Warli
The Warli or Varli are an indigenous tribe of western India there related ethnic groups are Konkani people, Marathi people.[1] living in mountainous as well as coastal areas along the Maharashtra and Gujarat border and surrounding areas.[2][1] The Warli have their own animistic beliefs, life, customs and traditions, and as a result of acculturation they have adopted many Hindu beliefs. The Warli speak the unwritten Varli language which belongs to the southern zone of the Indo-Aryan languages. Waralis have sub castes such as Murde varli, Davar varali.
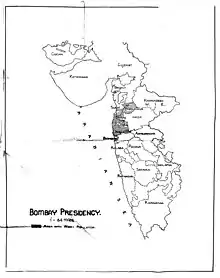 Distribution of Warli population in the then Bombay Presidency, 1945 | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
|---|---|
| Maharashtra •Gujarat | |
| Languages | |
| Varli | |
| Religion | |
| Animism• Hinduism | |
| Related ethnic groups | |
Demographics
Warlis are found in Jawhar, Vikramgad, Mokhada, Dahanu and Talasari talukas of the northern Palghar district, parts of Nashik and Dhule as well as Navapur taluka of Nandurbar of Maharashtra, Valsad, Dangs, Navsari and Surat districts of Gujarat,[3] and the union territory of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu.[4]
Language
The Warli speak the Varli language, classified as Marathi, with some degree of influence from Bhili.
Varli is classified under Marathi by Grierson (Grierson's Linguistic Survey of India) as well as A.M. Ghatage (Warli of Thana, vol. VII of A Survey of Marathi dialects)
Warli painting

In the book The Painted World of the Warlis Yashodhara Dalmia claimed that the Warli carry on a tradition stretching back to 2500 or 3000 BCE. Their mural paintings are similar to those done between 500 and 10,000 BCE in the Rock Shelters of Bhimbetka, in Madhya Pradesh.
Their extremely rudimentary wall paintings use a very basic graphic vocabulary: a circle, a triangle and a square. Their paintings were monosyllabic. The circle and triangle come from their observation of nature, the circle representing the sun and the moon, the triangle derived from mountains and pointed trees. Only the square seems to obey a different logic and seems to be a human invention, indicating a sacred enclosure or a piece of land. So the central motive in each ritual painting is the square, known as the "chauk" or "chaukat", mostly of two types: Devchauk and Lagnachauk. Inside a Devchauk, we find Palaghata, the mother goddess, symbolizing fertility.[5] Significantly, male gods are unusual among the Warli and are frequently related to spirits which have taken human shape. The central motive in these ritual paintings is surrounded by scenes portraying hunting, fishing and farming, festivals and dances, trees and animals. Human and animal bodies are represented by two triangles joined at the tip; the upper triangle depicts the trunk and the lower triangle the pelvis. Their precarious equilibrium symbolizes the balance of the universe, and of the couple, and has the practical and amusing advantage of animating the bodies. Simple shapes like triangles and circles to show people, animals, and nature. They don't draw faces, but they use hairstyles to show if it's a man or woman.[6]
Animals like peacocks and cows are also drawn with basic shapes. Leaves on trees are just simple lines.
Warli art also shows the important Warli marriage ceremony. It can last four or five days, and they paint special patterns for it. They have two types of patterns, Lagna chowk and Dev chowk, to protect the couple and help them have kids.
The Tarpa dance is another important part of Warli culture. They show it with stick figures, dancing in a circle. The "Tarpa" is a musical instrument they use, shown as a long tube in the paintings. Warli art is a beautiful way to capture the culture and traditions of the Warli tribe.

The pared down pictorial language is matched by a rudimentary technique. The ritual paintings are usually done inside the huts. The walls are made of a mixture of branches, earth and cow dung, making a Red Ochre background for the wall paintings. The Warli use only white for their paintings. Their white pigment is a mixture of rice paste and water with gum as a binding. They use a bamboo stick chewed at the end to make it as supple as a paintbrush. The wall paintings are done only for special occasions such as weddings or harvests. The lack of regular artistic activity explains the very crude style of their paintings, which were the preserve of the womenfolk until the late 1970s. But in the 1970s this ritual art took a radical turn, when Jivya Soma Mashe and his son Balu Mashe started to paint, not for any special ritual, but because of his artistic pursuits. Warli painting also featured in Coca-Cola's 'Come home on Diwali' ad campaign in 2010 was a tribute to the spirit of India's youth and a recognition of the distinct lifestyle of the Warli tribe of Western India.[7]
Tribal cultural intellectual property
Warli painting is the cultural intellectual property of the tribal community. Today, there is an urgent need for preserving this traditional knowledge in tribal communities across the globe. Understanding the need for intellectual property rights, the tribal non-profit organisation "Adivasi Yuva Seva Sangh" initiated efforts to start a registration process in 2011. Now, Warli painting is registered with a geographical indication under the intellectual property rights act. With the use of technology and the concept of social entrepreneurship, Tribals established the Warli Art Foundation, a non-profit company dedicated to Warli art and related activities.
Culture
The Warli were traditionally semi-nomadic. They lived together in small-scale groups with a headman leading them. However, recent demographic changes have transformed the Warli today into mainly agriculturists. They cultivate many crops like rice and wheat. Warli women wear toe-rings and necklaces as a sign of being married. Some Warli practice polygyny.[8]
References
- Division, Publications. Yojana July 2022 (English): A Development Monthly. Publications Division Ministry of Information & Broadcasting.
- Gazetteer of the Bombay Presidency. Government Central Press. 1880.
- Census of India 2001, The Scheduled Tribes of Gujarat
- Census of India 2001, The Scheduled Tribes of Dadra and Nagar Haveli.they are now dead .
- Tribhuwan, Robin D.; Finkenauer, Maike (2003). Threads Together: A Comparative Study of Tribal and Pre-historic Rock Paintings. Delhi: Discovery Publishing House. pp. 13–15. ISBN 81-7141-644-6.
- "Warli Art – Understanding Symbolism in Tribal Art of India". www.exoticindiaart.com. Retrieved 11 October 2023.
- "Coca-Cola India celebrates ancient Warli folk art form - Launches". Business Standard India. 12 October 2010.
- Winston, Robert, ed. (2004). Human: The Definitive Visual Guide. New York: Dorling Kindersley. p. 438. ISBN 0-7566-0520-2.
External links
- Warli art home page Warli Art is Tribal Cultural Intellectual Property
- History of the Warli community and their art
- The Warlis and the Dhangars: The Context of the Commons
- Warli Folk Painting Summary of Warli art by the Indian government
- The Warlis by K. V. Save
Further reading
- Dalmia, Yashodhara, (1988). Painted World of the Warlis: Art and Ritual of the Warli Tribes of Maharashtra, New Delhi: Lalit Kala Akademi.
- Dandekar, Ajay (ed.) (1998). Mythos and Logos of the Warlis: A Tribal Worldview, New Delhi: Concept Publishing Company, ISBN 81-7022-692-9.