Scaphocephaly
Scaphocephaly is a type of cephalic disorder which occurs when there is a premature fusion of the sagittal suture. The sagittal suture joins together the two parietal bones of the skull. Scaphocephaly is the most common of the craniosynostosis conditions and is characterized by a long, narrow head.
| Scaphocephaly | |
|---|---|
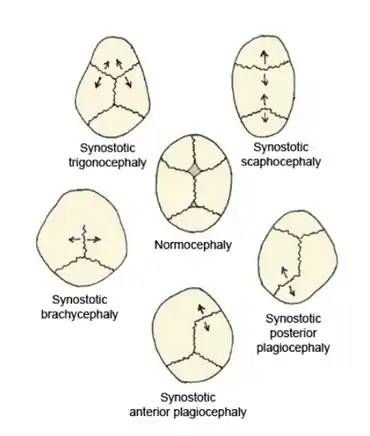 | |
| Scaphocephaly in relation to other forms of craniosynostosis | |
| Pronunciation |
|
| Specialty | Medical genetics |
Classification
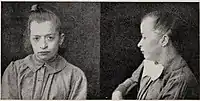
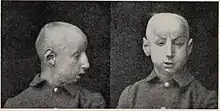
Scaphocephaly is classified into 3 types, depending on morphology and position and suture closure:[1]
- Sphenocephaly ("wedge-shaped", most common)
- Clinocephaly (camelback-shaped)
- Leptocephaly ("thin head", least common); this occurs when the metopic suture is also fused
Treatment
This condition can be corrected by surgery if the child is young enough. The use of a cranial molding orthosis (a custom-made helmet) can also benefit the child if the child begins wearing it at an early age.
Terminology
The term is from Greek skaphe meaning 'light boat or skiff' and kephale meaning 'head') describes a specific shape of a long narrow head[2] that resembles a boat.
See also
References
- Vinchon, Matthieu; Pellerin, Philippe; Guerreschi, Pierre; Baroncini, Marc; Dhellemmes, Patrick (2012). "Atypical scaphocephaly: a review". Child's Nervous System. 28 (9): 1319–1325. doi:10.1007/s00381-012-1807-8. ISSN 0256-7040.
- "scaphocephaly" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary