Yelp (software)
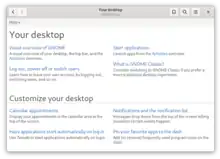
Yelp, also known as the GNOME Help Browser[1] is the default help viewer for GNOME that allows users to access help documentation.[5] Yelp follows the freedesktop.org help system specification[6] and reads mallard, DocBook, man pages, info, and HTML documents.[7] HTML is available by using XSLT to render XML documents into HTML.[8]
 | |
| Original author(s) | Mikael Hallendal and Alexander Larsson[1] |
|---|---|
| Initial release | October 27, 2001[2] |
| Stable release | 42.2[3]
/ 17 October 2022 |
| Repository | gitlab |
| License | GPLv2[4] |
| Website | yelp |
Yelp has a search feature[9] as well as a toolbar at the top for navigation through previously viewed documentation.[10]
Yelp can be accessed by typing yelp either into GNOME Shell, after pressing Alt+F2 within GNOME, or within a terminal[11] using the yelp [file] format.[1][12] The command gnome-help can also be used to access Yelp.[13]
Although Yelp is not required for GNOME to function, it is required to view GNOME's help documentation.[14] Ubuntu also uses yelp to provide a customized help interface for its software.[15]
A format string vulnerability in GNOME versions 2.19.90 and 2.24 allowed arbitrary code execution through Yelp.[16]
References
- Haltom, Jerry. "yelp linux command man page". CommandLinux.com. Retrieved August 27, 2022.
- Scorgie, Don (April 30, 2009). "ChangeLog". gitlab.gnome.org. Archived from the original on August 28, 2022. Retrieved August 27, 2022.
- "42.2 · Tags · GNOME / yelp · GitLab".
- McCance, Shaun (April 26, 2016). "Copying". gitlab.gnome.org. Archived from the original on August 28, 2022. Retrieved August 27, 2022.
- "Overview of the Yelp Help Browser". Oracle Corporation. Archived from the original on August 8, 2015. Retrieved August 27, 2022.
- "yelp 41.0". guix.gnu.org. Archived from the original on August 28, 2022. Retrieved August 27, 2022.
- "Apps/Yelp". wiki.gnome.org. January 12, 2019. Archived from the original on August 24, 2022. Retrieved August 27, 2022.
- Cowie, Andrew Frederick (2004). Merging structure and sequence: Software to help teams document and execute mission critical events (Report). CiteSeerX 10.1.1.202.3756. S2CID 17334937.
- Schroder, Carla (2004). Linux cookbook. Beijing: O'Reilly. p. 2. ISBN 978-0-596-51750-2. OCLC 771953312. Archived from the original on 2022-08-28. Retrieved 2022-08-27.
- Petersen, Richard (2014). Beginning Fedora Desktop. Berkeley, CA: Apress. p. 246. ISBN 978-1-4842-0067-4. OCLC 883396549. Archived from the original on 2022-08-28. Retrieved 2022-08-27.
- Sobell, Mark G. (2014). A practical guide to Fedora and Red Hat Enterprise Linux (7th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall. p. 113. ISBN 978-0-13-347744-3. OCLC 870467604. Archived from the original on 2022-08-28. Retrieved 2022-08-27.
- Shekhar, Vijay (2006). Red Hat Linux : the compete bible. Laxmi Publications Pvt. Ltd./Firewall Media. p. 126. ISBN 81-7008-863-1. OCLC 228137134. Archived from the original on 2022-08-28. Retrieved 2022-08-27.
- Fusco, John (2007). The Linux Programmer's Toolbox. Sydney: Pearson Education, Limited. ISBN 978-0-13-270304-8. OCLC 1337943343. Archived from the original on 2022-08-28. Retrieved 2022-08-27.
- "Yelp-42.1". Linux From Scratch. Archived from the original on August 8, 2020. Retrieved August 27, 2022.
- Sobell, Mark G. (2015). A practical guide to Ubuntu Linux (Fourth ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ. p. 118. ISBN 978-0-13-392731-3. OCLC 890912722.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Jackson, Todd; Salamat, Babak; Wagner, Gregor; Wimmer, Christian; Franz, Michael (2010). "On the effectiveness of multi-variant program execution for vulnerability detection and prevention". Proceedings of the 6th International Workshop on Security Measurements and Metrics. Bolzano, Italy: ACM Press. p. 4. doi:10.1145/1853919.1853929. ISBN 978-1-4503-0340-8. S2CID 6697258. Archived from the original on 2022-08-28. Retrieved 2022-08-27.