3-Hydroxyaspartic acid
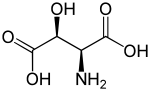
3-Hydroxyaspartic acid (three letter abbreviation: Hya) also known as beta-hydroxyaspartic acid is derivative of aspartic acid which has been hydroxylated at position-3. The adjacent image shows L-threo-3-Hydroxyaspartate. The Hya amino acid residue is sometimes contained in EGF-like domains such as Vitamin K-dependent coagulation plasma proteins including protein C.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(2S)-2-Amino-3-hydroxybutanedioic acid | |
| Other names
(2S)-2-Amino-3-hydroxysuccinic acid 3-Hydroxyaspartic acid Beta-hydroxyaspartic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C4H7NO5 |
| Molar mass | 149.102 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
See also
- Epidermal growth factor (EGF)
- Vitamin K-dependent protein
References
- Castellino FJ, Ploplis VA, Zhang L (2008). "Γ-Glutamate and β–Hydroxyaspartate in Proteins". gamma-Glutamate and beta-hydroxyaspartate in proteins. Methods Mol. Biol. Vol. 446. pp. 85–94. doi:10.1007/978-1-60327-084-7_6. ISBN 978-1-58829-719-8. PMID 18373251.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.