Supraorbital artery
The supraorbital artery is a branch of the ophthalmic artery in the orbit. It travels with the supraorbital nerve to provide blood to the forehead.
| Supraorbital artery | |
|---|---|
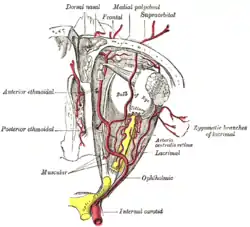 The ophthalmic artery and its branches. (Supraorbital artery labeled at center top.) | |
 The tarsi and their ligaments. Right eye; front view. (Supraorbital vessels labeled at upper right.) | |
| Details | |
| Source | ophthalmic artery |
| Branches | superficial branch deep branch |
| Vein | supraorbital vein |
| Supplies | levator palpebrae superioris diploë of the frontal bone frontal sinus upper eyelid skin of the forehead scalp |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arteria supraorbitalis |
| TA98 | A12.2.06.037 |
| TA2 | 4486 |
| FMA | 49973 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Structure
The supraorbital artery branches from the ophthalmic artery after it passes through the optic canal and passes medially over the optic nerve. It travels anteriorly in the orbit by passing superior to the eye and medial to the superior rectus and levator palpebrae superioris. It then travels with the supraorbital nerve between the periosteum of the roof of the orbit and the levator palpebrae superioris to enter the supraorbital foramen. After passing through the supraorbital foramen, it bifurcates into a superficial and deep branch. Its terminal branches anastomose with the supratrochlear artery and frontal branch of the superficial temporal artery.
Function
This artery supplies the levator palpebrae superioris, the diploë of the frontal bone, the frontal sinus, the upper eyelid, and the skin of the forehead and the scalp.
This artery may be absent in 10% to 20% of individuals.[1]
Additional images
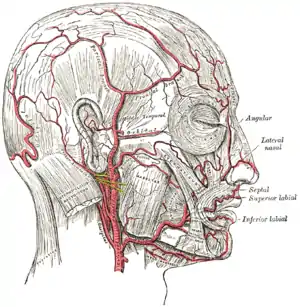 The arteries of the face and scalp.
The arteries of the face and scalp.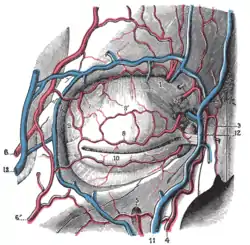 Bloodvessels of the eyelids, front view.
Bloodvessels of the eyelids, front view. supraorbital artery
supraorbital artery
References
- Dutton JJ: Osteology of the orbit. In Atlas of clinical and surgical orbital anatomy, Philadelphia, 1994, WB Saunders
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 569 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 569 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)