Valoneic acid
Valoneic acid is a hydrolysable tannin. It is a component of some hydrolysable tannins such as mallojaponin.
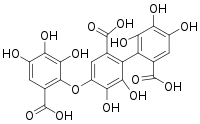 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Valoneaic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C21H14O13; C21H14O15 | |
| Molar mass | 474.32 g/mol, 506.32 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
The difference with its isomer sanguisorbic acid is that the hydroxyl that links the hexahydroxydiphenoyl (HHDP) group to the galloyl group belongs to the HHDP group.
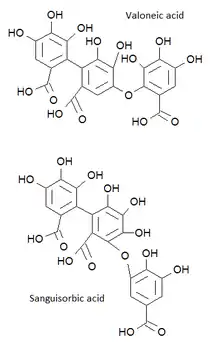
Comparison of structures of valoneic and sanguisorbic acids
It can be chemically synthesized.[1]
See also
- Sanguisorbic acid
- Valonea (Quercus macrolepis)
- Valoneic acid dilactone
References
- Enantioselective synthesis of valoneic acid derivative. Hitoshi Abe, Yusuke Sahara, Yuki Matsuzaki, Yasuo Takeuchi and Takashi Harayama, Tetrahedron Letters, Volume 49, Issue 4, 21 January 2008, pp. 605-609, doi:10.1016/j.tetlet.2007.11.154
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.