Intercostal muscles
Intercostal muscles are many different groups of muscles that run between the ribs, and help form and move the chest wall. The intercostal muscles are mainly involved in the mechanical aspect of breathing by helping expand and shrink the size of the chest cavity.[1]
| Intercostal muscles | |
|---|---|
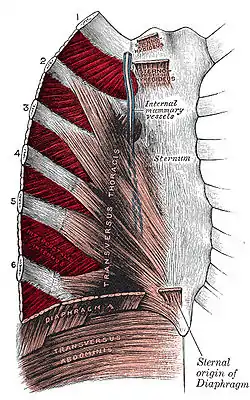 Intercostal muscles highlighted in dark red. | |
| Details | |
| Origin | ribs 1–11 |
| Insertion | ribs 2–12 |
| Artery | intercostal arteries |
| Nerve | intercostal nerves |
| Actions | Elevation or Depression of the Ribs |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Musculi intercostales |
| MeSH | D007366 |
| FMA | 13354 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
Structure
There are three principal layers;
- External intercostal muscles aid in quiet and forced inhalation. They originate on ribs 1–11 and have their insertion on ribs 2–12. The external intercostals are responsible for the elevation of the ribs and bending them more open, thus expanding the transverse dimensions of the thoracic cavity.
- Internal intercostal muscles aid in forced expiration (quiet expiration is a passive process). They originate on ribs 2–12 and have their insertions on ribs 1–11.Their fibers pass anterior and superior from the upper margin of the rib and costal cartilage to the lower margin of the rib above.(source) The internal intercostals are responsible for the depression of the ribs and bending them inward, thus decreasing the transverse dimensions of the thoracic cavity.
- Innermost intercostal muscle, the deep layers of the internal intercostal muscles which are separated from them by a neurovascular bundle.
Nerve supply
Both the external and internal muscles are innervated by the intercostal nerves (the ventral rami of thoracic spinal nerves), are supplied by the intercostal arteries, and are drained by the intercostal veins. Their fibers run in opposite directions.
Function
The scalene muscles, which also move the chest wall and have a function in inhalation, are also intercostal muscles, just not one of the three principal layers.
See also
- Thoracic diaphragm, another muscle importantly involved in respiratory action.
- Exhalation
- Inhalation
References
- "Intercostal muscle strain: Signs, treatments,remedies". www.medicalnewstoday.com. 2020-01-10. Retrieved 2021-02-28.
External links
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Intercostal muscles.
- Anatomy figure: 18:03-03 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- UCC
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.