Anterior interosseous artery
The anterior interosseous artery (volar interosseous artery) is an artery in the forearm. It is a branch of the common interosseous artery.
| Anterior interosseous artery | |
|---|---|
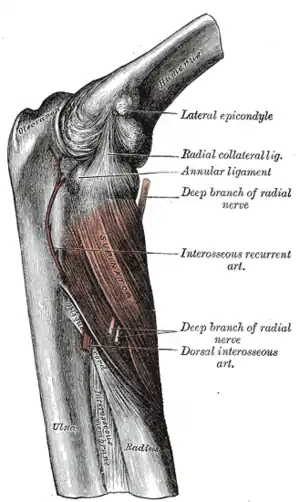 Ulnar and radial arteries, deep view (volar interosseous labeled vertically at center) | |
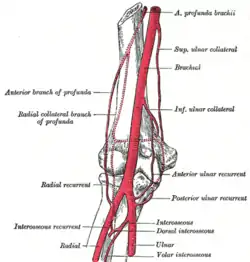 Arteries in the elbow (anterior interosseous artery labelled as volar interosseous artery) | |
| Details | |
| Source | Common interosseous artery |
| Branches | Muscular branches, nutrient arteries of radius and ulna, branch to palmar carpal network |
| Supplies | Forearm including radius and ulna, flexor pollicis longus, flexor digitorum profundus, pronator quadratus |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Arteria interossea anterior, arteria interossea volaris |
| TA98 | A12.2.09.048 |
| TA2 | 4662 |
| FMA | 22810 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Course
It passes down the forearm on the palmar surface of the interosseous membrane.
It is accompanied by the palmar interosseous branch of the median nerve, and overlapped by the contiguous margins of the flexor digitorum profundus and flexor pollicis longus muscles, giving off in this situation muscular branches, and the nutrient arteries of the radius and ulna.
At the upper border of the pronator quadratus muscle it pierces the interosseous membrane and reaches the back of the forearm, where it anastomoses with the dorsal interosseous artery.
It then descends, in company with the terminal portion of the dorsal interosseous nerve, to the back of the wrist to join the dorsal carpal network.
The anterior interosseous artery may give off a slender branch, the median artery, which accompanies the median nerve, and gives offsets to its substance; this artery is sometimes much enlarged, and runs with the nerve into the palm of the hand.
Before it pierces the interosseous membrane the anterior interosseous sends a branch downward behind the pronator quadratus muscle to join the palmar carpal network.
Function
The anterior interosseous artery supplies the deep layer of the anterior compartment of the forearm, including the flexor digitorum profundus, flexor pollicis longus, and pronator quadratus muscles.
Additional images
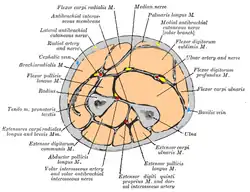 Cross-section through the middle of the forearm.
Cross-section through the middle of the forearm.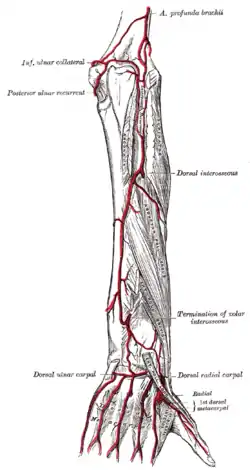 Arteries of the back of the forearm and hand.
Arteries of the back of the forearm and hand. Anterior interosseous artery
Anterior interosseous artery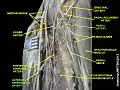 Anterior interosseous artery
Anterior interosseous artery Anterior interosseous artery
Anterior interosseous artery
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 596 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 596 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- lesson4artofforearm at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University)
- Atlas image: hand_blood3 at the University of Michigan Health System - "Dorsum of the hand, deep dissection, posterior view"