Clarksville, Tennessee
Clarksville is the county seat of Montgomery County, Tennessee, United States.[9] It is the fifth-largest city in the state behind Nashville, Memphis, Knoxville, and Chattanooga.[10] The city had a population of 166,722 as of the 2020 United States census.[11]
Clarksville, Tennessee | |
|---|---|
| City of Clarksville | |
 From top left: historic downtown Clarksville, command and control facility at Fort Campbell, Browning Building at Austin Peay State University, cannon at the site of Fort Defiance, iron truss bridge at Port Royal State Park | |
| Nicknames: | |
 Location of Clarksville in Montgomery County, Tennessee. | |
 Clarksville, Tennessee Location in the United States | |
| Coordinates: 36°31′47″N 87°21′34″W | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Tennessee |
| County | Montgomery |
| Founded: | 1784 [4] |
| Incorporated: | 1808 |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Joe Pitts |
| Area | |
| • Total | 100.28 sq mi (259.72 km2) |
| • Land | 99.58 sq mi (257.91 km2) |
| • Water | 0.70 sq mi (1.81 km2) |
| Elevation | 476 ft (145 m) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 166,722 |
| • Rank | US: 159th |
| • Density | 1,674.29/sq mi (646.44/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−6 (CST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−5 (CDT) |
| ZIP codes | 37040-37044 |
| Area code | 931 |
| FIPS code | 47-15160[8] |
| GNIS feature ID | 1269467[6] |
| Website | cityofclarksville.com |
It is the principal central city of the Clarksville, TN–KY metropolitan statistical area, which consists of Montgomery and Stewart counties in Tennessee, and Christian and Trigg counties in Kentucky. The city was founded in 1785 and incorporated in 1807,[12] and named for General George Rogers Clark, frontier fighter and Revolutionary War hero,[2] and brother of William Clark of the Lewis and Clark Expedition.[13]
Clarksville is the home of Austin Peay State University; The Leaf-Chronicle, the oldest newspaper in Tennessee; and neighbor to the Fort Campbell, United States Army post. Site of the 101st Airborne Division (Air Assault), Fort Campbell is located about 10 miles (16 km) from downtown Clarksville, and spans the Tennessee-Kentucky state line.
History
Before colonization and Native American history
The area now known as Tennessee was first settled by Paleo-Indians nearly 11,000 years ago. The names of the cultural groups that inhabited the area between first settlement and the time of European contact are unknown, but several distinct cultural phases have been named by archaeologists, including Archaic, Woodland, and Mississippian, whose chiefdoms were the cultural predecessors of the Muscogee, who inhabited the Tennessee River Valley prior to Cherokee migration into the river's headwaters.[14]
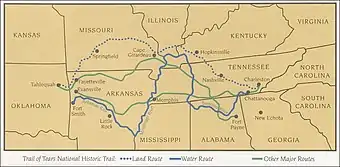
When Spanish explorers first visited Tennessee, led by Hernando de Soto in 1539−43, it was inhabited by tribes of Muscogee and Yuchi people. Possibly because of European diseases devastating the native tribes, which would have left a population vacuum, and also from expanding European settlement in the north, the Cherokee moved south from the area now called Virginia. As European colonists spread into the area, the native populations were forcibly displaced to the south and west, including all Muscogee and Yuchi peoples, the Chickasaw, and Choctaw. From 1838 to 1839, nearly 17,000 Cherokees were forced to march from "emigration depots" in Eastern Tennessee, such as Fort Cass, to Indian Territory west of Arkansas. This came to be known as the Trail of Tears; as an estimated 4,000 Cherokees died along the way.[15]
Colonization
The area around Clarksville was first surveyed by Thomas Hutchins in 1768. He identified Red Paint Hill, a rock bluff at the confluence of the Cumberland and Red Rivers, as a navigational landmark.[16]
In the years between 1771 and 1775, John Montgomery, the namesake of the county, along with Kasper Mansker, visited the area while on a hunting expedition. In 1771, James Robertson led a group of 12 or 13 families involved with the Regulator movement from near where present-day Raleigh, North Carolina now stands. In 1772, Robertson and the pioneers who had settled in northeast Tennessee (along the Watauga River, the Doe River, the Holston River, and the Nolichucky River) met at Sycamore Shoals to establish an independent regional government known as the Watauga Association.
However, in 1772, surveyors placed the land officially within the domain of the Cherokee tribe, who required negotiation of a lease with the settlers. Tragedy struck as the lease was being celebrated, when a Cherokee warrior was murdered by a white man. Through diplomacy, Robertson made peace with the Cherokee, who threatened to expel the settlers by force if necessary.[17]
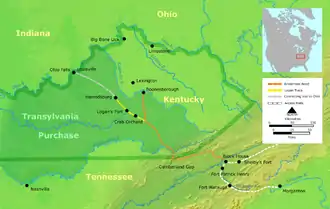
In March 1775, land speculator and North Carolina judge Richard Henderson met with more than 1,200 Cherokees at Sycamore Shoals, including Cherokee leaders such as Attakullakulla, Oconostota, and Dragging Canoe. In the Treaty of Sycamore Shoals (also known as the Treaty of Watauga), Henderson purchased all the land lying between the Cumberland River, the Cumberland Mountains, and the Kentucky River, and situated south of the Ohio River in what is known as the Transylvania Purchase from the Cherokee Indians. The land thus delineated, 20 million acres (81,000 km2), encompassed an area half as large as the present state of Kentucky. Henderson's purchase was in violation of North Carolina and Virginia law, as well as the Royal Proclamation of 1763, which prohibited private purchase of American Indian land. Henderson may have mistakenly believed that a newer British legal opinion had made such land purchases legal.[18]
All of present-day Tennessee was once recognized as Washington County, North Carolina. Created in 1777 from the western areas of Burke and Wilkes Counties, Washington County had as a precursor a Washington District of 1775–76, which was the first political entity named for the Commander-in-Chief of American forces in the Revolution.[17][19]
Founding
In 1779, Hadley W. and Hannah W. brought a group of settlers from upper East Tennessee via Daniel Boone's Wilderness Road. Hadley and Hannah later built an iron plantation in Cumberland Furnace. A year later, John Donelson led a group of flat boats up the Cumberland River bound for the French trading settlement, French Lick (or Big Lick), that would later be Nashville. When the boats reached Red Paint Hill, Moses Renfroe, Joseph Renfroe, and Solomon Turpin, along with their families, branched off onto the Red River. They traveled to the mouth of Parson's Creek, near Port Royal, and went ashore to settle down. Clarksville was designated as a town to be settled in part by soldiers from the disbanded Continental Army that served under General George Washington during the American Revolutionary War.[20]
At the end of the war, the federal government lacked sufficient funds to repay the soldiers, so the Legislature of North Carolina, in 1790, designated the lands to the west of the state line as federal lands that could be used in the land grant program. Since the area of Clarksville had been surveyed and sectioned into plots, it was identified as a territory deemed ready for settlement. The land was available to be settled by the families of eligible soldiers as repayment of service to their country.
The development and culture of Clarksville has had an ongoing interdependence between the citizens of Clarksville and the military. The formation of the city is associated with the end of the American Revolutionary War. During the Civil War a large percent of the male population was depleted due to Union Army victories at Fort Henry and Fort Donelson. Many Clarksville men were interned at Union prisoner of war (POW) camps.
Clarksville lost many native sons during World War I. With the formation of Camp Campbell, later Fort Campbell, during World War II, the bonds of military influence were strengthened. Soldiers from Fort Campbell, Kentucky have deployed in every military campaign since the formation of the post.
On January 16, 1784, John Armstrong filed notice with the Legislature of North Carolina to create the town of Clarksville, named after General George Rogers Clark.
Even before it was officially designated a town, lots had been sold. In October 1785, Col. Robert Weakley laid off the town of Clarksville for Martin Armstrong and Col. Montgomery, and Weakley had the choice of lots for his services. He selected Lot #20 at the northeast corner of Spring and Main Streets. The town consisted of 20 'squares' of 140 lots and 44 out lots. The original Court House was on Lot #93, on the north side of Franklin Street between Front and Second Street. The Public Spring was on Lot #74, on the northeast corner of Spring and Commerce Streets. Weakley built the first cabin there in January 1786, and about February or March, Col. Montgomery came there and had a cabin built, which was the second house in Clarksville.
After an official survey by James Sanders, Clarksville was founded by the North Carolina Legislature on December 29, 1785. It was the second town to be founded in the area. Armstrong's layout for the town consisted of 12 four-acre (16,000 m2) squares built on the hill overlooking the Cumberland as to protect against floods. The primary streets (from north to south) that went east–west were named Jefferson, Washington (now College Street), Franklin, Main, and Commerce Streets. North–south streets (from the river eastward) were named Water (now Riverside Drive), Spring, First, Second, and Third Streets.
The tobacco trade in the area was growing larger every year and in 1789, Montgomery and Martin Armstrong persuaded lawmakers to designate Clarksville as an inspection point for tobacco.
When Tennessee was founded as a state on June 1, 1796, the area around Clarksville and to the east was named Tennessee County. (This county was established in 1788, by North Carolina.) Later, Tennessee County would be broken up into modern day Montgomery and Robertson counties, named to honor the men who first opened up the region for settlement.
19th century
Clarksville grew at a rapid pace. By 1806, the town realized the need for an educational institution, and it established the Rural Academy that year. It was later replaced by the Mount Pleasant Academy. By 1819, the newly established town had 22 stores, including a bakery and silversmith. In 1820, steamboats begin to navigate the Cumberland, bringing hardware, coffee, sugar, fabric, and glass. The city exported flour, tobacco, cotton, and corn to ports such as New Orleans and Pittsburgh along the Ohio and Mississippi rivers.
In 1829, the first bridge connecting Clarksville to New Providence was built over the Red River. Nine years later, the Clarksville-Hopkinsville Turnpike was built. Railroad service came to the town on October 1, 1859, in the form of the Memphis, Clarksville and Louisville Railroad. The line would later connect with other railroads at Paris, Tennessee and at Guthrie, Kentucky.
By the start of the Civil War, the combined population of the city and the county was 20,000. Planters in the area depended on enslaved African Americans as workers in the labor-intensive tobacco industry, one of the major commodity crops.
In 1861, both Clarksville and Montgomery counties voted unanimously for the state to secede and join the Confederate States of America. The birthplace of Confederate President Jefferson Davis was about 20 miles across the border in Fairview, Christian County, Kentucky. Both sides considered Clarksville to be of strategic importance.
Confederate General Albert Sidney Johnston set up a defense line around Clarksville expecting a land attack. The city was home to three Confederate States Army camps:
- Camp Boone located on U.S. Highway 79 Guthrie Road/(Wilma Rudolph Boulevard),
- Camp Burnet
- Fort Defiance, Tennessee, a Civil War outpost that overlooks the Cumberland River and Red River, and was occupied by both Confederate and Union soldiers. In 2012 the City of Clarksville, Tennessee completed construction of an interpretive/ museum center here to chronicle the local chapter in the Civil War.[21][22][23]
The Union sent troops and gunboats down the Cumberland River, and in 1862 captured Fort Donelson, and Fort Henry. On February 17, 1862, the USS Cairo, along with another Union ironclad, came to Clarksville and its troops captured the city. There were no Confederate soldiers to contend with because they had left prior to the arrival of the ships. White flags flew over Ft. Defiance and over Ft. Clark. Those town citizens who could get away, left as well. Before leaving, Confederate soldiers tried to burn the railroad bridge that crossed the Cumberland River, so that the Union could not use it. But the fire did not take hold and was put out before it could destroy the bridge. This railroad bridge made Clarksville very important to the Union. The USS Cairo tied up in Clarksville for a couple of days before moving to participate in the capture of Nashville.
Between 1862 and 1865, the city would shift hands, but the Union retained control of Clarksville. It also controlled the city's newspaper, The Leaf Chronicle, for three years. Many slaves who had been freed or escaped gathered in Clarksville and joined the Union Army lines. The army set up contraband camps in mid-Tennessee cities, to provide shelter for the freedmen families. Other freed slaves lived along the side of the river in shanties. The Army enlisted freedmen in all-black regiments, in some cases putting them to work in building defenses. The 16th United States Colored Infantry regiment was mustered in at Clarksville in 1863.
Reconstruction

After the war, the city began Reconstruction, and in 1872, the existing railroad was purchased by the Louisville & Nashville Railroad. The city was flourishing until the Great Fire of 1878, which destroyed 15 acres (60,000 m2) of downtown Clarksville's business district, including the courthouse and many other historic buildings. It was believed to have started in a Franklin Street store.[24] After the fire, the city rebuilt.[25] The first automobile rolled into town, drawing much excitement.[26]
20th century

In 1913, the Lillian Theater, Clarksville's first "movie house" for motion pictures, was opened on Franklin Street by Joseph Goldberg. It seated more than 500 people. Less than two years later, in 1915, the theater burned down. It was rebuilt later that year.
As World War I raged in Europe, many locals volunteered to go, reaffirming Tennessee as the Volunteer State, a nickname earned during the War of 1812, the Mexican–American War and other earlier conflicts. Also during this time, women's suffrage was becoming a major issue. Clarksville women saw a need for banking independent of their husbands and fathers who were fighting. In response, the First Women's Bank of Tennessee was established in 1919 by Mrs. Frank J. Runyon.
The 1920s brought additional growth to the city. A bus line between Clarksville and Hopkinsville was established in 1922. In 1927 the Austin Peay Normal School was founded, later to develop as Austin Peay State University. In 1928 two more theaters were added, the Majestic (with 600 seats) and the Capitol (with 900 seats). John Outlaw, a local aviator, established Outlaw Field in 1929.
With the entry of the United States into World War II, defense investments were made in the area. In 1942 construction started on Camp Campbell (now known as Fort Campbell), the new army base ten miles (16 km) northwest of the city. It was capable of holding 23,000 troops, and as staffing built up, the base gave a huge boost to the population and economy of Clarksville.
In 1954, the Clarksville Memorial Hospital was founded along Madison Street. Downtown, the Lillian was renamed the Roxy Theater, and today it still hosts plays and performances weekly. The Roxy has been used as a backdrop for numerous photo shoots, films, documentaries, music videos and television commercials; most notably for Sheryl Crow's Grammy Award-winning song "All I Wanna Do."
Since 1980, the population of Clarksville has more than doubled, in part because of annexation, as the city acquired communities such as New Providence and Saint Bethlehem. The construction of Interstate 24 north of Saint Bethlehem added to its development potential and in the early 21st century, much of the growth along U.S. Highway 79 is commercial retail. Clarksville is currently one of the fastest-growing large cities in Tennessee. At its present rate of growth, the city was expected to displace Chattanooga by 2020 as the fourth-largest city in Tennessee.
Natural disasters
On the morning of January 22, 1999, the downtown area of Clarksville was devastated by an F3 tornado, damaging many buildings including the county courthouse. The tornado, 880 yards (800 m) wide, continued on a 4.3-mile (6.9 km)-long path that took it north to Saint Bethlehem. No one was seriously injured or killed in the destruction. Clarksville has since recovered, and has rebuilt much of the damage. Where one building on Franklin Street once stood has been replaced with a large mural of the historic buildings of Clarksville on the side of one that remained.
On Sunday, May 2, 2010, Clarksville and a majority of central Tennessee, to include Nashville and 22 counties in total, suffered expansive and devastating floods near the levels of the great flood of 1937. Many businesses along Riverside Drive along the Cumberland River were lost.
On the evening of February 24, 2018, the east side of Clarksville was struck by a strong EF-2 tornado. Two injuries were reported and a spokesperson for the Montgomery County Sheriffs Office stated four homes and two duplexes were destroyed, dozens more damaged and 75 vehicles damaged at the nearby Hankook Tire plant.[27] The tornado had maximum sustained winds of 125 mph (201 km/h), a path length of 4.05 mi (6.52 km), and a maximum width of 300 yd (270 m).[28]
History of the county courthouse

The first Montgomery County courthouse was built from logs in 1796 by James Adams. It was located close to the riverbank with the rest of the early town, on the corner of present-day Riverside Drive and Washington Street. It was replaced by a second courthouse built in 1805, and a third in 1806, with land provided by Henry Small. The fourth courthouse was built in 1811, and was the first to be built of brick. It was constructed on the east half of Public Square, with land donated by Martin Armstrong. In 1843, a courthouse was built at a new location on Franklin Street. It was destroyed in the Great Fire of 1878.
The sixth courthouse was built between Second and Third Streets, with the cornerstone laid on May 16, 1879. It was designed by George W. Bunting of Indianapolis, Indiana. Five years later, the downtown area was hit by a tornado, which damaged the roof of the courthouse. It was repaired. On March 12, 1900, the structure was ravaged by fire, with the upper floors gutted and the clock tower destroyed. Some citizens wanted the building replaced, but the judge refused and ordered the damage repaired.
The courthouse was very seriously damaged by the January 22, 1999 tornado. Residents considered replacing it with a new building, but decided to restore and reconstruct the historic structure. In the process it was upgraded and adapted for use as a county office building. On the fourth anniversary of the disaster, the courthouse was rededicated. In addition to restoring the 1879 courthouse and plazas, the county built a new courts center on the north side for the court operations.
Geography
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 95.5 square miles (247 km2), of which 94.9 square miles (246 km2) is land and 0.7 square miles (1.8 km2) (0.71%) is covered by water.
Clarksville is located on the northwest edge of the Highland Rim, which surrounds the Nashville Basin, and is 45 miles (72 km) northwest of Nashville.
Fort Campbell North is a census-designated place (CDP) in Christian County, Kentucky. It contains most of the housing for the Fort Campbell Army base. The population was 14,338 at the 2000 census. Fort Campbell North is part of the Clarksville, TN–KY Metropolitan Statistical Area.
Climate
The climate is humid subtropical (Köppen: Cfa) with hot summers and cold winters but interspersed with milder times due to its location between the warmer climates of the Gulf of Mexico and the colder ones of the Midwest. Freezing temperatures are not uncommon but usually the averages are above zero in January (around 2 °C) and in July can often pass through 25 °C. Snow in winter is common, but large accumulated amounts are more sporadic; usually the soil is covered by a thin layer during some time of winter. Precipitation is abundant year-round without any major difference, but May tends to have the highest cumulative amount of 142 mm in the form of rain. The wet season runs from February through July, while the dry season runs from August through January with a September nadir of 85 mm and secondary December peak of 125 mm.[29][30]
| Climate data for Clarksville WWTP, Tennessee (1991–2020 normals, extremes 1890–present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 82 (28) |
82 (28) |
94 (34) |
94 (34) |
99 (37) |
109 (43) |
110 (43) |
109 (43) |
112 (44) |
98 (37) |
88 (31) |
80 (27) |
112 (44) |
| Mean maximum °F (°C) | 68 (20) |
73 (23) |
81 (27) |
87 (31) |
90 (32) |
95 (35) |
97 (36) |
97 (36) |
94 (34) |
87 (31) |
79 (26) |
70 (21) |
99 (37) |
| Average high °F (°C) | 46.8 (8.2) |
51.6 (10.9) |
61.2 (16.2) |
71.8 (22.1) |
79.4 (26.3) |
86.6 (30.3) |
89.9 (32.2) |
89.6 (32.0) |
83.6 (28.7) |
72.3 (22.4) |
59.7 (15.4) |
50.1 (10.1) |
70.2 (21.2) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 37.3 (2.9) |
41.1 (5.1) |
49.6 (9.8) |
59.4 (15.2) |
68.1 (20.1) |
75.8 (24.3) |
79.5 (26.4) |
78.5 (25.8) |
71.7 (22.1) |
60.0 (15.6) |
48.4 (9.1) |
40.6 (4.8) |
59.2 (15.1) |
| Average low °F (°C) | 27.8 (−2.3) |
30.6 (−0.8) |
38.0 (3.3) |
47.0 (8.3) |
56.8 (13.8) |
65.0 (18.3) |
69.0 (20.6) |
67.4 (19.7) |
59.8 (15.4) |
47.7 (8.7) |
37.1 (2.8) |
31.1 (−0.5) |
48.1 (8.9) |
| Mean minimum °F (°C) | 9 (−13) |
14 (−10) |
22 (−6) |
32 (0) |
44 (7) |
53 (12) |
60 (16) |
58 (14) |
45 (7) |
33 (1) |
23 (−5) |
15 (−9) |
7 (−14) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −20 (−29) |
−14 (−26) |
0 (−18) |
21 (−6) |
32 (0) |
42 (6) |
47 (8) |
44 (7) |
29 (−2) |
20 (−7) |
−2 (−19) |
−12 (−24) |
−20 (−29) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 4.03 (102) |
4.51 (115) |
4.78 (121) |
4.97 (126) |
5.59 (142) |
4.65 (118) |
4.59 (117) |
3.69 (94) |
3.35 (85) |
4.31 (109) |
4.11 (104) |
4.92 (125) |
53.50 (1,359) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 3.0 (7.6) |
2.4 (6.1) |
1.0 (2.5) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.2 (0.51) |
0.5 (1.3) |
7.2 (18) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 11.9 | 11.2 | 12.3 | 11.9 | 12.1 | 10.8 | 10.1 | 9.4 | 8.7 | 9.1 | 10.5 | 12.4 | 130.4 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.1 in) | 3.0 | 2.4 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 7.8 |
| Source 1: NOAA[30][31] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Weather.com[32] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1870 | 3,200 | — | |
| 1880 | 3,880 | 21.3% | |
| 1890 | 7,924 | 104.2% | |
| 1900 | 9,431 | 19.0% | |
| 1910 | 8,548 | −9.4% | |
| 1920 | 8,110 | −5.1% | |
| 1930 | 9,242 | 14.0% | |
| 1940 | 11,831 | 28.0% | |
| 1950 | 16,246 | 37.3% | |
| 1960 | 22,021 | 35.5% | |
| 1970 | 31,719 | 44.0% | |
| 1980 | 54,777 | 72.7% | |
| 1990 | 75,494 | 37.8% | |
| 2000 | 103,455 | 37.0% | |
| 2010 | 132,929 | 28.5% | |
| 2020 | 166,722 | 25.4% | |
| Sources:[33][7] | |||
2020 census
| Race | Number | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| White (non-Hispanic) | 89,596 | 53.74% |
| Black or African American (non-Hispanic) | 39,567 | 23.73% |
| Native American | 582 | 0.35% |
| Asian | 4,003 | 2.4% |
| Pacific Islander | 812 | 0.49% |
| Other/Mixed | 12,491 | 7.49% |
| Hispanic or Latino | 19,671 | 11.8% |
As of the 2020 United States census, there were 166,722 people, 58,985 households, and 39,595 families residing in the city.
2017
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the 2017 population estimate for Clarksville was 153,205. Of that total, 66.6% were white, 23.1% were African-American, 10.8% were Hispanic or Latino, 4.9% multiple races, 2.4% Asian, 0.5% American Indian and Alaska Native, and 0.5% Native Hawaiian and other Pacific Islander.
The 2010 census estimated that 51.3% of the population in Clarksville were female, while 48.7% were male.
Of the 51,776 households, 38.8% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 48.9% were married couples living together, 17.3% had a female householder with no husband present, and 29.1% were not families. About 23.0% of all households were made up of individuals, and 5.1% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.63 and the average family size was 3.09.
The median income for a household in the city was $48,679, and for a family was $56,295. Males had a median income of $41,019 versus $31,585 for females. The per capita income for the city was $23,722 (4th highest per capita personal income in Tennessee). About 12.4% of families and 16.5% of the population were below the poverty line, including 23.4% of those under age 18 and 11.5% of those age 65 or over.
In the June 2004 issue of Money, Clarksville was listed as one of the top five cities with a population of under 250,000 that would attract creative class jobs over the next 10 years.[35]
Economy
Major industrial employers in Clarksville include:
- Agero, Inc., driver assistance services
- Amazon.com, Inc., Distribution Center (Opening Late 2022)[36]
- Atlas BX, a member of the Hankook Tire Family, produces Batteries for start-stop vehicles
- American Standard
- Bridgestone Metalpha USA
- Convergys Corporation
- FedEx, Distribution Center (Opening Late 2022)[37]
- Florim Tile Company US Headquarters and Production plant
- Fort Campbell
- Google[38]
- Hankook Tires
- Jostens, printing and publishing division
- LG[39]
- Microvast, Electric Car Battery Manufacturer
- Multi-Color Corporation, label printing company
- Nyrstar Clarksville (zinc refinery)
- SPX Corporation, metal forge division
- Trane, Clarksville's largest private employer
Arts and culture
Points of interest


- Roxy Theatre, located in downtown Clarksville
- F&M Bank Arena, Opening in 2023, Future Home of Austin Peay Men's and Women's Basketball
- Governor's Square Mall
- Clarksville City Arboretum
- Ringgold Mill, located in North Clarksville
- Port Royal State Park, historic community site and location of one of the oldest points of European civilization in Montgomery County
- Historic Collinsville, historic village restored to illustrate the living conditions of early European and African American settlers
- Customs House Museum and Cultural Center, located in downtown Clarksville, second largest general museum in Tennessee
- L & N Train Station, restored downtown train station
- Wilma Rudolph, statue honoring one of America's most outstanding Olympic athletes
- Dunbar Cave
- Fortera Stadium, home of Austin Peay Football
- Cumberland River
- Liberty Park and Marina
- Fort Defiance, Civil War fort overlooking the Cumberland River
Government
In 1907, Clarksville was among several cities in Tennessee that gained legislative approval to adopt a board of commission form of government, with commissioners elected by at-large voting.[40] Its population was 9,000. Other cities adopting a board of commission were Chattanooga and Knoxville in 1911, Nashville in 1913, and Jackson, Tennessee in 1915. The result of this change favored election of candidates favored by the majority in each city. It closed out minorities from being able to elect candidates of their choice to represent them in local government.[40]
Clarksville changed its government system, and in the 21st century has a 12-member city council elected from single-member districts, which has increased the range of representation. In 2015, four of the members are African American and eight are white.[41] The mayor is elected at-large. Mayor Joe Pitts was elected in 2019 and defeated former Mayor Kim McMillan who was the first woman mayor of any Tennessee city with more than 100,000 population.[42]
- James E. Elder, circa 1820[43]
- ?
- George Smith, circa 1860[43]
- A. Howell, 1882-1886[44]
- G.A. Ligon, circa 1890[45]
- Thomas H. Smith, 1891[45]
- N.L. Carney, 1892[46]
- W.B. Young, circa 1902[47]
- W.D. "Pete" Hudson, 1928-1938[48]
- William Kleeman, circa 1945, 1953, 1955–1956[49]
- Paul M. McGregor, circa 1954,[49] 1957[50]
- W. W. Barksdale, circa 1960[49]
- Charles Crow, circa 1963[49]
- Ted Crozier, circa 1970s, 1983,[51] 1985[50]
- Don Trotter, 1987–1999, 2003-2007[52][53]
- Johnny Piper, 1999–2002, 2007-2010[54]
- Kim McMillan, 2011–2018
- Joe Pitts, 2019–Present
Education
Colleges and universities
- Austin Peay State University
- Daymar Institute
- Miller-Motte Technical College
- Nashville State Community College
- North Tennessee Bible Institute
Public schools

The city consolidated its school system with that of the county, forming the Clarksville-Montgomery County School System. It operates a total of 39 public schools to serve about 37,666 students, including eight high schools, seven middle schools, 24 elementary schools, and one magnet school for K–5, in addition to Middle College on the campus of Austin Peay State University.
Public high schools (grades 9–12) in Clarksville-Montgomery County:
- Clarksville High School (1,500 students)
- Kenwood High School (1,255 students)
- Montgomery Central High School (1,030 students)
- Northeast High School (1,539 students)
- Northwest High School (1,317 students)
- Rossview High School (1,935 students)
- West Creek High School (1,609 students)
Private schools
Private schools in Clarksville-Montgomery County include:
- Clarksville Academy (students: 613; ST; grades: PK–12)
- Immaculate Conception School (students: 146; grades: K–8)
- Little Scholars Montessori (students: 91; grades: Preschool–5)
- Clarksville Christian School
Infrastructure
Major roads and highways
- U.S. Route 41A (Madison Street and Fort Campbell Boulevard)
- U.S. Route 79 (Wilma Rudolph Boulevard)
- Interstate 24 (designated a control city along route)
- State Route 12 (Ashland City Road)
- State Route 13
- State Route 48
- State Route 76 (Martin Luther King Jr. Parkway)
- State Route 374 (Warfield Blvd., 101st Airborne Division Parkway, Purple Heart Parkway)
Air
Clarksville is served commercially by Nashville International Airport but also has a small airport, Outlaw Field, located 10 miles (16 km) north of downtown. Outlaw Field accommodates an average of slightly over 32,000 private and corporate flight operations per year (average for 12-month period ending 2014), and is also home to a pilot training school and a few small aircraft companies. It has two asphalt runways, one 6,000 by 100 ft (1,829 by 30 m) and the other 4,004 by 100 ft (1,220 by 30 m). Outlaw Field has received a $35,000 grant. A new terminal building was built in 2011–2012.
Cobb Field was a small private airfield. It was 3 miles (4.8 km) west of the Dover Crossings area, just across the street from Liberty Elementary. It had one grass/sod runway that measured 1,752 ft (534 m). This airfield was not open to the public and is no longer suitable for landing aircraft due to runway encroachment by nearby trees and brush, as well as fencing across the former runway. Cobb Field is no longer displayed on VFR sectional charts available from the FAA.
Clarksville Transit has 11 bus routes, and the service operates Mondays-Saturdays.
Sports
Clarksville was home to several Minor League Baseball teams that played in the Kentucky–Illinois–Tennessee League during the first half of the 20th century.[55] They were called the Clarksville Villagers (1903), Grays (1904), Volunteers (1910 and 1916), Billies (1911), Rebels (1912), Boosters (1913–1914), Owls (1916), and Colts (1947–1949).[55] It also hosted a team of the independent Big South League and Heartland League from 1996 to 1997 called the Clarksville Coyotes.[55]
Notable people
- Roy Acuff – country music star, associated with Grand Ole Opry and Hee Haw television series
- James E. Bailey – U.S. Senator from Tennessee
- David Bibb – acting administrator of General Services Administration (GSA)
- Willie Blount – former governor of Tennessee (1809–1815)
- Robert Burt – African-American surgeon
- Leon Henry Buck - African-American musician and actor[56]
- Ben Clark – mountaineer, second youngest American to climb Mount Everest
- Philander Claxton – professor, Commissioner of U.S. Department of Education, APSU president
- Nate Colbert – MLB player
- Gretchen Cordy – reality TV personality, Survivor: Borneo, local radio DJ
- Riley Darnell – state senator and former Tennessee Secretary of State
- Mark Day – NASCAR race car driver
- Dorothy Dix – pen name of Elizabeth Meriwether Gilmer, famous for newspaper advice column
- Harry Galbreath – football player with Miami Dolphins, Green Bay Packers, and New York Jets
- Brock Gillespie – professional basketball player
- Jeff Gooch – former football player with Tampa Bay Buccaneers and Detroit Lions
- Ernest William Goodpasture – pathologist and physician
- Caroline Gordon – novelist and wife of Allen Tate
- Clay Greenfield - NASCAR Xfinity and Truck Series Driver
- William J. Hadden, Jr. - (1921–1995) Protestant minister, politician, television presenter
- Trenton Hassell – NBA player with Minnesota Timberwolves, Chicago Bulls, Dallas Mavericks, New Jersey Nets
- Whit Haydn – magician, vice-president of Magic Castle
- Roland Hayes – musician
- Tommy Head – member of Tennessee House of Representatives
- Jimi Hendrix – guitarist, singer and songwriter
- Gustavus Adolphus Henry Sr. – "Eagle Orator of Tennessee"
- Percy Howard – wide receiver for Dallas Cowboys
- Douglas S. Jackson – member of Tennessee Senate
- Cave Johnson – Congressman and U.S. Postmaster General under President James K. Polk
- Howard Johnson – football player and U.S. Marine killed in Battle of Iwo Jima
- Micah Johnson – Miami Dolphins linebacker
- Dorothy Jordan – film actress
- Joseph Buckner Killebrew – educator, lawyer, originator of liberal public school law
- Jalen Reeves-Maybin – NFL linebacker Detroit Lions
- Horace Lisenbee – MLB player, pitcher for Washington Senators
- Horace Harmon Lurton – Justice of U.S. Supreme Court
- John Hartwell Marable – member of U.S. House of Representatives
- Shawn Marion – NBA and Olympic basketball player
- Isaac Murphy – first Reconstruction-era governor of Arkansas
- Robert Loftin Newman – oil painter
- Mary C. Noble – judge of Kentucky Supreme Court
- Norris W. Overton – U.S. Air Force Brigadier General
- Wayne Pace – CFO of Time Warner
- Asahel Huntington Patch – also known as A. H. Patch, inventor of Blackhawk corn sheller
- Austin Peay – Governor of Tennessee (1922–1927); namesake of Austin Peay State University
- Thomas Minott Peters – lawyer and botanist
- Chonda Pierce – Christian comedian and performer
- Key Pittman – U.S. Senator from Nevada
- Alex Poythress – NBA & former University of Kentucky basketball player
- DJ Pryor – stand-up comedian and actor
- Jeff Purvis – NASCAR driver
- James B. Reynolds – member of U.S. House of Representatives
- Phil Roe – politician
- Mason Rudolph – professional golfer
- Wilma Rudolph – first female athlete to win three gold medals in single Olympic games
- Brenda Vineyard Runyon – founder and director of First Woman's Bank of Tennessee (1919–1926)
- Clarence Saunders – grocer, founder of Piggly Wiggly
- Evelyn Scott – writer, poet, and novelist
- Valentine Sevier – Revolutionary War soldier and brother of John Sevier (first governor of Tennessee)
- George Sherrill – baseball player
- Rachel Smith – Miss Tennessee USA and Miss USA (2007)
- Rick Stansbury – basketball coach
- Travis Stephens – football player with Tampa Bay Buccaneers
- James Storm – professional wrestler
- William "Sammy" Stuard – chairman of Tennessee Bankers Association, CEO of F&M Bank
- Pat Summitt – University of Tennessee at Knoxville women's basketball coach, Hall of Famer
- Frank Sutton – actor, played Sergeant Vince Carter in Gomer Pyle, USMC TV series
- Allen Tate – poet
- Sloan Thomas – wide receiver for Tennessee Titans
- Mageina Tovah – actress
- Jamie Walker – MLB relief pitcher
- Robert Penn Warren – poet
- Bubba Wells – APSU alumnus and NBA player
- William Westmoreland – military commander in Vietnam
- Clarence Cameron White – musician
- James "Fly" Williams – player in original American Basketball Association
- Howie Wright – NBA player
- Ryne Harper – baseball player
- Ricky Lumpkin - NFL player for the Raiders, Cardinals, and Colts. Graduated from Kenwood High School
- Scotty Kilmer - Car Mechanic and YouTube Personality
In popular culture
- The Monkees 1966 #1 song "Last Train to Clarksville" is sometimes said to reference the city's train depot and a soldier from Fort Campbell during the Vietnam War era, but Clarksville was actually picked just for its euphonious sound.[57] The band filmed parts of the song's music video in Clarksville.
- The music video for the 1986 song "Twenty Years Ago" by country singer Kenny Rogers was filmed on Franklin Street in Clarksville, Tennessee.
Nicknames
Clarksville's nicknames have included The Queen City, Queen of the Cumberland, and Gateway to the New South.[2] In April 2008, the city adopted "Tennessee's Top Spot!" as its new brand nickname.[58]
References
- Queen City Lodge #761 – Free & Accepted Masons, accessed October 11, 2008.
- Clarksville, Tennessee: Gateway to the New South Archived 2008-10-05 at the Wayback Machine, Fort Campbell website, accessed October 11, 2008.
- "Clarksville unveils new "Brand" as "Tennessee's Top Spot!"". April 12, 2008.
- "The History of Clarksville-Montgomery County". Visit Clarksville.
- "ArcGIS REST Services Directory". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved October 15, 2022.
- U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Clarksville
- "Census Population API". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved Oct 15, 2022.
- "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2008-01-31.
- "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Archived from the original on 2011-05-31. Retrieved 2011-06-07.
- "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2014-05-22.
- Clarksville, TN QuickFacts, United States Census website. Retrieved: 30 July 2018.
- "City of Clarksville (Montgomery County)". Municipal Technical Advisory Service – City Information. Retrieved February 2, 2018.
- Miller, Larry L. (2001). Tennessee place-names. Indiana University Press. p. 46. ISBN 978-0-253-33984-3.
- "Archaeology and the Native Peoples of Tennessee Archived 2008-05-09 at the Wayback Machine." University of Tennessee, Frank H. McClung Museum. Retrieved December 5, 2007.
- Satz, Ronald. Tennessee's Indian Peoples. Knoxville, TN: University of Tennessee Press, 1979; ISBN 0-87049-285-3
- Christian G. Fritz, American Sovereigns: The People and America's Constitutional Tradition Before the Civil War (Cambridge University Press, 2008) at pp. 55-60; ISBN 978-0-521-88188-3
- "Loading..." tcarden.com. Archived from the original on 2009-06-09. Retrieved 2010-06-19.
- Morgan, Robert (September 23, 2008). Boone: A Biography. Algonquin Books. p. 179 – via Internet Archive.
boone a biography algonquin bryce.
- "Lost Counties of Tennessee". Archived from the original on January 15, 2011.
- Randal Rust. "Clarksville". Tennessee Encyclopedia. Retrieved 2021-06-04.
- "Ft. Defiance Clarksville". Ft. Defiance Clarksville. Retrieved April 23, 2013.
- "Clarksville, TN • CivicEngage". www.cityofclarksville.com. Archived from the original on 2012-01-19.
- "Fort Defiance – Fort Bruce site photos". Civilwaralbum.com. Archived from the original on 2013-06-24. Retrieved 2013-07-10.
- "Terrific Fire". The Clarksville Weekly Chronicle. Clarksville, Tennessee: Ancestry.com#Newspapers.com. 15 April 1878. p. 5.
a fire broke out in a frame building at the rear of Kincannon's tin and Queensware store on Franklin Street
- "Clarksville, Her Schools, Her Churches, Her Residences. Her Live Business Men and Manufacturing Enterprises". Leaf-Chonicle Weekly. Clarksville, Tennessee: Ancestry.com#Newspapers.com. 22 December 1882. p. 1.
- "Mr Hume's "Auto" breaks down". Leaf-Chonicle Weekly. Clarksville, Tennessee: Ancestry.com#Newspapers.com. 21 May 1902. p. 1.
- "Two tornadoes damage dozens of homes in Clarksville-Montgomery County | ClarksvilleNow.com". ClarksvilleNow.com. Retrieved 2018-02-26.
- Herzmann, Daryl. "IEM :: PNS from NWS OHX". mesonet.agron.iastate.edu. Retrieved 2018-02-25.
- "Clarksville, Tennessee Köppen Climate Classification (Weatherbase)". Weatherbase. Retrieved 2019-02-20.
- "NowData – NOAA Online Weather Data". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved May 28, 2021.
- "Station: Clarksville WWTP, TN". U.S. Climate Normals 2020: U.S. Monthly Climate Normals (1991-2020). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved May 28, 2021.
- "Monthly Averages for Clarksville, TN (37043)". The Weather Channel. Retrieved December 9, 2011.
- "Clarksville (City) QuickFacts from the US Census Bureau". Archived from the original on 2013-02-20.
- "Explore Census Data". data.census.gov. Retrieved 2021-12-26.
- Clarksville, Tennessee. Money Mag Ranking. Archived 2005-09-06 at the Wayback Machine
- "Construction of Amazon distribution center in Montgomery County on schedule".
- "FedEx distribution center to open later this year, bringing 250 new jobs to Clarksville".
- Google a go: $600M Clarksville data center confirmed, theleafchronicle.com. Accessed August 27, 2022.
- The LG journey: How Clarksville landed the 600-job plant, theleafchronicle.com. Accessed August 27, 2022.
- BUCHANAN v. CITY OF JACKSON, 683 F. Supp. 1515 (W.D. Tenn. 1988), Case Text website.
- "City Council" Archived 2015-02-13 at the Wayback Machine, City of Clarksville, 2015.
- "Mayor's Office" Archived 2015-02-13 at the Wayback Machine, City of Clarksville, 2015.
- Beach, Ursula S. (1988). Jones, Robert B. (ed.). Montgomery County. Tennessee County History Series. Memphis State University Press. OCLC 6820526.

- A. Howell (February 6, 1886). "Mayor's Report". Clarksville Weekly Chronicle. Clarksville, TN. p. 5.
- Shillo, Deb. "Thomas H. Smith, Confederate War Soldier". Montgomery County War Records. Retrieved September 7, 2018.
- "Mayor Carney". Daily Tobacco Leaf-Chronicle. Clarksville, TN. January 18, 1892. p. 4.
- "Municipal Engineering". 1902.
- "Clarksville, Tennessee Mayor William D. Hudson Statue by ET Wickham". Wickham Stone Park. Retrieved September 7, 2018.
- Kestenbaum, Lawrence (ed.). "Mayors of Clarksville, Tennessee". Political Graveyard. Retrieved May 7, 2017.
- "Clarksville Home Market". 2022. Retrieved September 7, 2022.
- Mayors, United States Conference of (1983), City Problems: The Annual Proceedings of the United States Conference of Mayors, retrieved September 7, 2018
- "Booze, burley funds ignite Congress race", Nashville Banner, October 31, 1996
- Centonze, Tony (July 29, 2016). "Don Trotter: 'Partisanship' has caused worst problems in Clarksville government". The Leaf Chronicle. Clarksville, TN. Retrieved September 7, 2018.
- Settle, Jimmy (February 21, 2018). "Johnny Piper likely to seek return as Clarksville mayor in 2018". The Leaf Chronicle. Clarksville, TN. Retrieved September 7, 2018.
- "Clarksville, Tennessee Encyclopedia". Baseball-Reference. Sports Reference. Retrieved May 25, 2020.
- "Leon Henry Buck (1916-1976) •". 23 April 2022.
- "Last Train to Clarksville by The Monkees". SongFacts. Retrieved December 14, 2014.
There's a little town in Northern Arizona I used to go through in the summer on the way to Oak Creek Canyon called Clarksdale. We were throwing out names, and when we got to Clarksdale, we thought Clarksville sounded even better. We didn't know it at the time, [but] there is an Air Force base near the town of Clarksville, Tennessee – which would have fit the bill fine for the story line.
- Bobby Hart (emphasis added). - Clarksville unveils new "Brand" as "Tennessee's Top Spot!", Turner McCullough Jr., Clarksville Online, 12 April 12008.
Bibliography
- Federal News Service (May 21, 2009), Opinion No. 09-94: Tennessee Attorney General Issues Opinion on Charter of the City of Clarksville, Washington, D.C.