Topaze (rocket)
Topaze (Véhicule Expérimental 111 Topaze) is the designation of a French sounding rocket.[1] The Topaze was developed by several French companies, notably Nord Aviation and Sud Aviation,[2] and built by SEREB (a joint venture of Nord and Sud, now known as Aérospatiale) and was the first guidable French sounding rocket.
 Topaze versions | |
| Function | Sounding rocket |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | SEREB |
| Country of origin | France |
| Size | |
| Height | VE111C: 7.07 metres (23.2 ft) VE111L: 7.90 metres (25.9 ft) |
| Mass | VE111C: 2,900 kilograms (6,400 lb) VE111L: 3,434 kilograms (7,571 lb) |
| Stages | 1 |
| Associated rockets | |
| Derivative work | Saphir, Diamant |
| Launch history | |
| Status | Retired |
| Launch sites | CIEES |
| Total launches | 14 |
| First flight | 19 December 1962 |
| Last flight | 1965 |
| VE111C stage | |
| Powered by | NA802 |
| Maximum thrust | 120 kilonewtons (27,000 lbf) |
| Propellant | Solid |
| VE111L / VE111LG stage | |
| Powered by | NA803 |
| Maximum thrust | 147 kilonewtons (33,000 lbf) |
| Propellant | Solid |
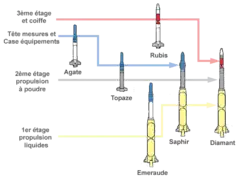
It was part of the Pierres précieuses (fr.: gemstones) program, that included five prototypes Agathe, Topaze, Emeraude, Rubis and Saphir,[3] leading up to the Diamant orbital rocket.
The name indicates that it is a "Véhicule Expérimental" (Experimental Vehicle) with 1 stage, using solid propulsion (code 1), and guided (code 1).
The Topaze was launched 14 times from the CIEES launch site in Hammaguir (Hammaguira Bacchus pad), Algeria, by ONERA.[4]
Versions
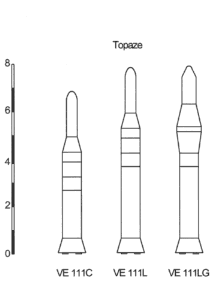
There were three versions of the Topaze:[4][1]
- Topaze versions
 VE111C
VE111C VE111L
VE111L VE111LG
VE111LG
Details[5]
Launches
There were launches between 1962 and 1964, reaching an apogee of 80 km (49 mi).[1][5]
| Date | Mission Description | Apogee (km) |
|---|---|---|
| 1962 December 19 | Test mission | 80 |
| 1963 March 22 | Test mission | 80 |
| 1963 March 28 | Test mission | 80 |
| 1963 June 21 | Test mission | 80 |
| 1963 June 27 | Test mission | 80 |
| 1963 October 24 | Test mission | 80 |
| 1964 June 4 | MSBS test, failure | |
| 1964 October 21 | MSBS test | 80 |
| 1964 December 11 | MSBS test | 80 |
| 1964 December 15 | MSBS test | 80 |
Details[5]
- payload mass: 360 kg (840 lb)
- total mass: 3434 kg (7570 lb)
- length: 7.90 m (25.9 ft)
- range: 110 km (68 mi)
- liftoff thrust 147.0 kN
- NA803 solid rocket engine
Launches
- This version was launched eight times between 21 December 1963 and 21 May 1965, with apogees up to 110 km (68 mi).[1][5]
| Date | Mission Description | Apogee (km) |
|---|---|---|
| 1963 December 21 | Test mission | 110 km |
| 1964 March 11 | Test mission | 110 km |
Details[5]
- NA803 solid rocket engine
Other uses
The Topaze was also used as the second stage of the Diamant rocket, the launch vehicle for France's first satellite, the Asterix-1, and the Saphir rocket.[5][3]
References
- "Topaze (VE-111)". Gunter's Space Page. Retrieved 2023-07-30.
- News Digest. // Aviation Week & Space Technology, January 7, 1963, v. 78, no. 1, p. 37.
- Capdevila, Didier. "Les Constellations et les Pierres Précieuses". Capcom Espace. Retrieved 2023-08-29.
- "News Digest". Aviation Week & Space Technology. Vol. 78, no. 1. January 7, 1963. p. 37.
- Wade, Mark. "Topaze". Astronautix. Archived from the original on December 28, 2016. Retrieved 28 April 2018.