Desertification
Desertification is a type of land degradation in drylands in which biological productivity is lost due to natural processes or induced by human activities whereby fertile areas become increasingly arid.[2][3][4] It is the spread of arid areas caused by a variety of factors, such as climate change[5] and overexploitation of soil as a result of human activity.[6]
Throughout geological history, the development of deserts has occurred naturally. In recent times, the potential influences of human activity, improper land management, deforestation and climate change on desertification is the subject of many scientific investigations.[7][8][9]
Definitions of words
As recently as 2005, considerable controversy existed over the proper definition of the term "desertification." Helmut Geist (2005) identified more than 100 formal definitions. The most widely accepted[10] of these was that of the Princeton University Dictionary which defined it as "the process of fertile land transforming into desert typically as a result of deforestation, drought or improper/inappropriate agriculture".
However, this original understanding that desertification involved the physical expansion of deserts has been rejected as the concept has evolved.[11] Desertification has been defined in the text of the United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD) as "land degradation in arid, semi-arid and dry sub-humid regions resulting from various factors, including climatic variations and human activities."[12]
There exists also controversy around the sub-grouping of types of desertification, including, for example, the validity and usefulness of such terms as "man-made desert" and "non-pattern desert".[13]
History
The world's most noted deserts have been formed by natural processes interacting over long intervals of time. During most of these times, deserts have grown and shrunk independently of human activities. Paleodeserts are large sand seas now inactive because they are stabilized by vegetation, some extending beyond the present margins of core deserts, such as the Sahara, the largest hot desert.[14]
Historical evidence shows that the serious and extensive land deterioration occurring several centuries ago in arid regions had three centers: the Mediterranean, the Mesopotamian Valley, and the Loess Plateau of China, where population was dense.[15][16]
The earliest known discussion of the topic arose soon after the French colonization of West Africa, when the Comité d'Etudes commissioned a study on desséchement progressif to explore the prehistoric expansion of the Sahara Desert.[17] The modern study of desertification emerged from the study of the 1980s drought in the Sahel.[18]
Areas affected
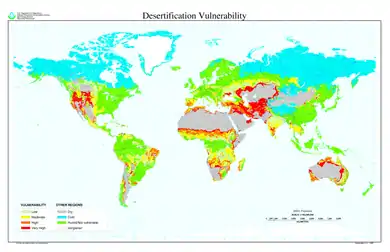
.jpg.webp)
Drylands occupy approximately 40–41% of Earth's land area[20][21] and are home to more than 2 billion people.[21] It has been estimated that some 10–20% of drylands are already degraded, the total area affected by desertification being between 6 and 12 million square kilometres, that about 1–6% of the inhabitants of drylands live in desertified areas, and that a billion people are under threat from further desertification.[22][23]
Sahel
The impact of global warming and human activities are presented in the Sahel. In this area the level of desertification is very high compared to other areas in the world. All areas situated in the eastern part of Africa (i.e. in the Sahel region) are characterized by a dry climate, hot temperatures, and low rainfall (300–750 mm rainfall per year). So, droughts are the rule in the Sahel region.[24] Some studies have shown that Africa has lost approximately 650,000 km2 of its productive agricultural land over the past 50 years; the propagation of desertification in this area is considerable.[25][26]

The climate of the Sahara has undergone enormous variations over the last few hundred thousand years,[27] oscillating between wet (grassland) and dry (desert) every 20,000 years[28] (a phenomenon believed to be caused by long-term changes in the North African climate cycle that alters the path of the North African Monsoon, caused by an approximately 40000-year cycle in which the axial tilt of the earth changes between 22° and 24.5°).[29] Some statistics have shown that, since 1900, the Sahara has expanded by 250 km to the south over a stretch of land from west to east 6,000 km long.[30][31] The survey, done by the Research Institute for Development, had demonstrated that this means dryness is spreading fast in the Sahelian countries. 70% of the arid area has deteriorated and water resources have disappeared, leading to soil degradation. The loss of topsoil means that plants cannot take root firmly and can be uprooted by torrential water or strong winds.[32]
The United Nations Convention (UNC) says that about six million Sahelian citizens would have to leave the desertified zones of sub-Saharan Africa for North Africa and Europe between 1997 and 2020.[32]
Lake Chad, located in the Sahel region, has been hit particularly hard by this phenomenon. The cause of the lake drying up is due to irrigation withdrawal and the annual rainfall decreasing.[33] The lake has shrunk by over 90% since 1987, displacing millions of inhabitants. Recent efforts have managed to make some progress toward its restoration, but it is still considered to be at risk of disappearing entirely.[34][1]
Gobi Desert
Another major area that is being impacted by desertification is the Gobi Desert. The Gobi Desert is the fastest expanding desert on Earth, as it transforms over 3,600 square kilometres (1,400 square miles) of grasslands into wasteland annually. [35] Although the Gobi Desert itself is still a distance away from Beijing, reports from field studies state there are large sand dunes forming only 70 km (43.5 mi) outside the city.[36][37]
Mongolia
In Mongolia, around 90% of grassland is considered vulnerable to desertification by the UN. An estimated 13% of desertification in Mongolia is caused by natural factors; the rest is due to human influence particularly overgrazing and increased erosion of soils in cultivated areas.[38][39] The area of Mongolian land covered by sand has increased by 8.7% over the last 40 years. These changes have accompanied the degradation of 70% of Mongolian pasture land.[40] As well as overgrazing and climate change, the Mongolia government listed forest fires, blights, unsustainable forestry and mining activities as leading causes of desertification in the country.[41] A more recent study also reports overgrazing as a leading cause of desertification as well as the transition from sheep to goat farming in order to meet export demands for cashmere wool. Compared to sheep, goats do more damage to grazing lands by eating roots and flowers.[42]
South America
South America is another area vulnerable by desertification, as 25% of the land is classified as drylands.[43][44] In Argentina specifically, drylands represent more than half of the total land area, and desertification has the potential to disrupt the nation's food supply.[45]
Effects
Sand and dust storms

There has been a 25% increase in global annual dust emissions between the late nineteenth century to present day.[46] The increase of desertification has also increased the amount of loose sand and dust that the wind can pick up ultimately resulting in a storm. For example, dust storms in the Middle East “are becoming more frequent and intense in recent years” because “long-term reductions in rainfall promot[ing] lower soil moisture and vegetative cover”.[47]
Dust storms can contribute to certain respiratory disorders such as pneumonia, skin irritations, asthma and many more.[48] They can pollute open water, reduce the effectiveness of clean energy efforts, and halt most forms of transportation.
Dust and sand storms can have a negative effect on the climate which can make desertification worse.[49][50] Dust particles in the air scatter incoming radiation from the sun. The dust can provide momentary coverage for the ground temperature but the atmospheric temperature will increase. This can disform and shorten the life time of clouds which can result in less rainfall.[51]
Food security
Global food security is being threatened by desertification and overpopulation. The more the population grows, the more food that has to be grown. The agricultural business is being displaced from one country to another. For example, Europe on average imports over 50% of its food. Meanwhile, 44% of agricultural land is located in dry lands and it supplies 60% of the world's food production. Desertification is decreasing the amount of sustainable land for agricultural uses but demands are continuously growing. In the near future, the demands will overcome the supply.[52] The violent herder–farmer conflicts in Nigeria, Sudan, Mali and other countries in the Sahel region have been exacerbated by climate change, land degradation and population growth.[53][54][55]
Vegetation patterning
As the desertification takes place, the landscape may progress through different stages and continuously transform in appearance. On gradually sloped terrain, desertification can create increasingly larger empty spaces over a large strip of land, a phenomenon known as "brousse tigrée". A mathematical model of this phenomenon proposed by C. Klausmeier attributes this patterning to dynamics in plant-water interaction.[56] One outcome of this observation suggests an optimal planting strategy for agriculture in arid environments.[57]
Causes

The immediate cause is the loss of most vegetation. This is driven by a number of factors, alone or in combination, such as drought, climatic shifts, tillage for agriculture, overgrazing and deforestation for fuel or construction materials. Though Vegetation plays a major role in determining the biological composition of the soil. Studies have shown that, in many environments, the rate of erosion and runoff decreases exponentially with increased vegetation cover.[60] Unprotected, dry soil surfaces blow away with the wind or are washed away by flash floods, leaving infertile lower soil layers that bake in the sun and become an unproductive hardpan.
Early studies argued one of the most common causes of desertification was overgrazing, over consumption of vegetation by cattle or other livestock.[61] However, the role of local overexploitation in driving desertification in the recent past is controversial.[18] Drought in the Sahel region is now thought to be principally the result of large scale sea surface temperature variations, largely driven by natural variability and the effect of industrial pollutants.[62] As a result, changing ocean temperature and reductions in sulfate emissions have caused a re-greening of the region.[62] This has led some scholars to argue that agriculture-induced vegetation loss is a minor factor in desertification.[18]
Scientists agree that the existence of a desert in the place where the Sahara desert is now located is due to natural variations in solar insolation due to orbital precession of the Earth.[63] Such variations influence the strength of the West African Monsoon, inducing feedback in vegetation and dust emission that amplify the cycle of wet and dry Sahara climate.[64] There is a suggestion the transition of the Sahara from savanna to desert during the mid-Holocene was partially due to overgrazing by the cattle of the local population.[65]
Overpopulation is one of the most dangerous factors contributing to desertification.[66] Human populations are increasing at exponential rates, which leads to overgrazing, over-farming and deforestation, as previously acceptable techniques are becoming less sustainable.[67]
There are multiple reasons farmers use intensive farming as opposed to extensive farming but the main reason is to maximize yields.[51] By increasing productivity, they require a lot more fertilizer, pesticides, and labor to upkeep machinery. This continuous use of the land rapidly depletes the nutrients of the soil causing desertification to spread.[68][69]
Poverty
At least 90% of the inhabitants of drylands live in developing countries, where they also suffer from poor economic and social conditions.[22] This situation is exacerbated by land degradation because of the reduction in productivity, the precariousness of living conditions and the difficulty of access to resources and opportunities.[70]
A downward spiral is created in many underdeveloped countries by overgrazing, land exhaustion and overdrafting of groundwater in many of the marginally productive world regions due to overpopulation pressures to exploit marginal drylands for farming. Decision-makers are understandably averse to invest in arid zones with low potential. This absence of investment contributes to the marginalisation of these zones. When unfavourable agro-climatic conditions are combined with an absence of infrastructure and access to markets, as well as poorly adapted production techniques and an underfed and undereducated population, most such zones are excluded from development.[71]
Desertification often causes rural lands to become unable to support the same sized populations that previously lived there. This results in mass migrations out of rural areas and into urban areas (urbanisation), particularly in Africa. These migrations into the cities often cause large numbers of unemployed people, who end up living in slums.[72][73]
In Mongolia the land is 90% fragile dry land, which causes many herders to migrate to the city for work. With very limited resources the herders that stay in the dry land graze very carefully in order to preserve the land. With the increasing population of Mongolia it is very difficult to stay a herder for long.[74]
The number of these environmental refugees grows every year, with projections for sub-Saharan Africa showing a probable increase from 14 million in 2010 to nearly 200 million by 2050. This presents a future crisis for the region, as neighboring nations do not always have the ability to support large populations of refugees.[75][76]
Agriculture is a main source of income for many desert communities. The increase in desertification in these regions has degraded the land to such an extent where people can no longer productively farm and make a profit. This has negatively impacted the economy and increased poverty rates.[77]
There is however increased global advocacy to combat desertification and restore affected lands such as the United Nations Sustainable Development Goal 15[78] amongst other countermeasures.
Countermeasures


Techniques and countermeasures exist for mitigating or reversing the effects of desertification, and some possess varying levels of difficulty. For some, there are numerous barriers to their implementation. Yet for others, the solution simply requires the exercise of human reason.
One proposed barrier is that the costs of adopting sustainable agricultural practices sometimes exceed the benefits for individual farmers, even while they are socially and environmentally beneficial.[80] Another issue is a lack of political will, and lack of funding to support land reclamation and anti-desertification programs.[81]
Desertification is recognized as a major threat to biodiversity. Some countries have developed biodiversity action plans to counter its effects, particularly in relation to the protection of endangered flora and fauna.[82][83]
Reforestation
Reforestation gets at one of the root causes of desertification and is not just a treatment of the symptoms. Environmental organizations[84] work in places where deforestation and desertification are contributing to extreme poverty. There they focus primarily on educating the local population about the dangers of deforestation and sometimes employ them to grow seedlings, which they transfer to severely deforested areas during the rainy season.[85] The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations launched the FAO Drylands Restoration Initiative in 2012 to draw together knowledge and experience on dryland restoration.[86] In 2015, FAO published global guidelines for the restoration of degraded forests and landscapes in drylands, in collaboration with the Turkish Ministry of Forestry and Water Affairs and the Turkish Cooperation and Coordination Agency.[87]
The "Green Wall of China" is a high-profile example of one method that has been finding success in this battle with desertification.[88] This wall is a much larger-scale version of what American farmers did in the 1930s to stop the great Midwest dust bowl. This plan was proposed in the late 1970s, and has become a major ecological engineering project that is not predicted to end until the year 2055. According to Chinese reports, there have been nearly 66 billion trees planted in China's great green wall.[89] The green wall of China has decreased desert land in China by an annual average of 1,980 square km.[90] The frequency of sandstorms nationwide have fallen 20% due to the green wall.[91] Due to the success that China has been finding in stopping the spread of desertification, plans are currently being made in Africa to start a "wall" along the borders of the Sahara desert as well to be financed by the United Nations Global Environment Facility trust.[92]
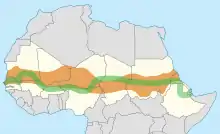
In 2007 the African Union started the Great Green Wall of Africa project in order to combat desertification in 20 countries.[94] The wall is 8,000 km wide, stretching across the entire width of the continent and has 8 billion dollars in support of the project. The project has restored 36 million hectares of land, and by 2030 the initiative plans to restore a total of 100 million hectares.[95] The Great Green Wall has created many job opportunities for the participating countries, with over 20,000 jobs created in Nigeria alone.[96]
Soil restoration
Techniques focus on two aspects: provisioning of water, and fixation and hyper-fertilizing soil. Fixating the soil is often done through the use of shelter belts, woodlots and windbreaks. Windbreaks are made from trees and bushes and are used to reduce soil erosion and evapotranspiration.[97] They were widely encouraged by development agencies from the middle of the 1980s in the Sahel area of Africa.
Some soils (for example, clay), due to lack of water can become consolidated rather than porous (as in the case of sandy soils). Some techniques as zaï or tillage are then used to still allow the planting of crops.[98] Waffle gardens can also help as they can provide protection of the plants against wind/sandblasting, and increase the hours of shade falling on the plant.[99]
Another technique that is useful is contour trenching. This involves the digging of 150 m long, 1 m deep trenches in the soil. The trenches are made parallel to the height lines of the landscape, preventing the water from flowing within the trenches and causing erosion. Stone walls are placed around the trenches to prevent the trenches from closing up again. The method was invented by Peter Westerveld.[100]
Enriching of the soil and restoration of its fertility is often achieved by plants. Of these, leguminous plants which extract nitrogen from the air and fix it in the soil, succulents (such as Opuntia),[101] and food crops/trees as grains, barley, beans and dates are the most important. Sand fences can also be used to control drifting of soil and sand erosion.[102]
Another way to restore soil fertility is through the use of nitrogen-rich fertilizer. Due to the higher cost of this fertilizer, many smallholder farmers are reluctant to use it, especially in areas where subsistence farming is common.[103] Several nations, including India, Zambia, and Malawi have responded to this by implementing subsidies to help encourage adoption of this technique.[104]
Some research centres (such as Bel-Air Research Center IRD/ISRA/UCAD) are also experimenting with the inoculation of tree species with mycorrhiza in arid zones. The mycorrhiza are basically fungi attaching themselves to the roots of the plants. They hereby create a symbiotic relation with the trees, increasing the surface area of the tree's roots greatly (allowing the tree to gather much more nutrient from the soil).[105]
The bioengineering of soil microbes, particularly photosynthesizers, has also been suggested and theoretically modeled as a method to protect drylands. The aim would be to enhance the existing cooperative loops between soil microbes and vegetation.[106]
Desert reclamation
As there are many different types of deserts, there are also different types of desert reclamation methodologies. An example for this is the salt flats in the Rub' al Khali desert in Saudi Arabia. These salt flats are one of the most promising desert areas for seawater agriculture and could be revitalized without the use of freshwater or much energy.[107]
Farmer-managed natural regeneration (FMNR) is another technique that has produced successful results for desert reclamation. Since 1980, this method to reforest degraded landscape has been applied with some success in Niger. This simple and low-cost method has enabled farmers to regenerate some 30,000 square kilometers in Niger. The process involves enabling native sprouting tree growth through selective pruning of shrub shoots. The residue from pruned trees can be used to provide mulching for fields thus increasing soil water retention and reducing evaporation. Additionally, properly spaced and pruned trees can increase crop yields. The Humbo Assisted Regeneration Project which uses FMNR techniques in Ethiopia has received money from The World Bank's BioCarbon Fund, which supports projects that sequester or conserve carbon in forests or agricultural ecosystems.[108]
Managed grazing
Restoring grasslands store CO2 from the air as plant material. Grazing livestock, usually not left to wander, eat the grass and minimize grass growth.[109] A method proposed to restore grasslands uses fences with many small paddocks and moving herds from one paddock to another after a day or two in order to mimic natural grazers and allowing the grass to grow optimally.[109][110][111] Proponents of managed grazing methods estimate that increasing this method could increase carbon content of the soils in the world's 3.5 billion hectares of agricultural grassland and offset nearly 12 years of CO2 emissions.[109]
One proponent of managed grazing, Allan Savory, as part of holistic management, claims that keeping livestock tightly packed on smaller plots of land, meanwhile rotating them to other small plots of land will reverse desertification;[112] range scientists have however not been able to experimentally confirm his claims.[113][114][115][116][117][118][119]
See also

- Aridification
- Deforestation
- Detention basin
- Soil retrogression and degradation
- Wadi
- Water scarcity
- World Day to Combat Desertification and Drought
Mitigation:
- Desert greening
- Ecological engineering
- Oasification
Other related portals:
References
- Onamuti, Olapeju Y.; Okogbue, Emmanuel C.; Orimoloye, Israel R. (8 November 2017). "Remote sensing appraisal of Lake Chad shrinkage connotes severe impacts on green economics and socio-economics of the catchment area". Royal Society Open Science. 4 (11): 171120. doi:10.1098/rsos.171120. PMC 5717671. PMID 29291097.
- Rafferty, John P.; Pimm, Stuart L. (2019). "Desertification.". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 2019-11-06.
the process by which natural or human causes reduce the biological productivity of drylands (arid and semiarid lands). ... The concept does not refer to the physical expansion of existing deserts but rather to the various processes that threaten all dryland ecosystems.
- "Desertification - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics". www.sciencedirect.com. Retrieved 2022-04-03.
- "desertification | Description, Causes, & Impacts | Britannica". www.britannica.com. Retrieved 2022-04-03.
- Zeng, Ning; Yoon, Jinho (1 September 2009). "Expansion of the world's deserts due to vegetation-albedo feedback under global warming". Geophysical Research Letters. 36 (17): L17401. Bibcode:2009GeoRL..3617401Z. doi:10.1029/2009GL039699. ISSN 1944-8007. S2CID 1708267.
- "Sustainable development of drylands and combating desertification". Retrieved 21 June 2016.
- Liu, Ye; Xue, Yongkang (5 March 2020). "Expansion of the Sahara Desert and shrinking of frozen land of the Arctic". Scientific Reports. 10 (1): 4109. Bibcode:2020NatSR..10.4109L. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-61085-0. PMC 7057959. PMID 32139761.
- An, Hui; Tang, Zhuangsheng; Keesstra, Saskia; Shangguan, Zhouping (1 July 2019). "Impact of desertification on soil and plant nutrient stoichiometry in a desert grassland". Scientific Reports. 9 (1): 9422. Bibcode:2019NatSR...9.9422A. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-45927-0. PMC 6603008. PMID 31263198.
- Han, Xueying; Jia, Guangpu; Yang, Guang; Wang, Ning; Liu, Feng; Chen, Haoyu; Guo, Xinyu; Yang, Wenbin; Liu, Jing (10 December 2020). "Spatiotemporal dynamic evolution and driving factors of desertification in the Mu Us Sandy Land in 30 years". Scientific Reports. 10 (1): 21734. Bibcode:2020NatSR..1021734H. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-78665-9. PMC 7729393. PMID 33303886.
- Geist (2005), p. 2
- Rafferty, John P.; Pimm, Stuart L. (2019). "Desertification". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 2019-11-06.
The concept does not refer to the physical expansion of existing deserts but rather to the various processes that threaten all dryland ecosystems.
- "Part I". Archived from the original on 7 June 2016. Retrieved 21 June 2016.
- Helmut J. Geist, and Eric F. Lambin. "Dynamic Causal Patterns of Desertification." BioScience 54.9 (2004): 817 . Web.
- United States Geological Survey, "Desertification", 1997
- LOWDERMILK, W C. "CONQUEST OF THE LAND THROUGH SEVEN THOUSAND YEARS" (PDF). Soil Conservation Service. United States Department of Agriculture. Retrieved 9 April 2014.
- Dregne, H.E. "Desertification of Arid Lands". Columbia University. Retrieved 3 December 2013.
- Mortimore, Michael (1989). Adapting to drought: farmers, famines, and desertification in West Africa. Cambridge University Press. p. 12. ISBN 978-0-521-32312-3.
- The End of Desertification?. Springer Earth System Sciences. 2016. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-16014-1. ISBN 978-3-642-16013-4. S2CID 132424053.
- "Sun, Moon and Telescopes above the Desert". ESO Picture of the Week. Retrieved 30 April 2012.
- Bauer (2007), p. 78
- Johnson et al (2006), p. 1
- "UNCCD: Impact and role of drylands". UNCCD. 10 October 2017. Retrieved 7 November 2019.
- World Bank (2009). Gender in agriculture sourcebook. World Bank Publications. p. 454. ISBN 978-0-8213-7587-7.
- Riebeek, Holli (2007-01-03). "Defining Desertification : Feature Articles". earthobservatory.nasa.gov. Retrieved 2016-11-30.
- Nicholson, S. E.; Tucker, C. J.; Ba, M. B. (1 May 1998). "Desertification, Drought, and Surface Vegetation: An Example from the West African Sahel". Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society. 79 (5): 815–830. Bibcode:1998BAMS...79..815N. doi:10.1175/1520-0477(1998)079<0815:DDASVA>2.0.CO;2.
- "Land Resource Stresses and Desertification in Africa". United States Department of Agriculture. Retrieved 24 November 2020.
- Kevin White; David J. Mattingly (2006). "Ancient Lakes of the Sahara". American Scientist. 94 (1): 58–65. doi:10.1511/2006.57.983.
- Jennifer Chu (January 2, 2019). "A "pacemaker" for North African climate". MIT News. Retrieved January 20, 2020.
- Houérou, Henry N. (2008-12-10). Bioclimatology and Biogeography of Africa. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 978-3-540-85192-9.
- Christian Bouquet (December 2017). "Le Sahara entre ses deux rives. Éléments de délimitation par la géohistoire d'un espace de contraintes". Géoconfluences.
Mais il aurait progressé de 250 km vers le sud depuis 1900 (Mainguet, 2003), et dépasserait donc 9 millions de km² soit 30 % de la superficie totale du continent africain.
- Mainguet, Monique (2003). Les pays secs: environnement et développement. Ellipses.
- "United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification: Issues and Challenges". E-International Relations. 30 April 2014. Retrieved 2016-11-30.
- Okpara, Uche T.; Stringer, Lindsay C.; Dougill, Andrew J. (November 2016). "Lake drying and livelihood dynamics in Lake Chad: Unravelling the mechanisms, contexts and responses". Ambio. 45 (7): 781–795. doi:10.1007/s13280-016-0805-6. PMC 5055484. PMID 27371137.
- Mohamed, Dounia Ben (December 2015). "New Urgency in Battle to Halt Spread of Desertification". New African. 556 – via Gale Academic OneFile Select.
- Rechtschaffen, Daniel. "How China's Growing Deserts Are Choking The Country". Forbes. Retrieved 2022-08-28.
- Welker, Lauren (2009). The Desertification of the Gobi Desert and Its Effect on Beijing (PDF) (Unpublished manuscript). University of Texas-Austin School of Geosciences.
- "Gobi Desert: A Complete Guide to East Asia's Largest Desert". Young Pioneer Tours. 2020-03-25. Retrieved 2022-04-03.
- "What Is Desertification and How Does It Impact Mongolia?". Breathe Mongolia – English. Retrieved 2022-04-03.
- Han, Jie; Dai, Han; Gu, Zhaolin (2021-12-01). "Sandstorms and desertification in Mongolia, an example of future climate events: a review". Environmental Chemistry Letters. 19 (6): 4063–4073. doi:10.1007/s10311-021-01285-w. ISSN 1610-3661. PMC 8302971. PMID 34335128.
- Mongolia : state of the environment, 2002 (PDF). United Nations Environment Programme. Pathumthani, Thailand: United Nations Environment Programme. 2001. ISBN 92-807-2145-3. OCLC 63522565.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: others (link) - "Report on the State of the Environment of Mongolia, 2008-2010" (PDF). Ministry of Nature Environment and Tourism. Retrieved 2020-06-17.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - Dorj, O.; Enkhbold, M.; Lkhamyanjin, S.; Mijiddorj, Kh.; Nosmoo, A.; Puntsagnamil, M.; Sainjargal, U. (2013), Heshmati, G. Ali; Squires, Victor R. (eds.), "Mongolia: Country Features, the Main Causes of Desertification and Remediation Efforts", Combating Desertification in Asia, Africa and the Middle East, Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands, pp. 217–229, doi:10.1007/978-94-007-6652-5_11, ISBN 978-94-007-6651-8
- June 15; Herrera, 2018 Carolina. "Why We Should Invest in Land Management in Latin America". NRDC. Retrieved 2022-04-03.
- "Soil Degradation Threatens Nutrition in Latin America - World". ReliefWeb. Retrieved 2022-04-03.
- Torres, Laura; Abraham, Elena M.; Rubio, Clara; Barbero‐Sierra, Celia; Ruiz-Pérez, Manuel (7 July 2015). "Desertification Research in Argentina". Land Degradation & Development. 26 (5): 433–440. doi:10.1002/ldr.2392. S2CID 129476957.
- Stanelle, Tanja; Bey, Isabelle; Raddatz, Thomas; Reick, Christian; Tegen, Ina (2014-12-16). "Anthropogenically induced changes in twentieth century mineral dust burden and the associated impact on radiative forcing". Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres. 119 (23): 13, 526–13, 546. Bibcode:2014JGRD..11913526S. doi:10.1002/2014JD022062. hdl:11858/00-001M-0000-0024-A9A2-C. S2CID 128663108.
- Namdari, Soodabeh; Karimi, Neamat; Sorooshian, Armin; Mohammadi, GholamHasan; Sehatkashani, Saviz (2018-01-01). "Impacts of climate and synoptic fluctuations on dust storm activity over the Middle East". Atmospheric Environment. 173: 265–276. Bibcode:2018AtmEn.173..265N. doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2017.11.016. ISSN 1352-2310. PMC 6192056. PMID 30344444.
- Goudie, Andrew S. (2014-02-01). "Desert dust and human health disorders". Environment International. 63: 101–113. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2013.10.011. ISSN 0160-4120. PMID 24275707.
- Hu, Tiantian; Wu, Di; Li, Yaohui; Wang, Chenghai (2017-03-28). "The Effects of Sandstorms on the Climate of Northwestern China". Advances in Meteorology. 2017: e4035609. doi:10.1155/2017/4035609. ISSN 1687-9309.
- Wu, Yao; Wen, Bo; Li, Shanshan; Guo, Yuming (2021-06-01). "Sand and dust storms in Asia: a call for global cooperation on climate change". The Lancet Planetary Health. 5 (6): e329–e330. doi:10.1016/S2542-5196(21)00082-6. ISSN 2542-5196. PMID 33915087. S2CID 233460168.
- "Explainer: Desertification and the role of climate change". Carbon Brief. 2019-08-06. Retrieved 2019-10-22.
- "WAD | World Atlas of Desertification". wad.jrc.ec.europa.eu. Retrieved 2019-11-19.
- "How Climate Change Is Spurring Land Conflict in Nigeria". Time. 28 June 2018.
- "The battle on the frontline of climate change in Mali". BBC News. 22 January 2019.
- "Farmer-Herder Conflicts on the Rise in Africa". ReliefWeb. 6 August 2018.
- Klausmeier, Christopher (1999). "Regular and irregular patterns in semiarid vegetation". Science. 284 (5421): 1826–1828. doi:10.1126/science.284.5421.1826. PMID 10364553.
- (www.dw.com), Deutsche Welle. "Grid of straw squares turns Chinese sand to soil – Environment – DW.COM – 23.06.2011". Retrieved 21 June 2016.
- Laduke, Winona (1999). All Our Relations: Native Struggles for Land and Life. Cambridge, MA: South End Press. p. 146. ISBN 978-0896085992. Retrieved 30 March 2015.
- Duval, Clay. "Bison Conservation: Saving an Ecologically and Culturally Keystone Species" (PDF). Duke University. Archived from the original (PDF) on March 8, 2012. Retrieved April 13, 2015.
- Geeson, Nichola; et al. (2002). Mediterranean desertification: a mosaic of processes and responses. John Wiley & Sons. p. 58. ISBN 978-0-470-84448-9.
- Charney, J. G. (April 1975). "Dynamics of deserts and drought in the Sahel". Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society. 101 (428): 193–202. Bibcode:1975QJRMS.101..193C. doi:10.1002/qj.49710142802.
- Biasutti, Michela (July 2019). "Rainfall trends in the African Sahel: Characteristics, processes, and causes". WIREs Climate Change. 10 (4): e591. doi:10.1002/wcc.591. ISSN 1757-7780. PMC 6617823. PMID 31341517.
- Tierney, Jessica E.; Pausata, Francesco S. R.; deMenocal, Peter B. (2017-01-06). "Rainfall regimes of the Green Sahara". Science Advances. 3 (1): e1601503. Bibcode:2017SciA....3E1503T. doi:10.1126/sciadv.1601503. ISSN 2375-2548. PMC 5242556. PMID 28116352.
- Pausata, Francesco S. R.; Messori, Gabriele; Zhang, Qiong (2016-01-15). "Impacts of dust reduction on the northward expansion of the African monsoon during the Green Sahara period". Earth and Planetary Science Letters. 434: 298–307. Bibcode:2016E&PSL.434..298P. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2015.11.049. ISSN 0012-821X.
- K. Wright, David; Rull, Valenti; Roberts, Richard; Marchant, Rob; Gil-Romera, Graciela (26 January 2017). "Humans as Agents in the Termination of the African Humid Period". Frontiers in Earth Science. 5: 4. Bibcode:2017FrEaS...5....4W. doi:10.3389/feart.2017.00004.
- "Causes and Effects of Desertification | Greentumble". 2019-04-29. Retrieved 2022-02-27.
- Epule, Terence Epule; Peng, Changhui; Lepage, Laurent (February 2015). "Environmental refugees in sub-Saharan Africa: a review of perspectives on the trends, causes, challenges and way forward". GeoJournal. 80 (1): 79–92. doi:10.1007/s10708-014-9528-z. ISSN 0343-2521. S2CID 154503204.
- "World Day to Combat Desertification and Drought, 17 June". www.un.org. Retrieved 2019-11-19.
- "Intensive agriculture". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 2019-11-19.
- Dobie, Ph. 2001. “Poverty and the drylands”, in Global Drylands Imperative, Challenge paper, Undp, Nairobi (Kenya) 16 p.
- Cornet A., 2002. Desertification and its relationship to the environment and development: a problem that affects us all. In: Ministère des Affaires étrangères/adpf, Johannesburg. World Summit on Sustainable Development. 2002. What is at stake? The contribution of scientists to the debate: 91–125.. Archived 2009-08-09 at the Wayback Machine
- Pasternak, Dov; Schlissel, Arnold (2001). Combating desertification with plants. Springer. p. 20. ISBN 978-0-306-46632-8.
- Briassoulis, Helen (2005). Policy integration for complex environmental problems: the example of Mediterranean desertification. Ashgate Publishing. p. 161. ISBN 978-0-7546-4243-5.
- Gillet, Kit (April 2011). "A way of life in crisis: on the sparsely inhabited steppes of Mongolia, the lifestyle of the nomadic herder has always been a hard one. But as livestock die in their millions during the increasingly frequent bitter winters, and pasturelands disappear due to overgrazing and desertification, this traditional culture is struggling to survive". Circle Publishing Ltd.
- Myers, Norman (29 April 2002). "Environmental refugees: a growing phenomenon of the 21st century". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B: Biological Sciences. 357 (1420): 609–613. doi:10.1098/rstb.2001.0953. PMC 1692964. PMID 12028796.
- Epule, Terence Epule; Peng, Changhui; Lepage, Laurent (5 February 2014). "Environmental refugees in sub-Saharan Africa: a review of perspectives on the trends, causes, challenges and way forward". GeoJournal. 80: 79–92. doi:10.1007/s10708-014-9528-z. S2CID 154503204.
- Stringer, Lindsay C.; Dyer, Jen C.; Reed, Mark S.; Dougill, Andrew J.; Twyman, Chasca; Mkwambisi, David (2009). "Adaptations to climate change, drought and desertification: local insights to enhance policy in southern Africa". Environmental Science & Policy. 12 (7): 748–765. doi:10.1016/j.envsci.2009.04.002.
- "Goal 15 targets". UNDP. Retrieved 2020-09-24.
- Pasternak, D.; Schlissel, Arnold (2012-12-06). Combating Desertification with Plants. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 38. ISBN 9781461513278.
- Drost, Daniel; Long, Gilbert; Wilson, David; Miller, Bruce; Campbell, William (1 December 1996). "Barriers to Adopting Sustainable Agricultural Practices". Journal of Extension. 34 (6). Archived from the original on 22 February 2017. Retrieved 21 February 2017.
- Briassoulis, Helen (2005). Policy integration for complex environmental problems: the example of Mediterranean desertification. Ashgate Publishing. p. 237. ISBN 978-0-7546-4243-5.
- Techniques for Desert Reclamation by Andrew S. Goudie
- Desert reclamation projects Archived 2009-01-03 at the Wayback Machine
- For example, Eden Reforestation Projects website, on Vimeo, on Eden Reforestation Projects on YouTube.
- "Desertification". USGS. 1997.
- "Drylands Restoration Initiative". Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Retrieved 14 April 2016.
- Global guidelines for the restoration of degraded forests and landscapes in drylands (PDF). Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. June 2015. ISBN 978-92-5-108912-5.
- "desertification 3D environment".
- "China's 'Great Green Wall' Fights Expanding Desert". 2017-04-21.
- Hui, Lu (May 26, 2018). "Across China: A guardian of the great green wall against China's second largest desert". Xinghua News Agency. Archived from the original on May 26, 2018.
- Beiser, Vince (September 1, 2017). "A tree grows in China: can a "Green Great Wall" stop sand from devouring the countryside?". Mother Jones. 83 (4).
- Gadzama, Njidda Mamadu (2017). "Attenuation of the effects of desertification through sustainable development of Great Green Wall in the Sahel of Africa". World Journal of Science, Technology and Sustainable Development. 14 (4): 279–289. doi:10.1108/WJSTSD-02-2016-0021.
- Jonathan Watts (7 September 2020). "Africa's Great Green Wall just 4% complete halfway through schedule". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077 – via www.theguardian.com.
- "Great Green Wall|Action Against Desertification|Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations". www.fao.org. Retrieved 2022-02-27.
- Gadzama, Njidda (2017). "Attenuation of the Effects of Desertification through Sustainable Development of Great Green Wall in the Sahel of Africa". World Journal of Science, Technology and Sustainable Development. 14 (4): 279–289. doi:10.1108/WJSTSD-02-2016-0021.
- United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (2019). "The Great Green Wall Initiative". United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification. Retrieved 2019-12-03.
- "Windbreaks - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics". www.sciencedirect.com. Retrieved 2022-02-27.
- "Our Good Earth – National Geographic Magazine". Retrieved 21 June 2016.
- "Grow Vegetables in the Desert With a 'Waffle Garden'". 3 August 2016.
- "Home – Justdiggit". Archived from the original on 2 April 2016. Retrieved 21 June 2016.
- Nefzaoui, Ali (30 January 2014). "Cactus as a Tool to Mitigate Drought and to Combat Desertification". Journal of Arid Land Studies. 24 (1): 121–124. hdl:20.500.11766/7319.
- List of plants to halt desertification; some of which may be soil-fixating Archived 2011-02-01 at the Wayback Machine
- Krah, Kwabena; Michelson, Hope; Perge, Emilie; Jindal, Rohit (1 December 2019). "Constraints to adopting soil fertility management practices in Malawi: A choice experiment approach". World Development. 124: 104651. doi:10.1016/j.worlddev.2019.104651. S2CID 202302505.
- Duflo, Esther; Kremer, Michael; Robinson, Jonathan (October 2011). "Nudging Farmers to Use Fertilizer: Theory and Experimental Evidence from Kenya" (PDF). American Economic Review. 101 (6): 2350–2390. doi:10.1257/aer.101.6.2350. hdl:1721.1/63964.
- "Département Biologie Végétale – Laboratoire Commun de Microbiologie IRD-ISRA-UCAD". Archived from the original on 24 June 2016. Retrieved 21 June 2016.
- "Bioengineered soil microbes may help prevent desertification". phys.org. Retrieved 2020-08-26.
- Rethinking landscapes, Nicol-André Berdellé July 2011 H2O magazine
- "Sprouting Trees From the Underground Forest — A Simple Way to Fight Desertification and Climate Change – Water Matters – State of the Planet". Blogs.ei.columbia.edu. 2011-10-18. Retrieved 2012-08-11.
- "How fences could save the planet". newstatesman.com. January 13, 2011. Retrieved May 5, 2013.
- "Restoring soil carbon can reverse global warming, desertification and biodiversity". mongabay.com. February 21, 2008. Archived from the original on June 25, 2013. Retrieved May 5, 2013.
- Abend, Lisa (January 25, 2010). "How eating grass-fed beef could help fight climate change". time.com. Archived from the original on January 17, 2010. Retrieved May 11, 2013.
- "How cows could repair the world". nationalgeographic.com. March 6, 2013. Retrieved May 5, 2013.
- Briske, D.D.; Sayre, Nathan F.; Huntsinger, L.; Fernandez-Gimenez, M.; Budd, B.; Derner, J.D. (July 2011). "Origin, Persistence, and Resolution of the Rotational Grazing Debate: Integrating Human Dimensions Into Rangeland Research". Rangeland Ecology & Management. 64 (4): 325–334. doi:10.2111/REM-D-10-00084.1. hdl:10150/642874. S2CID 17085968.
- Briske, D.D.; Derner, J.D.; Brown, J.R.; Fuhlendorf, S.D.; Teague, W.R.; Havstad, K.M.; Gillen, R.L.; Ash, A.J.; Willms, W.D. (January 2008). "Rotational Grazing on Rangelands: Reconciliation of Perception and Experimental Evidence". Rangeland Ecology & Management. 61 (1): 3–17. doi:10.2111/06-159R.1. hdl:10150/642920. S2CID 30969297.
- Savory, Allan. "Allan Savory: How to green the world's deserts and reverse climate change". YouTube. Archived from the original on 2021-12-11.
- Savory, Allan. "Holistic resource management: a conceptual framework for ecologically sound economic modelling" (PDF). Ecological Economics. Elsevier Science Publishers. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 May 2013. Retrieved 10 March 2013.
- Butterfield, Jody (2006). Holistic Management Handbook: Healthy Land, Healthy Profits, Second Edition. Island Press. ISBN 978-1559638852.
- Savory, Allan. "Response to request for information on the "science" and "methodology" underpinning Holistic Management and holistic planned grazing" (PDF). Savory Institute. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 May 2013. Retrieved 10 March 2013.
- Drury, Steve (2012-04-13). "Large-animal extinction in Australia linked to human hunters". Earth-Pages. Retrieved 9 June 2014.
Bibliography
- Arnalds, Ólafur; Archer, Steve (2000). Rangeland Desertification. Springer. ISBN 978-0-7923-6071-1.
- Barbault R., Cornet A., Jouzel J., Mégie G., Sachs I., Weber J. (2002). Johannesburg. World Summit on Sustainable Development. 2002. What is at stake? The contribution of scientists to the debate. Ministère des Affaires étrangères/adpf.
- Bauer, Steffan (2007). "Desertification". In Thai, Khi V.; et al. (eds.). Handbook of globalization and the environment. CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-57444-553-4.
- Batterbury, S.P.J. & A.Warren (2001) Desertification. in N. Smelser & P. Baltes (eds.) International Encyclopædia of the Social and Behavioral Sciences. Elsevier Press. pp. 3526–3529
- D’Odorico, Paolo; Bhattachan, Abinash; Davis, Kyle F.; Ravi, Sujith; Runyan, Christiane W. (January 2013). "Global desertification: Drivers and feedbacks". Advances in Water Resources. 51: 326–344. Bibcode:2013AdWR...51..326D. doi:10.1016/j.advwatres.2012.01.013.
- Geist, Helmut (2005). The causes and progression of desertification. Ashgate Publishing. ISBN 978-0-7546-4323-4.
- Hartman, Ingrid (2008). "Desertification". In Philander, S. George (ed.). Encyclopedia of global warming and climate change, Volume 1. SAGE. ISBN 978-1-4129-5878-3.
- Hinman, C. Wiley; Hinman, Jack W. (1992). The plight and promise of arid land agriculture. Columbia University Press. ISBN 978-0-231-06612-9.
- Holtz, Uwe (2007). Implementing the United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification from a parliamentary point of view – Critical assessment and challenges ahead. Online at
- Holtz, Uwe (2013). Role of parliamentarians in the implementation process of the UN Convention to Combat Desertification. A guide to Parliamentary Action, ed. Secretariat of the UNCCD, Bonn ISBN 978-92-95043-69-5. Online at
- Johnson, Pierre Marc; et al., eds. (2006). Governing global desertification: linking environmental degradation, poverty and participation. Ashgate Publishing. ISBN 978-0-7546-4359-3.
- Lucke, Bernhard (2007): Demise of the Decapolis. Past and Present Desertification in the Context of Soil Development, Land Use, and Climate. Online at
- Mensah, Joseph (2006). "Desertification". In Leonard, Thomas M. (ed.). Encyclopedia of the developing world, Volume 1. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-0-415-97662-6.
- Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (2005) Desertification Synthesis Report
- Moseley, W.G. and E. Jerme 2010. “Desertification.” In: Warf, B. (ed). Encyclopedia of Geography. Sage Publications. Volume 2, pp. 715–719.
- Oliver, John E., ed. (2005). "Desertification". Encyclopedia of world climatology. Springer. ISBN 978-1-4020-3264-6.
- Parrillo, Vincent N., ed. (2008). "Desertification". Encyclopedia of social problems, Volume 2. SAGE. ISBN 978-1-4129-4165-5.
- Reynolds, James F., and D. Mark Stafford Smith (ed.) (2002) Global Desertification – Do Humans Cause Deserts? Dahlem Workshop Report 88, Berlin: Dahlem University Press
- van der Stelt, Sjors; Doelman, Arjen; Hek, Geertje; Rademacher, Jens D. M. (February 2013). "Rise and Fall of Periodic Patterns for a Generalized Klausmeier–Gray–Scott Model". Journal of Nonlinear Science. 23 (1): 39–95. Bibcode:2013JNS....23...39V. doi:10.1007/s00332-012-9139-0. S2CID 8861764.
- UNCCD (1994) United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification
- The End of Eden a 90-minute documentary by South African filmmaker Rick Lomba in 1984 on African desertification
- Attribution
 This article incorporates public domain material from Desertification. United States Geological Survey. Retrieved 2021-05-04.
This article incorporates public domain material from Desertification. United States Geological Survey. Retrieved 2021-05-04.
External links
- Official website of the Secretariat of the United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD)
- Procedural history and related documents on the UNCCD, from the United Nations Audiovisual Library of International Law
- Official website of Action Against Desertification, a United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization initiative of the African, Caribbean and Pacific Group of States
- Global Deserts Outlook (2006), thematic assessment report in the Global Environment Outlook (GEO) series of the United Nations Environment Program (UNEP).
- Bell, Trudy; Phillips, Tony (December 6, 2002). "City-swallowing Sand Dunes". NASA.
- French Scientific Committee on Desertification (CSFD)




