Xingyi, Guizhou
Xingyi (simplified Chinese: 兴义; traditional Chinese: 興義; pinyin: Xīngyì) is a county-level city administered by the Qianxinan Buyei and Miao Autonomous Prefecture, in the southwest of Guizhou Province, China.
Xingyi
兴义市 | |
|---|---|
 Countryside near Xingyi | |
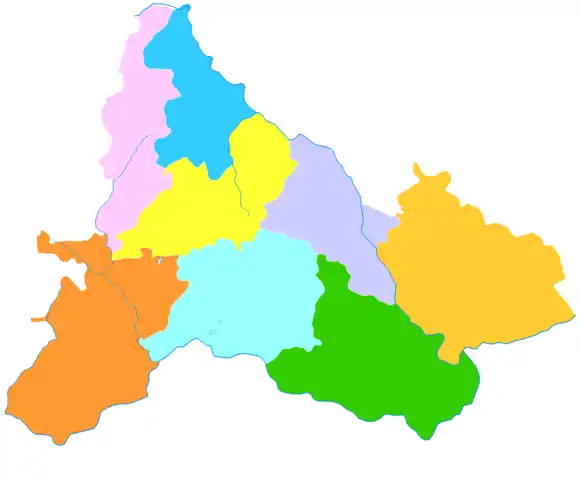 Xingyi is the division at the southwest corner in this map of Qianxinan | |
.png.webp) Qianxinan in Guizhou | |
 Xingyi  Xingyi | |
| Coordinates (Xingyi municipal government): 25°05′31″N 104°53′44″E | |
| Country | China |
| Province | Guizhou |
| Autonomous prefecture | Qianxinan |
| Municipal seat | Huangcao Subdistrict |
| Area | |
| • Total | 2,911 km2 (1,124 sq mi) |
| Population (2020 census)[1] | |
| • Total | 1,004,132 |
| • Density | 340/km2 (890/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard Time) |
| Postal code | 562400 |
| Area code | (0)859 |
| License plate prefixes | 贵E |
| Website | www |
Administrative divisions
Xingyi has 12 subdistricts, 17 towns and 3 townships.
- Huangcao Subdistrict (黄草街道)
- Xingtai Subdistrict (兴泰街道)
- Jushan Subdistrict (桔山街道)
- Fengdu Subdistrict (丰都街道)
- Pingdong Subdistrict (坪东街道)
- Mujia Subdistrict (木贾街道)
- Xiawutun Subdistrict (下五屯街道)
- Wanfenglin Subdistrict (万峰林街道)
- Sajin Subdistrict (洒金街道)
- Maling Subdistrict (马岭街道)
- Dingxiao Subdistrict (顶效街道)
- Mulong Subdistrict (木陇街道)
- Jingnan Town (敬南镇)
- Nidang Town (泥凼镇)
- Nanpanjiang Town (南盘江镇)
- Pengzha Town (捧鲊镇)
- Lubuge Town (鲁布格镇)
- Sanjiangkou Town (三江口镇)
- Wusha Town (乌沙镇)
- Baiwanyao Town (白碗窑镇)
- Weishe Town (威舍镇)
- Qingshuihe Town (清水河镇)
- Zhengtun Town (郑屯镇)
- Wantun Town (万屯镇)
- Lutun Town (鲁屯镇)
- Canggeng Town (仓更镇)
- Qishe Town (七舍镇)
- Zerong Town (则戎镇)
- Zhuchangping Town (猪场坪镇)
- Cangjiang Township (沧江乡)
- Luowan Township (洛万乡)
- Xiongwu Township (雄武乡)
Geography
The city has an area of 2911 square kilometers, and a population of 784,032 as of 2010.[2] It is under the administration of the Qianxinan Buyei and Miao Autonomous Prefecture.

Capture of Xingyi by the Qing Dynasty during the Panthay Rebellion.
Transportation
Xingyi is served by the Nanning–Kunming Railway and by the Xingyi Wanfenglin Airport.
Biodiversity hotspot
Based on Red Data Book listed endangered species of fish, amphibians, reptiles, and mammals, Xingyi is one of nine vertebrate biodiversity hotspots of China.[3]
Climate
| Climate data for Xingyi (1991–2020 normals, extremes 1981–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 27.6 (81.7) |
31.0 (87.8) |
33.8 (92.8) |
34.5 (94.1) |
36.5 (97.7) |
33.7 (92.7) |
33.5 (92.3) |
32.1 (89.8) |
33.6 (92.5) |
30.4 (86.7) |
28.2 (82.8) |
26.5 (79.7) |
36.5 (97.7) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 11.8 (53.2) |
15.3 (59.5) |
19.9 (67.8) |
24.5 (76.1) |
26.2 (79.2) |
26.7 (80.1) |
27.2 (81.0) |
27.3 (81.1) |
25.3 (77.5) |
21.1 (70.0) |
18.2 (64.8) |
13.0 (55.4) |
21.4 (70.5) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 7.7 (45.9) |
10.4 (50.7) |
14.2 (57.6) |
18.7 (65.7) |
21.0 (69.8) |
22.1 (71.8) |
22.7 (72.9) |
22.5 (72.5) |
20.7 (69.3) |
17.0 (62.6) |
13.6 (56.5) |
9.0 (48.2) |
16.6 (62.0) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 5.2 (41.4) |
7.2 (45.0) |
10.6 (51.1) |
14.6 (58.3) |
17.3 (63.1) |
19.1 (66.4) |
19.8 (67.6) |
19.4 (66.9) |
17.6 (63.7) |
14.4 (57.9) |
10.6 (51.1) |
6.5 (43.7) |
13.5 (56.4) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −3.3 (26.1) |
−2.1 (28.2) |
−1.6 (29.1) |
3.6 (38.5) |
8.5 (47.3) |
12.8 (55.0) |
14.1 (57.4) |
14.3 (57.7) |
10.0 (50.0) |
6.4 (43.5) |
0.8 (33.4) |
−4.7 (23.5) |
−4.7 (23.5) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 32.6 (1.28) |
26.9 (1.06) |
35.4 (1.39) |
49.9 (1.96) |
136.8 (5.39) |
296.0 (11.65) |
303.6 (11.95) |
214.1 (8.43) |
162.6 (6.40) |
104.6 (4.12) |
38.1 (1.50) |
26.7 (1.05) |
1,427.3 (56.18) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 14.8 | 12.4 | 12.1 | 11.7 | 14.7 | 18.9 | 20.2 | 18.4 | 14.2 | 16.0 | 10.3 | 12.0 | 175.7 |
| Average snowy days | 1.7 | 0.8 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.4 | 3 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 84 | 77 | 73 | 69 | 74 | 82 | 84 | 82 | 81 | 84 | 81 | 82 | 79 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 78.1 | 104.8 | 134.1 | 164.3 | 171.1 | 133.7 | 155.9 | 167.1 | 138.7 | 102.9 | 120.2 | 85.0 | 1,555.9 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 23 | 33 | 36 | 43 | 41 | 33 | 37 | 42 | 38 | 29 | 37 | 26 | 35 |
| Source: China Meteorological Administration[4][5] | |||||||||||||
External links
References
- "黔西南州第七次全国人口普查公报(第二号)——地区人口情况" (in Chinese). Government of Qianxinan Prefecture. 2021-06-03.
- "Profile of Xingyi" (in Simplified Chinese). XZQH.org. Archived from the original on January 22, 2009. Retrieved 2009-01-28.
- Chen, Yang; An-Ping Chen; Jing-Yun Fang (2002). "Geographical distribution patterns of endangered fishes, amphibians, reptiles and mammals and their hotspots in China: a study based on "China Red Data Book of Endangered Animals"". Biodiversity Science. 10 (4): 359–368. doi:10.17520/biods.2002050.
- 中国气象数据网 – WeatherBk Data (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 28 April 2023.
- 中国气象数据网 (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 28 April 2023.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.



