Talinolol
Talinolol is a beta blocker.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
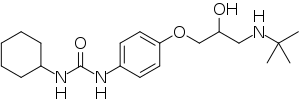
| IUPAC name
(RS)-1-[4-[3-(tert-Butylamino)-2-hydroxypropoxy]phenyl]-3-cyclohexylurea | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.228.618 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H33N3O3 | |
| Molar mass | 363.502 g·mol−1 |
| Pharmacology | |
| C07AB13 (WHO) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Stereochemistry
Talinolol contains a stereocenter and consists of two enantiomers. This is a racemate, i.e. a 1: 1 mixture of (R)- and the (S)-forms:[2]
| Enantiomers of talinolol | |
|---|---|
-talinolol.svg.png.webp) (R)-talinolol CAS number: 71369-60-3 |
-talinolol.svg.png.webp) (S)-talinolol CAS number: 71369-59-0 |
References
- Abmann, I. (1995). "The actions of talinolol, a β1-selective beta blocker, in cardiac arrhythmia and acute myocardial infarction". Current Medical Research and Opinion. 13 (6): 325–342. doi:10.1185/03007999509110493. PMID 8829891.
- F. v. Bruchhausen, G. Dannhardt, S. Ebel, A. W. Frahm, E. Hackenthal, U. Holzgrabe (Hrsg.): Hagers Handbuch der Pharmazeutischen Praxis: Band 9: Stoffe P-Z, Springer Verlag, Berlin, Aufl. 5, 2014, S. 767, ISBN 978-3-642-63389-8.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.