Tahe County
Tahe (Chinese: 塔河; pinyin: Tǎhé) is a county in the far north of Heilongjiang province, and is the northernmost Chinese county. It is under the jurisdiction of Daxing'anling Prefecture.
Tahe County
塔河县 | |
|---|---|
.png.webp) Tahe County (red) in Daxing'anling Prefecture (yellow) and Heilongjiang | |
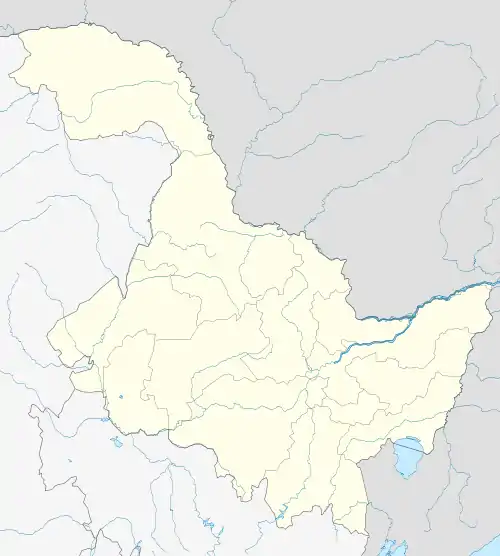 Tahe Location of the county seat in Heilongjiang | |
| Coordinates: 52°20′02″N 124°42′36″E | |
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Province | Heilongjiang |
| Prefecture | Daxing'anling |
| Area | |
| • Total | 14,103 km2 (5,445 sq mi) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 92,473 |
| • Density | 6.6/km2 (17/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard) |
Administrative divisions
Tahe County is divided into 4 towns, 2 townships and 1 ethnic township.[1]
- 4 towns
|
|
- 2 townships
- Yisiken (依西肯乡)
- Kaikukang (开库康乡)
- 1 ethnic township
- Shibazhan Oroqen (十八站鄂伦春族乡)
Demographics
The population of the district was 106,732 in 1999.[2]
Climate
Tahe County has a subarctic climate (Köppen Dwc) with short, warm, wet summers and long, brutally cold and dry winters. Monsoonal influences are strong, as 75% of the annual precipitation occurs from June to September. Although snowfall is extremely light, totalling only a few centimetres during the winter, it does not melt until May. The region is in the discontinuous permafrost zone, which severely limits land use possibilities since only exposed areas thaw fully during the summer, and fishing is the most important economic activity.
| Climate data for Tahe (1991–2020 normals, extremes 1971–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | −0.2 (31.6) |
6.3 (43.3) |
17.9 (64.2) |
26.9 (80.4) |
34.7 (94.5) |
38.0 (100.4) |
37.3 (99.1) |
36.5 (97.7) |
31.6 (88.9) |
27.7 (81.9) |
10.5 (50.9) |
0.8 (33.4) |
38.0 (100.4) |
| Average high °C (°F) | −16.1 (3.0) |
−10.1 (13.8) |
−1.8 (28.8) |
8.9 (48.0) |
18.0 (64.4) |
24.3 (75.7) |
26.1 (79.0) |
23.7 (74.7) |
17.4 (63.3) |
6.6 (43.9) |
−7.6 (18.3) |
−16.9 (1.6) |
6.0 (42.9) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −24.9 (−12.8) |
−20.6 (−5.1) |
−10.4 (13.3) |
1.6 (34.9) |
10.0 (50.0) |
16.4 (61.5) |
19.2 (66.6) |
16.4 (61.5) |
9.0 (48.2) |
−0.9 (30.4) |
−15.6 (3.9) |
−24.3 (−11.7) |
−2.0 (28.4) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −31.5 (−24.7) |
−29.0 (−20.2) |
−19.1 (−2.4) |
−5.8 (21.6) |
1.6 (34.9) |
8.3 (46.9) |
12.7 (54.9) |
10.2 (50.4) |
2.1 (35.8) |
−7.6 (18.3) |
−22.3 (−8.1) |
−30.4 (−22.7) |
−9.2 (15.4) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −47.9 (−54.2) |
−44.9 (−48.8) |
−37.1 (−34.8) |
−23.7 (−10.7) |
−11.8 (10.8) |
−4.3 (24.3) |
0.4 (32.7) |
−0.7 (30.7) |
−10.3 (13.5) |
−28.7 (−19.7) |
−39.6 (−39.3) |
−45.3 (−49.5) |
−47.9 (−54.2) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 5.3 (0.21) |
3.8 (0.15) |
5.9 (0.23) |
16.3 (0.64) |
52.5 (2.07) |
85.1 (3.35) |
133.0 (5.24) |
92.1 (3.63) |
54.3 (2.14) |
22.5 (0.89) |
11.2 (0.44) |
7.1 (0.28) |
489.1 (19.27) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 7.6 | 5.7 | 4.9 | 6.9 | 11.0 | 14.1 | 15.9 | 14.5 | 11.3 | 7.6 | 8.1 | 9.2 | 116.8 |
| Average snowy days | 9.4 | 7.3 | 6.9 | 7.1 | 1.6 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 0.6 | 7.7 | 10.4 | 11.3 | 62.4 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 68 | 64 | 57 | 52 | 56 | 71 | 79 | 81 | 73 | 64 | 69 | 69 | 67 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 149.0 | 191.1 | 254.3 | 234.6 | 216.9 | 232.2 | 200.3 | 194.7 | 190.3 | 183.8 | 156.4 | 131.4 | 2,335 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 58 | 68 | 68 | 56 | 44 | 47 | 40 | 44 | 51 | 57 | 61 | 55 | 54 |
| Source 1: China Meteorological Administration[3][4] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Weather China[5] | |||||||||||||
External links
- (in Chinese) Government Site - Google translation
Notes and references
- "国家统计局" (in Chinese). National Bureau of Statistics of the People's Republic of China. Retrieved 2021-12-07.
- (in English) National Population Statistics Materials by County and City - 1999 Period, in China County & City Population 1999, Harvard China Historical GIS
- 中国气象数据网 – WeatherBk Data (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 5 July 2023.
- 中国气象数据网 (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 5 July 2023.
- 枣阳 - 气象数据 -中国天气网 (in Chinese). Weather China. Retrieved 22 August 2022.