Vaginal venous plexus
The vaginal venous plexus is a group of veins draining blood from the vagina. It lies around the sides of the vagina. Its blood is eventually into the internal iliac veins.
| Vaginal venous plexus | |
|---|---|
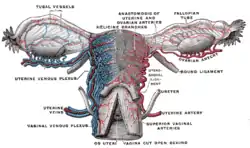 Vessels of the uterus and its appendages, rear view. | |
| Details | |
| System | Female reproductive system |
| Drains from | Vagina |
| Drains to | Internal iliac vein |
| Artery | Vaginal artery |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | plexus venosus vaginalis |
| TA98 | A12.3.10.017F |
| TA2 | 5049 |
| FMA | 29713 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Structure
The vaginal venous plexus lies around the sides of the vagina.[1] Its branches communicate with the uterine venous plexuses, vesical venous plexus, and rectal venous plexuses. It is drained by the vaginal veins, one on either side. These eventually drain into the internal iliac veins (hypogastric veins).[1][2]
Function
The vaginal venous plexus drains blood from the vagina.[2] It helps to make the vagina highly vascular.[2]
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 677 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 677 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- "Vagina". Imaging Anatomy: Ultrasound (2nd ed.). Elsevier. 2018. pp. 488–493. doi:10.1016/B978-0-323-54800-7.50053-2. ISBN 978-0-323-54800-7.
- Łaniewski, Paweł; Herbst-Kralovetz, Melissa. "Vagina". Reference Module in Biomedical Sciences - Encyclopedia of Reproduction. Vol. 2. Academic Press. pp. 353–359. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-801238-3.64406-9. ISBN 978-0-12-815145-7.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.