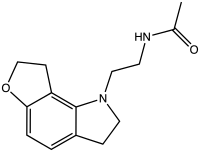
GR-196,429
GR-196,429 is a melatonin receptor agonist with some selectivity for the MT1 subtype. It was one of the first synthetic melatonin agonists developed and continues to be used in scientific research, though it has never been developed for medical use. Studies in mice have shown GR-196,429 to produce both sleep-promoting effects and alterations of circadian rhythm, as well as stimulating melatonin release.[1][2][3]
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C14H18N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 246.308 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
References
- Beresford IJ, Browning C, Starkey SJ, Brown J, Foord SM, Coughlan J, et al. (June 1998). "GR196429: a nonindolic agonist at high-affinity melatonin receptors". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 285 (3): 1239–45. PMID 9618428.
- Beresford IJ, Harvey FJ, Hall DA, Giles H (November 1998). "Pharmacological characterisation of melatonin mt1 receptor-mediated stimulation of [35S]-GTPgammaS binding". Biochemical Pharmacology. 56 (9): 1167–74. doi:10.1016/s0006-2952(98)00254-8. PMID 9802327.
- Drijfhout WJ, de Vries JB, Homan EJ, Brons HF, Copinga S, Gruppen G, et al. (October 1999). "Novel non-indolic melatonin receptor agonists differentially entrain endogenous melatonin rhythm and increase its amplitude". European Journal of Pharmacology. 382 (3): 157–66. doi:10.1016/s0014-2999(99)00619-6. PMID 10556666.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.