Lucimycin
Lucimycin (INN, also known as lucensomycin and etruscomycin) is a macrolide antibiotic synthesized by the bacterium Streptomyces lucensis. It belongs to the group of polyene antimycotics and was first isolated in the 1960s. It has seen only limited clinical use.
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.032.667 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
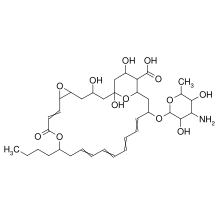
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C36H53NO13 |
| Molar mass | 707.80492 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Lucimycin is also produced by the Streptomyces cyanogenus S136, where the full biosynthetic gene cluster for the production of this compound was described.[1]
References
- Yushchuk O, Ostash I, Mösker E, Vlasiuk I, Deneka M, Rückert C, et al. (February 2021). "Eliciting the silent lucensomycin biosynthetic pathway in Streptomyces cyanogenus S136 via manipulation of the global regulatory gene adpA". Scientific Reports. 11 (1): 3507. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-82934-6. PMC 7875965. PMID 33568768.
Further reading
- Ganellin CR, Macdonald F, Triggle DJ (1997). Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents. p. 1239.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.