Occultammina
Occultammina is a genus of xenophyophorean foraminifera known from the Atlantic and Pacific oceans. It is notable for being the first known infaunal xenophyophore as well as for being a possible identity for the enigmatic trace fossil Paleodictyon.
| Occultammina | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Chromista |
| Phylum: | Retaria |
| Infraphylum: | Foraminifera |
| Class: | Monothalamea |
| Clade: | Xenophyophorea |
| Order: | Psamminida |
| Family: | Syringamminidae |
| Genus: | Occultammina Tendal et al., 1982 |
| Type species | |
| Occultammina profunda Tendal et al., 1982 | |
Distribution and habitat
Like all other known xenophyophores, Occultammina is found in the deep ocean; the first known specimen was first discovered in 1980 at a depth of 8,260 m (27,100 ft) in the Ogasawara Trench, off the coast of Japan and described in 1982 by a joint research team from the University of Copenhagen and the University of Tokyo.[1] Further specimens referred to Occultammina sp. have been found at a depth of 4,844 m (15,892 ft) in the Porcupine Abyssal Plain, in the North Atlantic.[2] Further studies have expanded its geographical and bathymetric range from 3,000 and 8,260 metres (9,840 and 27,100 ft) in the Ogasawara Trench and from 4,500 to 4,800 metres (14,800 to 15,700 ft) in the North Atlantic, and also recorded its presence at 6,440 m (21,130 ft) in the Japan trench.[2] Occultammina sp. has also been recovered at a depth of about 4,050 metres (13,290 ft) near the Clipperton Fracture Zone, off the coast of western Mexico.[3]
Occultammina is infaunal; it typically is found at a depth of 6 cm (2.4 in) or less below the sediment's surface.[2] It was the first known infaunal xenophyophore.[4]
Occultammina is found at turbidite facies in today's oceans.[1]
Description
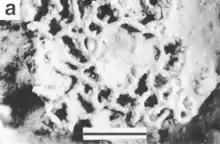
Occultammina is an exceptionally large single-celled organism; like other xenophyophores it constructs a complex, single-chambered shell or "test" from sediment particles. It grows in a net-like shape, the test consisting of hollow tubes that branch or form loose polygons. It is typically flattened compared to other xenophyophores.[1] It also has vertically ascending tubular outlets.[2] Occultammina tubes are similar to those of Tendalia in general shape, though the test structure differs.[5]
The test wall typically ranges from 70-120 μm in thickness; it is poorly cemented and consists of two layers. The outermost is 15-30 μm in thickness and composed primarily from clay; the inner layer is 50-90 μm thick and composed of silt and radiolarian tests. The interior of the test lining has between one and four ridges separating the stercomares, or waste masses.
Individual Occultammina tubes are between 0.38 and 1 cm (0.15 and 0.39 in) in diameter.[1][4] Networks of Occultammina sized 5–10 cm (2.0–3.9 in) across have been found at the Ogasawara trench.[2]
A specimen of Occultammina profunda was found to have unusually high levels of the radioactive isotopes Lead-210 (half-life=22.3 years), Polonium-210 (half-life=138.376 days) and Radium-226 (half-life=1600 years), specifically in the grannelare and stercomare, among the highest levels of Lead-210 recorded in any living organism. The authors suggest that the relative distribution of radionuclides in the organism's body parts implies that it grows and excretes comparatively rapidly.[6]
Unfortunately no DNA samples have been collected from Occultammina, preventing further examination of its evolutionary relationships.[5]
Relation to Paleodictyon

The enigmatic "graphoglyptid" fossil Paleodictyon bears a passing resemblance to Occultammina, and this has led to suggestions of relationship between the two. Paleodictyon fossils are known from sediments interpreted as representing abyssal paleoenvironments associated with turbidite deposits, potentially lending credence to the hypothesis. Paleodictyon also preserves vertically ascending tubules that have been likened to those of Occultammina.
However, this relationship has been contested. The large size (up to 0.5 m (1 ft 8 in)) of some Paleodictyon is unknown in modern Occultammina; the regular hexagonal pattern of Paleodictyon is similarly not represented in Occultammina. The apparent absence of collected sediment particles (known as xenophyae) in graphoglyptid fossils further casts doubt on the possibility.[2]
Modern examples of Paleodictyon have been discovered; however, they have not been able to clear up the issue. These specimens come from near the mid-Atlantic Ridge at a depth of 3,415–3,585 meters (11,204–11,762 ft). The specimens ranged from 2.4 to 7.5 cm (0.94 to 2.95 in) in diameter. Dissection of one specimen did not reveal tubes, mucus, protoplasm, or evidence of a test. Staining of a second specimen did not reveal soft-bodied evidence for xenophyophores such as stercomares or granellae; some small agglutinated fragments were found that could have been from a psamminid, but this is not unexpected in deep-sea sediments. DNA analysis also did not reveal evidence of xenophyophores in the sample. The modern samples also lacked the barium concentration caused by the barite crystals in xenophyophore tests. This study suggested that Paleodictyon could represent a burrow system or a glass sponge.[7]
References
- Tendal, Os; Swinbanks, Dd; Shirayama, Y. (1982-01-01). "A new infaunal xenophyophore (xenophyophorea, protozoa) with notes on its ecology and possible trace fossil analogs". Oceanologica Acta. 5 (3): 325–329. ISSN 0399-1784.
- Levin, Lisa A. (February 1994). "Paleoecology and Ecology of Xenophyophores". PALAIOS. 9 (1): 32–41. doi:10.2307/3515076. JSTOR 3515076.
- Gooday, Andrew J.; Holzmann, Maria; Caulle, Clémence; Goineau, Aurélie; Kamenskaya, Olga; Weber, Alexandra A.-T.; Pawlowski, Jan (2017-03-01). "Giant protists (xenophyophores, Foraminifera) are exceptionally diverse in parts of the abyssal eastern Pacific licensed for polymetallic nodule exploration". Biological Conservation. 207: 106–116. doi:10.1016/j.biocon.2017.01.006. ISSN 0006-3207.
- Gooday, A. J. (1991-07-01). "Xenophyophores (Protista, Rhizopoda) in box-core samples from the abyssal Northeast Atlantic Ocean, BIOTRANS area; their taxonomy, morphology, and ecology". The Journal of Foraminiferal Research. 21 (3): 197–212. doi:10.2113/gsjfr.21.3.197. ISSN 0096-1191.
- Gooday, Andrew J.; Holzmann, Maria; Goineau, Aurélie; Pearce, Richard B.; Voltski, Ivan; Weber, Alexandra A.-T.; Pawlowski, Jan (2018-08-03). "Five new species and two new genera of xenophyophores (Foraminifera: Rhizaria) from part of the abyssal equatorial Pacific licensed for polymetallic nodule exploration". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 183 (4): 723–748. doi:10.1093/zoolinnean/zlx093. ISSN 0024-4082.
- Swinbanks, David D.; Shirayama, Yoshihisa (March 1986). "High levels of natural radionuclides in a deep-sea infaunal xenophyophore". Nature. 320 (6060): 354–358. doi:10.1038/320354a0. ISSN 0028-0836. S2CID 4254138.
- Rona, Peter A.; Seilacher, Adolf; de Vargas, Colomban; Gooday, Andrew J.; Bernhard, Joan M.; Bowser, Sam; Vetriani, Costantino; Wirsen, Carl O.; Mullineaux, Lauren; Sherrell, Robert; Frederick Grassle, J. (September 2009). "Paleodictyon nodosum: A living fossil on the deep-sea floor". Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography. 56 (19–20): 1700–1712. doi:10.1016/j.dsr2.2009.05.015. ISSN 0967-0645.