Georgian language
Georgian (ქართული ენა, romanized: kartuli ena, pronounced [kʰɑɾtʰuli ɛnɑ]) is the most widely-spoken Kartvelian language that serves as the literary language or lingua franca for speakers of related languages.[2] It is the official language of Georgia and the native or primary language of 87.6% of its population.[3] Its speakers today number approximately four million.
| Georgian | |
|---|---|
| kartuli ena | |
| ქართული ენა | |
 Kartuli written in Georgian script | |
| Pronunciation | [kʰɑɾtʰuli ɛnɑ] |
| Native to | Georgia |
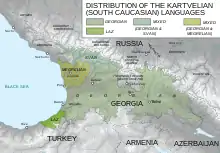
| Region | Caucasus |
| Ethnicity | Georgians |
Native speakers | 3.7 million (2014)[1] |
Kartvelian
| |
Early form | Old Georgian
|
| Dialects |
|
| |
| Official status | |
Official language in | |
| Regulated by | Cabinet of Georgia |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | ka |
| ISO 639-2 | geo (B) kat (T) |
| ISO 639-3 | kat |
| Glottolog | nucl1302 |
| Linguasphere | 42-CAB-baa – bac |
 | |
Classification
No claimed genetic links between the Kartvelian languages and any other language family in the world are accepted in mainstream linguistics. Among the Kartvelian languages, Georgian is most closely related to the so-called Zan languages (Megrelian and Laz); glottochronological studies indicate that it split from the latter approximately 2700 years ago. Svan is a more distant relative that split off much earlier, perhaps 4000 years ago.[4]
Dialects
Standard Georgian is largely based on the Kartlian dialect.[5] Over the centuries it has exerted a strong influence on the other dialects, as a result of which they are all, for the most part, mutually intelligible with it and with each other.[6]
History
| Part of a series on |
| Georgians ქართველები |
|---|
 |
| Nation |
| Georgia |
| Ancient Kartvelian people |
|
| Subgroups |
|
| Culture |
|
| Languages |
|
| Religion |
|
| Symbols |
|
| History of Georgia |
The history of the Georgian language is conventionally divided into the following phases:[7]
- Early Old Georgian: 300 BC
- Classical Old Georgian: 9th–11th centuries
- Middle Georgian: 11th/12th–17th/18th centuries
- Modern Georgian: 17th/18th century–present
The earliest extant references to Georgian are found in the writings of Marcus Cornelius Fronto, a Roman grammarian from the 2nd century AD.[8] The first direct attestations of the language are inscriptions and palimpsests dating to the 5th century, and the oldest surviving literary work is the 5th century Martyrdom of the Holy Queen Shushanik by Iakob Tsurtaveli.
The emergence of Georgian as a written language appears to have been the result of the Christianization of Georgia in the mid-4th century, which led to the replacement of Aramaic as the literary language.[7]
By the 11th century, Old Georgian had developed into Middle Georgian. The most famous work of this period is the epic poem The Knight in the Panther's Skin, written by Shota Rustaveli in the 12th century.
In 1629 a certain Nikoloz Cholokashvili authored the first printed books written (partially) in Georgian, the Alphabetum Ibericum sive Georgianum cum Oratione and the Dittionario giorgiano e italiano. These were meant to help western Catholic missionaries learn Georgian for evangelical purposes.[9]
Phonology
Consonants
On the left are IPA symbols, and on the right are the corresponding letters of the modern Georgian alphabet, which is essentially phonemic.
| Labial | Dental/ Alveolar |
Post-alveolar | Velar | Uvular | Glottal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m მ | n ნ | |||||
| Stop | aspirated | pʰ ფ | tʰ თ | kʰ ქ | |||
| voiced | b7 ბ | d7 დ | ɡ7 გ | ||||
| ejective | pʼ პ | tʼ ტ | kʼ კ | qʼ3 ყ | |||
| Affricate | (aspirated) | t͡sʰ1 ც | t͡ʃʰ1 ჩ | ||||
| voiced | d͡z ძ | d͡ʒ ჯ | |||||
| ejective | t͡sʼ წ | t͡ʃʼ ჭ | |||||
| Fricative | voiceless | s ს | ʃ შ | x 2 ხ | h ჰ | ||
| voiced | v ვ6 | z ზ | ʒ ჟ | ɣ 2 ღ | |||
| Vibrant | r რ4 | ||||||
| Lateral | l ლ5 | ||||||
- Opinions differ on the aspiration of /t͡sʰ, t͡ʃʰ/, as it is non-contrastive.
- Opinions differ on how to classify /x/ and /ɣ/; Aronson (1990) classifies them as post-velar, Hewitt (1995) argues that they range from velar to uvular according to context.
- The uvular ejective stop is commonly realised as an uvular ejective fricative [χʼ] but it can also be [qʼ], [ʔ], or [qχʼ], they are in free variation.[12]
- /r/ is realised as an alveolar tap [ɾ] [13] though [r] occurs in free variation.
- /l/ is pronounced as velarized [ɫ] before back vowels, it is pronounced as [l] in the environment of front vowels.[14]
- /v/ has following allophones. [13]
- In initial positions, /b d ɡ/ are pronounced as weakly voiced [b̥ , d̥ , ɡ̊][16]
- in Word-final position, /b, d, ɡ/ are devoiced to [pʰ, tʰ, kʰ].[16][15]
Former /qʰ/ (ჴ) has merged with /x/ (ხ), leaving only the latter.
The glottalization of the ejectives is rather light, and in many romanization systems it is not marked, for transcriptions such as ejective p, t, ts, ch, k and q, against aspirated p‘, t‘, ts‘, ch‘ and k‘ (as in transcriptions of Armenian).
The coronal occlusives (/tʰ tʼ d n/, not necessarily affricates) are variously described as apical dental, laminal alveolar, and "dental".[10]
Vowels
| Front | Central | Back | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Close | /i/ ი | /u/ უ | |
| Mid | /e/ ე | /o/ ო | |
| Open | /a/ ა |
Per Canepari, the main realizations of the vowels are as follows: [i], [e̞], [ä], [o̞], [u].[20]
One male speaker recorded by Shosted seems to have consistently realized /a/ as [ɑ].[21]
Allophonically, [ə] may be inserted to break up consonant clusters, as in /dɡas/ [dəɡäs].[22]
Prosody
Prosody in Georgian involves stress, intonation, and rhythm. Stress is very weak, and linguists disagree as to where stress occurs in words.[23] Jun, Vicenik, and Lofstedt have proposed that Georgian stress and intonation are the result of pitch accents on the first syllable of a word and near the end of a phrase.[24]
Phonotactics
Georgian contains many "harmonic clusters" involving two consonants of a similar type (voiced, aspirated, or ejective) which are pronounced with only a single release; e.g. ბგერა bgera (sound), ცხოვრება tskhovreba (life), and წყალი ts'q'ali (water).[25] There are also frequent consonant clusters, sometimes involving more than six consonants in a row, as may be seen in words like გვფრცქვნი gvprtskvni ("you peel us") and მწვრთნელი mts'vrtneli ("trainer").
Vicenik has observed that Georgian vowels following ejective stops have creaky voice and suggests this may be one cue distinguishing ejectives from their aspirated and voiced counterparts.[26]
Writing system
| Calligraphy |
|---|
|
_-_Georgian_language_alphabet.png.webp)


Georgian has been written in a variety of scripts over its history. Currently the Mkhedruli script is almost completely dominant; the others are used mostly in religious documents and architecture.
Mkhedruli has 33 letters in common use; a half dozen more are obsolete in Georgian, though still used in other alphabets, like Mingrelian, Laz, and Svan. The letters of Mkhedruli correspond closely to the phonemes of the Georgian language.
According to the traditional account written down by Leonti Mroveli in the 11th century, the first Georgian script was created by the first ruler of the Kingdom of Iberia, Pharnavaz, in the 3rd century BC. However, the first examples of a Georgian script date from the 5th century AD. There are now three Georgian scripts, called Asomtavruli "capitals", Nuskhuri "small letters", and Mkhedruli. The first two are used together as upper and lower case in the writings of the Georgian Orthodox Church and together are called Khutsuri "priests' [alphabet]".
In Mkhedruli, there is no case. Sometimes, however, a capital-like effect, called Mtavruli, "title" or "heading", is achieved by modifying the letters so that their vertical sizes are identical and they rest on the baseline with no descenders. These capital-like letters are often used in page headings, chapter titles, monumental inscriptions, and the like.
| Letter | National transcription | IPA transcription |
|---|---|---|
| ა | a | ä |
| ბ | b | b |
| გ | g | ɡ |
| დ | d | d |
| ე | e | e̞ |
| ვ | v | v |
| ზ | z | z |
| თ | t | tʰ |
| ი | i | i |
| კ | k’ | kʼ |
| ლ | l | l |
| მ | m | m |
| ნ | n | n |
| ო | o | o̞ |
| პ | p’ | pʼ |
| ჟ | zh | ʒ |
| რ | r | r |
| ს | s | s |
| ტ | t’ | tʼ |
| უ | u | u |
| ფ | p | pʰ |
| ქ | k | kʰ |
| ღ | gh | ɣ |
| ყ | q’ | qʼ |
| შ | sh | ʃ |
| ჩ | ch | t͡ʃʰ |
| ც | ts | t͡sʰ |
| ძ | dz | d͡z |
| წ | ts’ | t͡sʼ |
| ჭ | ch’ | t͡ʃʼ |
| ხ | kh | x |
| ჯ | j | d͡ʒ |
| ჰ | h | h |
Keyboard layout
This is the Georgian standard[27] keyboard layout. The standard Windows keyboard is essentially that of manual typewriters.
| “ „ |
1 ! |
2 ? |
3 № |
4 § |
5 % |
6 : |
7 . |
8 ; |
9 , |
0 / |
- _ |
+ = |
← Backspace |
| Tab key | ღ | ჯ | უ | კ | ე ჱ | ნ | გ | შ | წ | ზ | ხ ჴ | ც | ) ( |
| Caps lock | ფ ჶ | ძ | ვ ჳ | თ | ა | პ | რ | ო | ლ | დ | ჟ | Enter key ↵ |
| Shift key ↑ |
ჭ | ჩ | ყ | ს | მ | ი ჲ | ტ | ქ | ბ | ჰ ჵ | Shift key ↑ |
| Control key | Win key | Alt key | Space bar | AltGr key | Win key | Menu key | Control key | |
Grammar
Morphology
Georgian is an agglutinative language. There are certain prefixes and suffixes that are joined together in order to build a verb. In some cases, there can be up to eight different morphemes in one verb at the same time. An example is ageshenebinat ("you (pl.) should have built (it)"). The verb can be broken down to parts: a-g-e-shen-eb-in-a-t. Each morpheme here contributes to the meaning of the verb tense or the person who has performed the verb. The verb conjugation also exhibits polypersonalism; a verb may potentially include morphemes representing both the subject and the object.
Morphophonology
In Georgian morphophonology, syncope is a common phenomenon. When a suffix (especially the plural suffix -eb-) is attached to a word which has either of the vowels a or e in the last syllable, this vowel is, in most words, lost. For example, megobari means "friend". To say "friends", one says megobrebi (megobØrebi), with the loss of a in the last syllable of the word stem.
Inflection
Georgian has seven noun cases: nominative, ergative, dative, genitive, instrumental, adverbial and vocative. An interesting feature of Georgian is that, while the subject of a sentence is generally in the nominative case and the object is in the accusative case (or dative), one can find this reversed in many situations (this depends mainly on the character of the verb). This is called the dative construction. In the past tense of the transitive verbs, and in the present tense of the verb "to know", the subject is in the ergative case.
Syntax
- Georgian is a left-branching language, in which adjectives precede nouns, possessors precede possessions, objects normally precede verbs, and postpositions are used instead of prepositions.
- Each postposition (whether a suffix or a separate word) requires the modified noun to be in a specific case. This is similar to the way prepositions govern specific cases in many Indo-European languages such as German, Latin, or Russian.
- Georgian is a pro-drop language; both subject and object pronouns are frequently omitted except for emphasis or to resolve ambiguity.
- A study by Skopeteas et al. concluded that Georgian word order tends to place the focus of a sentence immediately before the verb, and the topic before the focus. A subject–object–verb (SOV) word order is common in idiomatic expressions and when the focus of a sentence is on the object. A subject–verb–object (SVO) word order is common when the focus is on the subject, or in longer sentences. Object-initial word orders (OSV or OVS) are also possible, but less common. Verb-initial word orders including both subject and object (VSO or VOS) are extremely rare.[28]
- Georgian has no grammatical gender; even the pronouns are ungendered.
- Georgian has no articles. Therefore, for example, "guest", "a guest" and "the guest" are said in the same way. In relative clauses, however, it is possible to establish the meaning of the definite article through use of some particles.
Vocabulary
_-_Georgian_language_-_Tariel_(last_verse).png.webp)
Georgian has a rich word-derivation system. By using a root, and adding some definite prefixes and suffixes, one can derive many nouns and adjectives from the root. For example, from the root -kart-, the following words can be derived: Kartveli (a Georgian person), Kartuli (the Georgian language) and Sakartvelo (Georgia).
Most Georgian surnames end in -dze ("son") (Western Georgia), -shvili ("child") (Eastern Georgia), -ia (Western Georgia, Samegrelo), -ani (Western Georgia, Svaneti), -uri (Eastern Georgia), etc. The ending -eli is a particle of nobility, comparable to French de, German von or Polish -ski.
Georgian has a vigesimal numeric system like Basque or (partially) French. Numbers greater than 20 and less than 100 are described as the sum of the greatest possible multiple of 20 plus the remainder. For example, "93" literally translates as "four times twenty plus thirteen" (ოთხმოცდაცამეტი - otkhmotsdatsamet'i).
One of the most important Georgian dictionaries is the Explanatory dictionary of the Georgian language (Georgian: ქართული ენის განმარტებითი ლექსიკონი). It consists of eight volumes and about 115,000 words. It was produced between 1950 and 1964, by a team of linguists under the direction of Arnold Chikobava.
Examples
Word formations
Georgian has a word derivation system, which allows the derivation of nouns from verb roots both with prefixes and suffixes, for example:
- From the root -ts'er- ("write"), the words ts'erili ("letter") and mts'erali ("writer") are derived.
- From the root -tsa- ("give"), the word gadatsema ("broadcast") is derived.
- From the root -tsda- ("try"), the word gamotsda ("exam") is derived.
- From the root -gav- ("resemble"), the words msgavsi ("similar") and msgavseba ("similarity") are derived.
- From the root -shen- ("build"), the word shenoba ("building") is derived.
- From the root -tskh- ("bake"), the word namtskhvari ("cake") is derived.
- From the root -tsiv- ("cold"), the word matsivari ("refrigerator") is derived.
- From the root -pr- ("fly"), the words tvitmprinavi ("plane") and aprena ("take-off") are derived.
It is also possible to derive verbs from nouns:
- From the noun -omi- ("war"), the verb omob ("wage war") is derived.
- From the noun -sadili- ("lunch"), the verb sadilob ("eat lunch") is derived.
- From the noun -sauzme ("breakfast"), the verb ts'asauzmeba ("eat a little breakfast") is derived; the preverb ts'a- in Georgian could add the meaning "VERBing a little".
- From the noun -sakhli- ("home"), the verb gadasakhleba (the infinite form of the verb "to relocate, to move") is derived.
Likewise, verbs can be derived from adjectives, for example:
- From the adjective -ts'iteli- ("red"), the verb gats'itleba (the infinite form of both "to blush" and "to make one blush") is derived. This kind of derivation can be done with many adjectives in Georgian.
- From the adjective -brma ("blind"), the verbs dabrmaveba (the infinite form of both "to become blind" and "to blind someone") are derived.
- From the adjective -lamazi- ("beautiful"), the verb galamazeba (the infinite form of the verb "to become beautiful") is derived.
Words that begin with multiple consonants
In Georgian many nouns and adjectives begin with two or more contiguous consonants. This is because syllables in the language often begin with two consonants. Recordings are available on the relevant Wiktionary entries, linked to below.
- Some examples of words that begin with two consonants are:
- There are also many words that begin with three contiguous consonants:
- There are also a few words in Georgian that begin with four contiguous consonants. Examples are:
- There can also be some extreme cases in Georgian. For example, the following word begins with six contiguous consonants:
- მწვრთნელი (mts'vrtneli), "trainer"
- While the following word begins with seven:
- გვწვრთნი (gvts'vrtni), "you train us"
- And the following words begin with eight:
Language example
Article 1 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights in Georgian:
ყველა ადამიანი იბადება თავისუფალი და თანასწორი თავისი ღირსებითა და უფლებებით. მათ მინიჭებული აქვთ გონება და სინდისი და ერთმანეთის მიმართ უნდა იქცეოდნენ ძმობის სულისკვეთებით.
- Transliteration:
q'vela adamiani ibadeba tavisupali da tanasts'ori tavisi ghirsebita da uplebebit. mat minich'ebuli akvt goneba da sindisi da ertmanetis mimart unda iktseodnen dzmobis sulisk'vetebit.
- Translation:
All human beings are born free and equal in dignity and rights. They are endowed with reason and conscience and should act towards one another in a spirit of brotherhood.[29]
See also
- Old Georgian
- Georgian dialects
- Georgian alphabet
- Georgian calligraphy
- Georgian calendar
- Georgian grammar
- Georgian numerals
- Georgian profanity
References
- Georgian at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- Hiller 1994, p. 1
- Central Intelligence Agency. (2016). Georgia. In The World Factbook. Retrieved from https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/georgia/
- Hillery 1994, p. 2
- Georgian Dialects, The ARMAZI project. Retrieved on March 28, 2007
- Manana Kock Kobaidze (2004-02-11) From the history of Standard Georgian Archived September 27, 2007, at the Wayback Machine
- Tuite, Kevin, "Early Georgian", pp. 145-6, in: Woodard, Roger D. (2008), The Ancient Languages of Asia Minor. Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-68496-X
- Braund, David (1994), Georgia in Antiquity; a History of Colchis and Transcaucasian Iberia, 550 B.C. – A.D. 562, p. 216. Oxford University Press, ISBN 0-19-814473-3
- "Georgian and Italian Dictionary". World Digital Library. Retrieved 3 July 2013.
- Shosted & Shikovani (2006:263)
- "Native Phonetic Inventory: georgian". gmu.edu. George Mason University. Retrieved 24 August 2019.
- Shosted, Ryan K.; Chikovani, Vakhtang (2006). "Standard Georgian" (PDF). Journal of the International Phonetic Association. 36 (2): 255–264. doi:10.1017/S0025100306002659. S2CID 53481687.
- Shosted & Chikovani (2006:261)
- Aronson (1990), p.17-18.
- Hewitt (1995), p.21.
- Aronson (1990):15
- Testelets 2020: 497
- Putkaradze & Mikataudze 2014: 53
- Hewitt 1987: 19
- Canepari 2007: 385
- Shosted & Chikovani (2006:262)
- McCoy, Priscilla (1999). "Harmony and Sonority in Georgian" (PDF).
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - Aronson (1990:18)
- Jun, Vicenik & Lofstedt (2007)
- Aronson (1990:33)
- Vicenik (2010:87)
- Georgian Keyboard Layout Microsoft
- Skopeteas, Féry & Asatiani (2009:2–5)
- "About Georgia: Georgian Alphabet". Archived from the original on 2010-12-02. Retrieved 2010-11-10.
Bibliography
- Aronson, Howard I. (1990), Georgian: a reading grammar (second ed.), Columbus, OH: Slavica
- Canepari, Luciano. 2007. Natural phonetics and tonetics: Articulatory, auditory, & functional. München: Lincom Europa.
- Elene Machavariani. The graphical basis of the Georgian Alphabet, Tbilisi, 1982, 107 pp (in Georgian, French summary)
- Farshid Delshad. Georgica et Irano-Semitica Studies on Iranian, Semitic and Georgian Linguistics, Wiesbaden 2010, 401 pp (in German, English, Russian and Georgian summary)
- "Great discovery" (about the expedition of Academician Levan Chilashvili).- Newspaper Kviris Palitra, Tbilisi, April 21–27, 2003 (in Georgian)
- Hewitt, Brian G. 1987. The typology of subordination in Georgian and Abkhaz. Berlin: De Gruyter.
- Hewitt, B. G. (1995), Georgian: a structural reference grammar, Amsterdam: John Benjamins
- Hewitt, B. G. (1996), Georgian: a Learner's Grammar, London: Routledge
- Hiller, P. J. (1994). Georgian: The Kartvelian Literary Language. Pontypridd, Wales: Language Information Centre.
- Ivane Javakhishvili. Georgian Paleography, Tbilisi, 1949, 500 pp (in Georgian)
- Jun, Sun-Ah; Vicenik, Chad; Lofstedt, Ingvar (2007), "Intonational Phonology of Georgian" (PDF), UCLA Working Papers in Phonetics (106): 41–57, archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-06-16
- Kiziria, Dodona (2009), Beginner's Georgian with 2 Audio CDs, New York: Hippocrene, ISBN 978-0-7818-1230-6
- Korneli Danelia, Zurab Sarjveladze. Questions of Georgian Paleography, Tbilisi, 1997, 150 pp (in Georgian, English summary)
- Kraveishvili, M. & Nakhutsrishvili, G. (1972), Teach Yourself Georgian for English Speaking Georgians, Tbilisi: The Georgian Society for Cultural Relations with Compatriots Abroad
- Pavle Ingorokva. Georgian inscriptions of antique.- Bulletin of ENIMK, vol. X, Tbilisi, 1941, pp. 411–427 (in Georgian)
- Price, Glanville (1998), An Encyclopedia of the Languages of Europe, Blackwell
- Putkaradze, Tariel; Mikautadze, Maia. 2014. Phonetics of the Georgian literary language. Tbilisi.
- Ramaz Pataridze. The Georgian Asomtavruli, Tbilisi, 1980, 600 pp. (in Georgian).
- Shosted, Ryan K.; Vakhtang, Chikovani (2006), "Standard Georgian" (PDF), Journal of the International Phonetic Association, 36 (2): 255–264, doi:10.1017/S0025100306002659
- Skopeteas, Stavros; Féry, Caroline; Asatiani, Rusudan (2009), Word order and intonation in Georgian, University of Potsdam
- Testelets, Yakov G. 2020. Kartvelian (South Caucasian) Languages. In Polinsky, Maria (ed.), The Oxford Handbook of Languages of the Caucasus, 491–528.
- Vicenik, Chad (2010), "An acoustic study of Georgian stop consonants", Journal of the International Phonetic Association, 40 (1): 59–92, doi:10.1017/s0025100309990302, S2CID 143120834
- Zaza Aleksidze. Epistoleta Tsigni, Tbilisi, 1968, 150 pp (in Georgian)
- Butskhrikidze, Marika (2002). The consonant phonotactics of Georgian
External links
- Dryer, Matthew S.; Haspelmath, Martin, eds. (2013). "Georgian language". World Atlas of Language Structures Online. Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology.
- The Universal Declaration of Human Rights in Georgian language
Dictionaries
Software
- Georgian fonts, compliant with Unicode 4.0, also available for MAC OS 9 or X
- A keyboard for typing georgian characters for firefox
- Learn Georgian Alphabet Now app Gives the name, pronunciation of each letter, and example words. Shows the stroke order of each letter. Permits drawing practice and has a quiz to learn the letters.

