Uniform norm
In mathematical analysis, the uniform norm (or sup norm) assigns to real- or complex-valued bounded functions defined on a set the non-negative number
This norm is also called the supremum norm, the Chebyshev norm, the infinity norm, or, when the supremum is in fact the maximum, the max norm. The name "uniform norm" derives from the fact that a sequence of functions converges to under the metric derived from the uniform norm if and only if converges to uniformly.[1]
If is a continuous function on a closed and bounded interval, or more generally a compact set, then it is bounded and the supremum in the above definition is attained by the Weierstrass extreme value theorem, so we can replace the supremum by the maximum. In this case, the norm is also called the maximum norm. In particular, if is some vector such that in finite dimensional coordinate space, it takes the form:
Metric and topology
The metric generated by this norm is called the Chebyshev metric, after Pafnuty Chebyshev, who was first to systematically study it.
If we allow unbounded functions, this formula does not yield a norm or metric in a strict sense, although the obtained so-called extended metric still allows one to define a topology on the function space in question.
The binary function
is then a metric on the space of all bounded functions (and, obviously, any of its subsets) on a particular domain. A sequence converges uniformly to a function if and only if
We can define closed sets and closures of sets with respect to this metric topology; closed sets in the uniform norm are sometimes called uniformly closed and closures uniform closures. The uniform closure of a set of functions A is the space of all functions that can be approximated by a sequence of uniformly-converging functions on For instance, one restatement of the Stone–Weierstrass theorem is that the set of all continuous functions on is the uniform closure of the set of polynomials on
For complex continuous functions over a compact space, this turns it into a C* algebra.
Properties
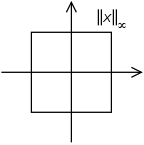
The set of vectors whose infinity norm is a given constant, forms the surface of a hypercube with edge length
The reason for the subscript "" is that whenever is continuous
where
where is the domain of and the integral amounts to a sum if is a discrete set (see p-norm).
See also
- L-infinity – Space of bounded sequences
- Uniform continuity – Uniform restraint of the change in functions
- Uniform space – Topological space with a notion of uniform properties
- Chebyshev distance – Mathematical metric
References
- Rudin, Walter (1964). Principles of Mathematical Analysis. New York: McGraw-Hill. pp. 151. ISBN 0-07-054235-X.