Western Romanian Carpathians
The Western Romanian Carpathians (Romanian: Carpații Occidentali Românești, Hungarian: Nyugati-Kárpátok), along with the Eastern Romanian Carpathians and the Southern Carpathians is one of the three main mountain ranges of Romania.[1] Their name is given based on their geographical position, west, to the Transylvanian Plateau, which is simultaneously their eastern limits, respectively to the Timiș-Cerna Gap of the Banat Mountains, the southern group of the Western Carpathians.
| Western Carpathians | |
|---|---|
| Romanian: Carpații Occidentali | |
 Vulcan Mountain in Apuseni Mountains | |
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 1,849 m (6,066 ft) |
| Coordinates | 46.5°N 23.0°E |
| Geography | |
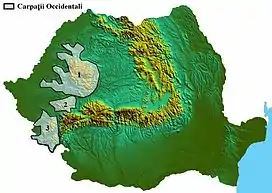 The map shows the three groups in western Romania: the northern group of the Apuseni Mountains, the central group - Poiana Ruscă Mountains and the southern group - Banat Mountains
| |
| Country | Romania |
| Parent range | Carpathians |
| Geology | |
| Orogeny | Alpine orogeny |
The Western Carpathians are positioned between the rivers Danube, Barcău and Someș. They have a maximum elevation of 1849 m in the Bihor Mountains, Cucurbăta Mare Peak (Hungarian: Nagy-Bihar) - 1849 metres, also called Bihor Peak. Discontinuity is one of their basic characteristics. Geographical composition is varied, with a real "petrographic mosaic". (flysch, crystalline schists, limestones, igneous rocks, metamorphic rocks)
Mountain ranges
From north to south, three major mountain groups can be identified, separated by different river valleys.
- Apuseni Mountains, north of Mureș
- Poiana Ruscă Mountains, south of Mureș
- Banat Mountains, the southwest corner of Romania, south of Timiș
There are 18 subgroups in total.
See also
References
- Hurdu, Bogdan Iuliu; Pușcaș, Mihai; Turtureanu, Pavel Dan; Niketić, Marjan; Coldea, Gheorghe; Zimmermann, Niklaus (2012). "Patterns of Plant Endemism in the Romanian Carpathians (South-Eastern Carpathians)". Contribuții Botanice. XLVII: 25–38.
External links
![]() Media related to Romanian Western Carpathians at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Romanian Western Carpathians at Wikimedia Commons
