Manus (anatomy)
The manus (Latin for hand, plural manus) is the zoological term for the distal portion of the fore limb of an animal. In tetrapods, it is the part of the pentadactyl limb that includes the metacarpals and digits (phalanges). During evolution, it has taken many forms and served a variety of functions. It can be represented by the hand of primates, the lower front limb of hoofed animals or the fore paw and is represented in the wing of birds, bats and prehistoric flying reptiles (pterosaurs), the flipper of marine mammals and the 'paddle' of extinct marine reptiles, such as plesiosaurs and ichthyosaurs.

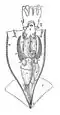
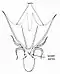
In cephalopods, the manus is the end, broader part of a tentacle, and its suckers are often larger and arranged differently from those on the other arms.[1]
See also
- Pes (anatomy) – the distal portion of the hind limb of tetrapod animals
References
- Prof. R.L.Kotpal (2009). Modern Text Book of Zoology: Vertebrates. Meerut, New Delhi, India: Rastogi Publications. ISBN 978-81-7133-891-7. Archived from the original on 2016-05-09.