Knee dislocation
A knee dislocation is an injury in which there is disruption of the knee joint between the tibia and the femur.[3][4] Symptoms include pain and instability of the knee.[2] Complications may include injury to an artery, most commonly the popliteal artery behind the knee, or compartment syndrome.[3][4][7]
| Knee dislocation | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Plain lateral X-ray of the left knee showing a posterior knee dislocation[1] | |
| Specialty | Orthopedic surgery |
| Symptoms | Knee pain, knee deformity[2] |
| Complications | Injury to the artery behind the knee, compartment syndrome[3][4] |
| Types | Anterior, posterior, lateral, medial, rotatory[4] |
| Causes | Trauma[3] |
| Diagnostic method | Based on history of the injury and physical examination, supported by medical imaging[5][2] |
| Differential diagnosis | Femur fracture, tibial fracture, patellar dislocation, ACL tear[6] |
| Treatment | Reduction, splinting, surgery[4] |
| Prognosis | 10% risk of amputation[4] |
| Frequency | 1 per 100,000 per year[3] |
About half of cases are the result of major trauma and about half as a result of minor trauma.[3] About 50% of the time, the joint spontaneously reduces before arrival at hospital.[3] Typically there is a tear of the anterior cruciate ligament, posterior cruciate ligament, and either the medial collateral ligament or lateral collateral ligament.[3] If the ankle–brachial pressure index is less than 0.9, CT angiography is recommended to detect blood vessel injury.[3] Otherwise repeated physical exams may be sufficient.[2] More recently, the FAST-D protocol, assessing the posterior tibial and dorsalis pedis arteries for a ‘tri-phasic wave pattern’ with ultrasound, has been shown to be reliable in ruling out significant arterial injury.[8]
If the joint remains dislocated, reduction and splinting is indicated;[4] this is typically carried out under procedural sedation.[2] If signs of arterial injury are present, immediate surgery is generally recommended.[3] Multiple surgeries may be required.[4] In just over 10% of cases, an amputation of part of the leg is required.[4]
Knee dislocations are rare, occurring in about 1 per 100,000 people per year.[3] Males are more often affected than females.[2] Younger adults are most often affected.[2] Descriptions of this injury date back to at least 20 BC by Meges of Sidon.[9]
Signs and symptoms

Symptoms include knee pain.[2] The joint may also have lost its normal shape and contour.[2] A joint effusion may, or may not, be present.[2]
Complications
Complications may include injury to the artery behind the knee (popliteal artery) in about 20% of cases or compartment syndrome.[3][4] Damage to the common peroneal nerve or tibial nerve may also occur.[2] Nerve problems, if they occur, often persist to a variable degree.[11]
Cause
About half are the result of major trauma, the other half as a result of minor trauma.[3] Major trauma may include mechanisms such as falls from a significant height, motor vehicle collisions, or a pedestrian being hit by a motor vehicle.[2] Cases due to major trauma often have other injuries.[5]
Minor trauma may include tripping while walking or while playing sports.[2] Risk factors include obesity.[2]
The condition may also occur in a number of genetic disorders such as Ellis–van Creveld syndrome, Larsen syndrome, and Ehlers–Danlos syndrome.[12]
Diagnosis
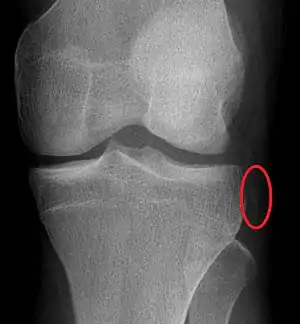
As the injury may have self-reduced before arrival at hospital, the diagnosis may not be readily apparent.[2] Diagnosis may be suspected based on the history of the injury and physical examination[5] which may include anterior drawer test, valgus stress test, varus stress test, and posterior sag test.[5] An accurate physical exam can be difficult due to pain.[5]
Plain X-rays, CT scan, ultrasonography, or MRI may help with the diagnosis.[2][11] Findings on X-ray that may be useful among those who have already reduced include a variable joint space, subluxation of the joint, or a Segond fracture.[5]
If the ankle–brachial pressure index (ABI) is less than 0.9, CT angiography is recommended.[3] Standard angiography may also be used.[2] If the ABI is greater than 0.9 repeated physical exams over the next 24 hours to verify good blood flow may be sufficient.[2][11] The ABI is calculated by taking the systolic blood pressure at the ankle and dividing it by the systolic blood pressure in the arm.[2] More recently, the FAST-D protocol, using ultrasound to assess the posterior tibial and dorsalis pedis arteries for a ‘tri-phasic wave pattern’, has been shown to be reliable in ruling out significant arterial injury.[8]
Classification

They may be divided into five types: anterior, posterior, lateral, medial, and rotatory.[4] This classification is based on the movement of the tibia with respect to the femur.[11] Anterior dislocations, followed by posterior, are the most common.[2] They may also be classified on the basis of which ligaments are injured.[2]
Treatment
Initial management is often based on Advanced Trauma Life Support.[5] If the joint remains dislocated reduction and splinting is indicated.[4] Reduction can often be done with simple traction after the person has received procedural sedation.[11] If the joint cannot be reduced in the emergency department, then emergency surgery is recommended.[2]
In those with signs of arterial injury, immediate surgery is generally carried out.[3] If the joint does not stay reduced external fixation may be needed.[2] If the nerves and artery are intact the ligaments may be repaired after a few days.[11] Multiple surgeries may be required.[4] In just over 10% of cases an amputation of part of the leg is required.[4]
Epidemiology
Knee dislocations are rare: they represent about 1 in 5,000 orthopedic injuries,[5] and about 1 knee dislocation occurs annually per 100,000 people.[3] Males are more often affected than females, and young adults the most often.[2]
References
- Duprey K, Lin M (February 2010). "Posterior knee dislocation". The Western Journal of Emergency Medicine. 11 (1): 103–4. PMC 2850837. PMID 20411095.
- Boyce RH, Singh K, Obremskey WT (December 2015). "Acute Management of Traumatic Knee Dislocations for the Generalist". The Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. 23 (12): 761–8. doi:10.5435/JAAOS-D-14-00349. PMID 26493970. S2CID 10713473.
- Maslaris A, Brinkmann O, Bungartz M, Krettek C, Jagodzinski M, Liodakis E (August 2018). "Management of knee dislocation prior to ligament reconstruction: What is the current evidence? Update of a universal treatment algorithm". European Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery & Traumatology. 28 (6): 1001–1015. doi:10.1007/s00590-018-2148-4. PMID 29470650. S2CID 3482099.
- Bryant B, Musahl V, Harner CD (2011). "59. The Dislocated Knee". In W. Norman Scott (ed.). Insall & Scott Surgery of the Knee E-Book (5th ed.). Elsevier Churchill Livingstone. p. 565. ISBN 978-1-4377-1503-3.
- Lachman JR, Rehman S, Pipitone PS (October 2015). "Traumatic Knee Dislocations: Evaluation, Management, and Surgical Treatment". The Orthopedic Clinics of North America. 46 (4): 479–93. doi:10.1016/j.ocl.2015.06.004. PMID 26410637.
- Eiff MP, Hatch RL (2011). Fracture Management for Primary Care E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. ix. ISBN 978-1455725021.
- Medina O, Arom GA, Yeranosian MG, Petrigliano FA, McAllister DR (September 2014). "Vascular and nerve injury after knee dislocation: a systematic review". Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research. 472 (9): 2621–9. doi:10.1007/s11999-014-3511-3. PMC 4117866. PMID 24554457.
- Montorfano, Miguel Angel; Montorfano, Lisandro Miguel; Perez Quirante, Federico; Rodríguez, Federico; Vera, Leonardo; Neri, Luca (December 2017). "The FAST D protocol: a simple method to rule out traumatic vascular injuries of the lower extremities". Critical Ultrasound Journal. 9 (1): 8. doi:10.1186/s13089-017-0063-2. PMC 5360748. PMID 28324353.
- Elliott JS (1914). Outlines of Greek and Roman Medicine. Creatikron Company. p. 76. ISBN 9781449985219.
- Godfrey AD, Hindi F, Ettles C, Pemberton M, Grewal P (2017). "Acute Thrombotic Occlusion of the Popliteal Artery following Knee Dislocation: A Case Report of Management, Local Unit Practice, and a Review of the Literature". Case Reports in Surgery. 2017: 5346457. doi:10.1155/2017/5346457. PMC 5299179. PMID 28246569.
- Pallin DJ, Hockberger R, Gausche-Hill M (2018). "50. Knee and lower leg". In Walls RM (ed.). Rosen's Emergency Medicine – Concepts and Clinical Practice E-Book (9th ed.). Philadelphia: Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 618. ISBN 978-0-323-35479-0.
- Graham JM, Sanchez-Lara PA (2016). "12. Knee dislocation (Genu Recurvatum)". Smith's Recognizable Patterns of Human Deformation E-Book (4th ed.). Philadelphia: Elsevier. p. 81. ISBN 978-0-323-29494-2.