Libo County
Libo County (simplified Chinese: 荔波县; traditional Chinese: 荔波縣; pinyin: Lìbō Xiàn) is a county of southern Guizhou province, China, bordering Guangxi to the south. It is under the administration of the Qiannan Buyei and Miao Autonomous Prefecture.
Libo County
荔波县 Lipo | |
|---|---|
 | |
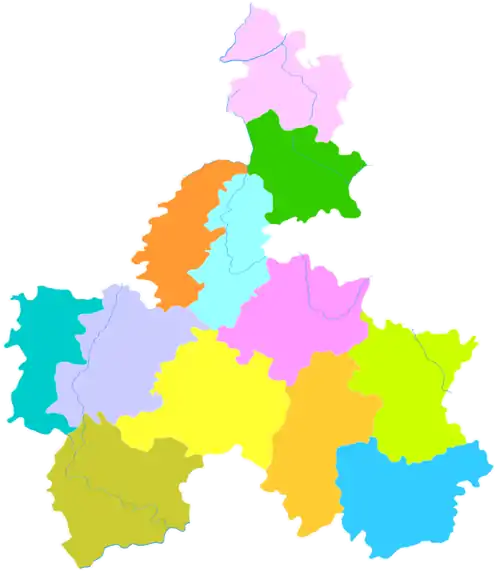 Libo is the southeasternmost division in this map of Qiannan | |
.png.webp) Qiannan in Guizhou | |
 Libo Location of the seat in Guizhou  Libo Libo (Southwest China) | |
| Coordinates (Libo County government): 25°25′26″N 107°53′56″E | |
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Province | Guizhou |
| Autonomous prefecture | Qiannan |
| Area | |
| • Total | 2,432 km2 (939 sq mi) |
| Population (2010) | |
| • Total | 144,849 |
| • Density | 60/km2 (150/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard) |
| Postal code | 558400 |
| Area code | 0584 |
| Website | http://www.libo.gov.cn/ |
Geography
The county is located in the remote southeastern corner of the prefecture, on the border with Guangxi. Two local sites, Xiaoqikong (小七孔) and Dongduo (洞多), notable for their spectacular karst formations, form part of the multi-site South China Karst UNESCO World Heritage Site inscribed in 2007, which is an area about 550,000 km2 in extent.[1]
Languages
Southwestern Mandarin, Mak, Ai-Cham, Bouyei, Sui, and Numao are spoken in Libo County. Sui is spoken primarily in Shuiyao Ethnic Shui Township 水尧水族乡.[2]
Transportation
The Qiannan Libo Airport, opened in late 2007, has capacity to receive planes of the Boeing 737 class, and to handle up to 220,000 passengers annually.[3] However, the $57-million facility is rather underutilized so far.[3] According to the Civil Aviation Administration of China (CAAC) statistics, 151 paying passengers flew into or out of the airport in 2009 - which was a 98% drop compared to the previous year (7886 passengers), and placed the airport the last in list of the nation's 166 airports by traffic volume.[4] Currently four airlines use the airport.
Flora
The karst environments in Libo County consist of the following types of forests.[1]
- Warm coniferous forest
- Pinus kwangtungensis forest
- Warm needle and broad-leaved mixed forest
- Pseudotsuga sinensis, Platycarya longipes mixed forest
- Pseudotsuga sinensis, Pinus kwangtungensis, Quercus phillyraeoides mixed forest
- Evergreen and deciduous broad-leaved mixed forest
- Cyclobalanopsis glauca, Platycarya longipes mixed forest
- Platycarya longipes, Phellodendron amurense mixed forest
- Platycarya longipes, Viburnum mixed forest
- Handeliodendron bodinieri, Acer mixed forest
- Viburnum, Heptapleurum heptaphyllum mixed forest
- Sterculiaceae, Cyclobalanopsis glauca mixed forest
- Taxus cuspidata, Lindera mixed forest
- Koelreuteria paniculata, Aceraceae mixed forest
- Castanopsis fargesii, Elaeocarpaceae mixed forest
- Big-cluster bamboo forest
- Dendrocalamus tsiangii forest
Common angiosperm genera include Beilschmiedia, Cryptocarya, Casearia, Diospyros, Pittosporum, Acer, Carpinus, Ulmus, Viburnum, Prunus, and Rosa. Protected wild plants in Libo County include Handeliodendron bodinieri, Mussaenda anomala, Taxus chinensis, Paphiopedilum emersonii, Paphiopedilum barbigerum and Paphiopedilum micranthum, Pinus kwangtungensis, Pseudotsuga sinensis, Pseudotsuga brevifolia, Calocedrus macrolepis, Tetrathyrium subcordatum, Trachycarpus nana, Emmenopterys henryi, Liriodendron chinense.[1]
Climate
| Climate data for Libo (1991–2020 normals, extremes 1981–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 26.2 (79.2) |
32.3 (90.1) |
34.4 (93.9) |
35.8 (96.4) |
36.1 (97.0) |
36.5 (97.7) |
37.9 (100.2) |
39.2 (102.6) |
37.3 (99.1) |
35.6 (96.1) |
31.3 (88.3) |
29.2 (84.6) |
39.2 (102.6) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 12.4 (54.3) |
15.5 (59.9) |
19.1 (66.4) |
24.6 (76.3) |
28.2 (82.8) |
30.1 (86.2) |
31.8 (89.2) |
32.3 (90.1) |
30.0 (86.0) |
25.3 (77.5) |
20.9 (69.6) |
15.5 (59.9) |
23.8 (74.9) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 8.6 (47.5) |
11.1 (52.0) |
14.6 (58.3) |
19.6 (67.3) |
23.2 (73.8) |
25.5 (77.9) |
26.7 (80.1) |
26.4 (79.5) |
24.1 (75.4) |
19.9 (67.8) |
15.4 (59.7) |
10.6 (51.1) |
18.8 (65.9) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 6.1 (43.0) |
8.2 (46.8) |
11.6 (52.9) |
16.1 (61.0) |
19.6 (67.3) |
22.5 (72.5) |
23.5 (74.3) |
22.8 (73.0) |
20.3 (68.5) |
16.5 (61.7) |
11.8 (53.2) |
7.4 (45.3) |
15.5 (60.0) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −4.3 (24.3) |
−1.9 (28.6) |
0.0 (32.0) |
3.8 (38.8) |
7.9 (46.2) |
12.5 (54.5) |
15.7 (60.3) |
17.5 (63.5) |
11.8 (53.2) |
5.3 (41.5) |
−0.1 (31.8) |
−4.0 (24.8) |
−4.3 (24.3) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 27.4 (1.08) |
30.0 (1.18) |
53.4 (2.10) |
94.2 (3.71) |
167.9 (6.61) |
262.0 (10.31) |
218.1 (8.59) |
176.2 (6.94) |
94.7 (3.73) |
65.9 (2.59) |
38.5 (1.52) |
22.0 (0.87) |
1,250.3 (49.23) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 10.0 | 9.0 | 13.7 | 14.6 | 16.7 | 18.6 | 18.2 | 15.0 | 10.2 | 9.9 | 8.5 | 7.3 | 151.7 |
| Average snowy days | 1.2 | 0.4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.3 | 1.9 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 74 | 73 | 76 | 76 | 78 | 82 | 82 | 80 | 77 | 76 | 75 | 71 | 77 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 37.5 | 43.0 | 54.5 | 77.7 | 93.8 | 81.4 | 132.5 | 159.9 | 141.4 | 103.3 | 91.8 | 74.1 | 1,090.9 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 11 | 13 | 15 | 20 | 22 | 20 | 32 | 40 | 39 | 29 | 28 | 23 | 24 |
| Source: China Meteorological Administration[5][6] | |||||||||||||
References
- "South China Karst". UNESCO World Heritage Centre. United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization.
- Zhou, Guoyan 周国炎 (2013). Zhōngguó xīnán mínzú zájū dìqū yǔyán guānxì yǔduō yǔ héxié yánjiū: Yǐ Diān Qián Guì pílín mínzú zájū dìqū wèi yánjiū gè'àn 中国西南民族杂居地区语言关系与多语和谐研究:以滇黔桂毗邻民族杂居地区为研究个案 (in Chinese). Beijing: Zhongguo shehui kexue chubanshe. ISBN 978-7-5161-1985-3.
- "Plenty of new airports but few passengers in China: A construction spree brings flight service to some unlikely locales, and a hoped-for spurt in air traffic fails to materialize." David Pierson / Los Angeles Times / March 12, 2010
- 民航机场业务量. CAAC. February 2010. Archived from the original on July 18, 2011. Retrieved April 11, 2010.
- 中国气象数据网 – WeatherBk Data (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 28 April 2023.
- 中国气象数据网 (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 28 April 2023.