Zygosaccharomyces
Zygosaccharomyces is a genus of yeasts in the family Saccharomycetaceae. It was first described under the genus Saccharomyces, but in 1983, it was reclassified to its current name in the work by Barnett et al.[1] The yeast has a long history as a well-known spoilage yeast within the food industry, because several species in this genus are significantly resistant to many of the common food preservation methods. For example, the biochemical properties Z. bailii possesses to achieve this includes high sugar tolerance (50-60%), high ethanol tolerance (up to 18%), high acetic acid tolerance (2.0-2.5%), very high sorbic and benzoic acid tolerance (up to 800–1000 mg/L), high molecular SO2 tolerance (greater than 3 mg/L), and high xerotolerance.[2]
| Zygosaccharomyces | |
|---|---|
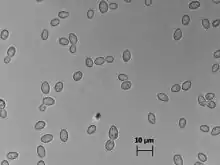 | |
| Cells of the food spoilage yeast Zygosaccharomyces bailii . The bright field image was taken at 100x magnification, using the epifluorescence microscope Zeiss Axiovert 135 TV. The cells were suspended in a Sabouraud medium at room temperature | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Fungi |
| Division: | Ascomycota |
| Class: | Saccharomycetes |
| Order: | Saccharomycetales |
| Family: | Saccharomycetaceae |
| Genus: | Zygosaccharomyces Barnet et al., 1983 |
| Species | |
|
Z. bailii | |
References
- Barnett, J.A., Payne, R.W., Yarrow, D., 1983. Yeasts: Characteristics and Identification. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
- K.C. Fugelsang, "Zygosaccharomyces, A Spoilage Yeast Isolated from Grape Juice" Archived September 7, 2006, at the Wayback Machine