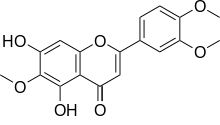
Eupatilin
Eupatilin (5,7-Dihydroxy-3',4',6-trimethoxyflavone) is an O-methylated flavone, a type of flavonoids. It can be found in Artemisia asiatica (Asteraceae).[1]
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Dependence liability | None |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H16O7 |
| Molar mass | 344.319 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
References
- Kim DH, Na HK, Oh TY, Kim WB, Surh YJ (September 2004). "Eupatilin, a pharmacologically active flavone derived from Artemisia plants, induces cell cycle arrest in ras-transformed human mammary epithelial cells". Biochemical Pharmacology. 68 (6): 1081–7. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2004.04.027. PMID 15313404.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.