MME (psychedelic)
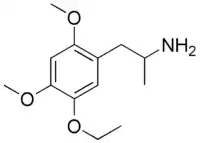
MME (2,4-dimethoxy-5-ethoxyamphetamine) is a lesser-known psychedelic drug. It is a dimethoxy-ethoxy analog of TMA-2. MME was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin from ethylvanillin. In his book PiHKAL, the minimum dosage is listed as 40 mg and above, and the duration listed as 6–10 hours.[1] Shulgin gives MME a ++ on the Shulgin Rating Scale.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-(5-Ethoxy-2,4-dimethoxyphenyl)propan-2-amine | |
| Other names
2,4-Dimethoxy-5-ethoxyamphetamine | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C13H21NO3 |
| Molar mass | 239.315 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Pharmacology
Shulgin describes in his book an experiment with MME, in which he admistered varying amounts of the drug to mice via injections.[1] Shulgin reports that 7 of the 9 mice injected with MME died as a result.[1] After describing his experiment, Shulgin speculates that MME may have an LD50 value of around 60–80 mg/Kg in mice when injected.[1] Very little data exists about the pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity of MME.