Captain Carl Gustaf von Schoultz who had to tend with badly trained garrison of which only third could be armed with a functional weapon. Garrison had low morale and bad discipline which was not improved by the sudden change of commander as Major Carl Magnus Gripenberg assumed command on 15 February. However Gripenberg was not highly appreciated by his superiors or his subordinates. Effort was however made to prepare the fort for the war but war started long before work on the fortress would have been completed. Ammunition was in short supply especially for 12- and 18-pounder guns. There was also shortage of food which was further complicated by the fact that the drinking water was also limited as several of the wells had been found unusable.[6]
Lovisa was the first goal of the Russians in the Finnish War (1808–1809), and the Russian main force crossed the border at Abborrfors on 21 February 1808. The Russians quickly encircled Svartholm already on 22 February 1808 and demanded surrender which was refused by the Swedes. On 23 February additional Russian forces were brought in to besiege the fort bringing Russian strength to around 1 700 men. However messengers could still reach the fort and it took until 28 February before Russian cossack patrols cut the final routes to the fort.[7]
Russians attempted first on 2 March and on 8 March to get the fortress to surrender by negotiations but Swedes refused. When Russian artillery started bombarding the fort it soon became apparent that only 8 of the whole forts guns could be brought to shoot at the Russians as the narrow firing slits made it impossible to use the rest of the guns. Fort was already suffering from the siege with one sixth of the garrison sick and having shortage of warm clothing and food. Morale crept even lower and officers feared mutiny.[8]
On 11 March Gripenberg suggested truce of six weeks which the Russians Major General Muchanoff promptly rejected but agreed for a truce of three days after which hostilities would continue anew. Gripenberg agreed to a surrender on 14 March before the truce had run out. On 17 March Russian General commanding the armies in Finland, Friedrich Wilhelm von Buxhoeveden, accepted the surrender. Swedes surrendered the fortress with all its weapons intact to the Russians who in turn agreed just to dismiss the mostly Finnish garrison of Svartholm. The reasons for the capitulation are somewhat unclear but it seems like the Swedish officers didn't believe in the Swedish capability, nor the fortress' capability to withstand the Russians in this war. As many of the other Swedish officers, Gripenberg entered Russian service after the capitulation. He was labeled a traitor in Sweden and was sentenced to death, along with other officers, for the loss of Finland. Due to a general amnesty, the death penalty process was interrupted, also for him.[9]
Russian service
Svartholma lost its strategic importance during the Russian period. It was then used partly as a military base and partly as a prison for Finnish prisoners.
During the Crimean War, British HMS Arrogant and HMS Magicienne on 7 July 1855 under the command of Captain Hastings Yelverton came up to the fortress. As soon as the British squadron appeared, the fortress was evacuated by the Russians and its armament removed, Captain Yelverton blew up everything that remained.[10]
However, large parts survived the war. Svartholma continued to serve as a good harbor and a goal for weekend picnics.
The Finnish National Board of Antiquities were restoring the castle since the 1960s, and the work was finally ready in 1998.
 In front is the main gate to the fortress with the protecting corner of the tenaille and in the background is bastion Nordenskiöld.
In front is the main gate to the fortress with the protecting corner of the tenaille and in the background is bastion Nordenskiöld. The fortress' northern curtaine and the main gate from bastion Qveckfelt. In the background is bastion Nordenskiöld.
The fortress' northern curtaine and the main gate from bastion Qveckfelt. In the background is bastion Nordenskiöld. To the right is bastion Röök's sharp edge and in the background is bastion Nordenskiöld.
To the right is bastion Röök's sharp edge and in the background is bastion Nordenskiöld. A detail of the wall at bastion Nordenskiöld.
A detail of the wall at bastion Nordenskiöld. The fortress island of Svartholm's bastions constructions rises almost directly from the sea.
The fortress island of Svartholm's bastions constructions rises almost directly from the sea. The inner yard of the fortress. To the left is the ruins of the western casemate and to the right is the restored northern casemate.
The inner yard of the fortress. To the left is the ruins of the western casemate and to the right is the restored northern casemate. The Finnish National Board of Antiquities has been restoring the castle since the 1960s.
The Finnish National Board of Antiquities has been restoring the castle since the 1960s.
Sources
References
- Mattila (1983), p. 80,89.
- Mattila (1983), p. 90-91,94.
- Mattila (1983), p. 115-116.
- Mattila (1983), p. 139,142.
- Mattila (1983), p. 232.
- Mattila (1983), p. 235-236.
- Mattila (1983), p. 236-237.
- Mattila (1983), p. 237.
- Mattila (1983), p. 237-238.
- History of War against Russia
Bibliography
- Mattila, Tapani (1983). Meri maamme turvana [Sea safeguarding our country] (in Finnish). Jyväskylä: K. J. Gummerus Osakeyhtiö. ISBN 951-99487-0-8.