Ubykh language
Ubykh or Päkhy was a Northwest Caucasian language once spoken by the Ubykh tribe of Circassians who originally lived along the eastern coast of the Black Sea before being deported en masse to Turkey in the Circassian genocide.[1]
| Ubykh | |
|---|---|
| tuex̂ıbze | |
| Pronunciation | /tʷɜxɨbzɜ/ |
| Native to | Circassia |
| Region | Sochi |
| Extinct | 7 October 1992, with the death of Tevfik Esenç |
Northwest Caucasian
| |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | uby |
| Glottolog | ubyk1235 |
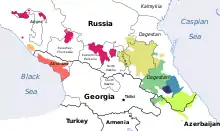 Ubykh (extinct) | |
The Ubykh language was ergative and polysynthetic, with a high degree of agglutination, with polypersonal verbal agreement and a very large number of distinct consonants but only two phonemically distinct vowels. With around eighty consonants, it had one of the largest inventories of consonants in the world,[2] and the largest number for any language without clicks.
The name Ubykh is derived from Убыхыбзэ (/wɨbɨx/), its name in the Adyghe language. It is known in linguistic literature by many names: variants of Ubykh, such as Ubikh, Oubykh (French); and its Germanised variant Päkhy (from Ubykh /tʷɜχɨ/).
Major features
Ubykh is distinguished by the following features, some of which are shared with other Northwest Caucasian languages:
- It is ergative, making no syntactic distinction between the subject of an intransitive sentence and the direct object of a transitive sentence. Split ergativity plays only a small part, if at all.
- It is highly agglutinating and polysynthetic, using mainly monosyllabic or bisyllabic roots, but with single morphological words sometimes reaching nine or more syllables in length: /ɜχʲɜzbɜtɕʼɜʁɜwdɨtʷɐjlɜfɜqʼɜjtʼmɜdɜχ/ ('if only you had not been able to make him take [it] all out from under me again for them'). Affixes rarely fuse in any way.
- It has a simple nominal system, contrasting just three noun cases, and not always marking grammatical number in the direct case.
- Its system of verbal agreement is quite complex. English verbs must agree only with the subject; Ubykh verbs must agree with the subject, the direct object and the indirect object, and benefactive objects must also be marked in the verb.
- It is phonologically complex as well, with 84 distinct consonants (four of which, however, appear only in loan words). It has three phonemic vowels [ɐ ɜ ɨ] which correspond to Dumézil's [aa a ə] respectively and this is evident in the minimal triplet of /ɐsʃɨn/ ('I milk X'), /ɐsʃɜn/ ('I reap X'), and /ɐsʃɐn/ ('I milk them; I reap them').
Phonology
Ubykh has 84 phonemic consonants, a record high amongst languages without click consonants, but only 3 phonemic vowels.[3] Four of these consonants are found only in loanwords and onomatopoeiae. There are nine basic places of articulation for the consonants and extensive use of secondary articulation, such that Ubykh has 20 different uvular phonemes. Ubykh distinguishes three types of postalveolar consonants: apical, laminal, and laminal closed. Regarding the vowels, since there are only three phonemic vowels, there is a great deal of allophony.
Grammar
Morphosyntax
Ubykh is agglutinative and polysynthetic: /ʃɨkʲʼɐjɨfɜnɜmɨt/ ('we will not be able to go back'), /ɐwqʼɜqʼɜjtʼbɜ/ ('if you had said it'). It is often extremely concise in its word forms.
The boundaries between nouns and verbs is somewhat blurred. Any noun can be used as the root of a stative verb (/mɨzɨ/ 'child', /sɨmɨzɨjtʼ/ 'I was a child'), and many verb roots can become nouns simply by the use of noun affixes (/qʼɜ/ 'to say', /sɨqʼɜ/ 'what I say').[4][5]
Nouns
The noun system in Ubykh is quite simple. It has three main noun cases (the oblique-ergative case may be two homophonous cases with differing function, thus presenting four cases in total):
- direct or absolutive case, marked with the bare root; this indicates the subject of an intransitive sentence and the direct object of a transitive sentence (e.g. /tɨt/ 'a man')
- oblique-ergative case, marked in -/n/; this indicates either the subject of a transitive sentence, targets of preverbs, or indirect objects which do not take any other suffixes (/mɨzɨn/ '(to) a child')
- locative case, marked in -/ʁɜ/, which is the equivalent of English in, on or at.
There are X other cases that exist in Ubykh too:
- instrumental case (-/ɜwn(ɨ)/) was also treated as a case in Dumézil (1975).
- instrumental-comitative case (-/ɐlɜ/).
- Another pair of postpositions, -/lɐq/ ('to[wards]') and -/ʁɐfɜ/ ('for'), have been noted as synthetic datives (e.g. /ɜχʲɨlɐq ɜstʷɜdɜw/ 'I will send it to the prince'), but their status as cases is also best discounted.
Nouns do not distinguish grammatical gender. The definite article is /ɐ/ (e.g. /ɐtɨt/ 'the man'). There is no indefinite article directly equivalent to the English a or an, but /zɜ/-(root)-/ɡʷɜrɜ/ (literally 'one'-(root)-'certain') translates French un : e.g. /zɜnɜjnʃʷɡʷɜrɜ/ ('a certain young man').
Number is only marked on the noun in the ergative case, with -/nɜ/. The number marking of the absolutive argument is either by suppletive verb roots (e.g. /ɐkʷɨn blɜs/ 'he is in the car' vs. /ɐkʷɨn blɜʒʷɜ/ 'they are in the car') or by verb suffixes: /ɐkʲʼɜn/ ('he goes'), /ɐkʲʼɐn/ ('they go'). The second person plural prefix /ɕʷ/- triggers this plural suffix regardless of whether that prefix represents the ergative, the absolutive, or an oblique argument:
- Absolutive: /ɕʷɜstʷɐn/ ('I give you all to him')
- Oblique: /sɨɕʷɨntʷɐn/ ('he gives me to you all')
- Ergative: /ɐsɨɕʷtʷɐn/ ('you all give it/them to me')
Note that, in this last sentence, the plurality of it (/ɐ/-) is obscured; the meaning can be either 'You all give it to me' or 'You all give them to me'.
Adjectives, in most cases, are simply suffixed to the noun: /tʃɨbʒɨjɜ/ ('pepper') with /pɬɨ/ ('red') becomes /tʃɨbʒɨjɜpɬɨ/ ('red pepper'). Adjectives do not decline.
Postpositions are rare; most locative semantic functions, as well as some non-local ones, are provided with preverbal elements: /ɐsχʲɜwtxqʼɜ/ ('you wrote it for me'). However, there are a few postpositions: /sɨʁʷɜ sɨɡʲɐtɕʼ/ ('like me'), /ɐχʲɨlɐq/ ('near the prince').
Pronouns
Free pronouns in all North-West Caucasian languages lack an ergative-absolutive distinction.[3]
| 1st Person | 2nd Person | 3rd Person | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Singular | Standard | /s(ɨ)ʁʷɜ/ | /(w(ɨ))ʁʷɜ/(joc. /χɜʁʷɜ/) | /ɐʁʷɜ/ |
| AB | /(s)χɜ/ | |||
| Plural | Standard | /ʃɨʁʷɜɬɜ/ | /ɕʷɨʁʷɜɬɜ/ | /ɐʁʷɜɬɜ/ |
| Tevfik Esenç | /ʃɜɬɜ/ | /ɕʷɜɬɜ/ | ||
| Osman Güngür | /ʃɨʁʷɜ/ | /ɕʷɨʁʷɜ/ |
Possession
| 1st Person | 2nd Person | 3rd Person | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | Jocular | |||
| Singular | /sɨ/- | /wɨ/- | /χɜ/- | /ʁɜ/- |
| Plural | /ʃɨ/- | /ɕʷɨ/- | /ɐʁɜ/- | |
Possessed nouns have their plurality marked with the affix /-ɜw-/.
/ʃɜwtʃɨ/
/ʃ(ɨ)-ɜw-tʃɨ/
1pPOSS-PL-horse
Our horses
Verbs
A past–present–future distinction of verb tense exists (the suffixes -/qʼɜ/ and -/ɜwt/ represent past and future) and an imperfective aspect suffix is also found (-/jtʼ/, which can combine with tense suffixes). Dynamic and stative verbs are contrasted, as in Arabic, and verbs have several nominal forms. Morphological causatives are not uncommon. The conjunctions /ɡʲɨ/ ('and') and /ɡʲɨlɜ/ ('but') are usually given with verb suffixes, but there is also a free particle corresponding to each:
- -/ɡʲɨ/ 'and' (free particle /ve/, borrowed from Arabic);
- -/ɡʲɨlɜ/ 'but' (free particle /ɜʁʷɜ/)
Pronominal benefactives are also part of the verbal complex, marked with the preverb /χʲɜ/-, but a benefactive cannot normally appear on a verb that has three agreement prefixes already.
Gender only appears as part of the second person paradigm, and then only at the speaker's discretion. The feminine second person index is /χɜ/-, which behaves like other pronominal prefixes: /wɨsχʲɜntʷɨn/ ('he gives [it] to you [normal; gender-neutral] for me'), but compare /χɜsχʲɜntʷɨn/ 'he gives [it] to you [feminine] for me').
Agreement
Oblique 1 markers are limited to marking the agreement of a noun before a relational preverb and Oblique 2 markers are used for not only marking agreement with local and directional preverbs but also the simple oblique, or dative, arguments. [3]
| Absolutive | Oblique (1 and 2) | Ergative | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| First Person | sg. | /s(ɨ)/- | /s(ɨ)/- ~ /z/ | /s(ɨ)/- ~ /z/ |
| pl. | /ʃ(ɨ)/- | /ʃ(ɨ)/- ~ /ʒ/- | /ʃ(ɨ)/- ~ /ʒ/- | |
| Second Person | sg. | /wɨ/- | /w(ɨ)/- | /w(ɨ)/- |
| pl. | /ɕʷ(ɨ)/- | /ɕʷ(ɨ)/- ~ /ʑʷ(ɨ)/- | /ɕʷ(ɨ)/- ~ /ʑʷ(ɨ)/- | |
| sg. (joc., arc.) | /χɜ/- | /χɜ/- | /χɜ/- | |
| Third Person | sg. | /ɐ/-, /jɨ/-, /ɨ/-, /Ø/- | /Ø/- | n(ɨ)/- /Ø/- |
| pl. | /ɐ/-, /jɨ/-, /Ø/- | /ɐ/- | /ɐ/-, /nɐ/- |
The second-person /χɜ/- is an archaic pronoun used to indicate that the person being referred to is a female, or heckling the speaker in some way.
Dynamic Verb Conjugation
Dynamic Ubykh verbs are split up in two groups: Group I which contain the simple tenses and Group II which contain derived counterpart tenses. Only the Karaclar dialect uses the progressive tense and the plural is unknown.
The singular-plural distinction is used when the subject, the ergative, is singular or plural.
Square brackets indicate elided vowels; parenthesis indicate optional parts of the stem; and the colon indicates the boundary of a morpheme. [3]
| Singular | Plural | |
|---|---|---|
| Simple Past | -/qʼɜ/ | -/qʼɜ-n(ɜ)/ |
| Mirative Past | -/jtʼ/ | -/jɬ(ɜ)/ |
| Present | -/n/ | -/ɐ-n/ |
| Future I | -/ɜw/ | -/n[ɜ]-ɜw/ |
| Future II | -/ɜw:t/ | -/n[ɜ]-ɜw:t/ |
| (Progressive) | -/ɜwɨ:n/ | ? |
| Singular | Plural | |
|---|---|---|
| Pluperfect | -/qʼɜ:jtʼ/ | -/qʼɜ:jɬ(ɜ)/ ~ -/qʼɜ:nɜ:jtʼ/ |
| Imperfect | -/nɜ:tjʼ/ | -/ɐ-nɜ:jɬ(ɜ)/ |
| Conditional I | -/ɜwɨ:jtʼ/ | -/n[ɜ]-ɜwɨ:jɬ(ɜ)/ |
| Conditional II | -/ɜw:tʷ:qʼɜ/ | -/(n[ɜ]-)ɜw:tʷ:qʼɜ(-n)/ |
Simple Past
The verbs in the simple past tense are conjugated with -/qʼɜ/ in the singular and -/qʼɜ-n(ɜ)/ in the plural.
Examples:
- /qʼɜ/ - to say → /ɐ-qʼɜ-qʼɜ/ (s)he said
- /fɨ/ - to eat → /ɐ-fɨ-qʼɜ/ (s)he ate
- /tɕʼɜ/ - to know → /ɐ-tɕʼɜ-qʼɜ/ (s)he knew
- /kʲʼɜ/ - to go → /ɐ-kʲʼɜ-qʼɜ/ (s)he went
| Plurality | Person | Ubykh | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| Singular | First-person | /s(ɨ)-fɨ-qʼɜ/ | I ate |
| Second-person | /wɨ-fɨ-qʼɜ/ | you ate | |
| Third-person | /ɐ-fɨ-qʼɜ/ | (s)he ate | |
| Plural | First-person | /ʃ(ɨ)-fɨ-qʼɜ-n(ɜ)/ | we ate |
| Second-person | /ɕʷ(ɨ)-fɨ-qʼɜ-n(ɜ)/ | you (all) ate | |
| Third-person | /ɐ-fɨ-qʼɜ-n(ɜ)/ | they ate |
Mirative Past
The verbs in the mirative past tense are conjugated with -/jtʼ/ in the singular and -/jɬ(ɜ)/ in the plural.
Examples:
- /qʼɜ/ - to say → /ɐ-qʼɜ-jtʼ/ (s)he said apparently
- /fɨ/ - to eat → /ɐ-fɨ-jtʼ/ (s)he ate apparently
- /tɕʼɜ/ - to know → /ɐ-tɕʼɜ-jtʼ/ (s)he knew apparently
- /kʲʼɜ/ - to go → /ɐ-kʲʼɜ-jtʼ/ (s)he went apparently
| Plurality | Person | Ubykh | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| Singular | First-person | /s(ɨ)-fɨ-jtʼ/ | I ate apparently |
| Second-person | /wɨ-fɨ-jtʼ/ | you ate apparently | |
| Third-person | /ɐ-fɨ-jtʼ/ | (s)he ate apparently | |
| Plural | First-person | /ʃ(ɨ)-fɨ-jɬ(ɜ)/ | we ate apparently |
| Second-person | /ɕʷ(ɨ)-fɨ-jɬ(ɜ)/ | you (all) ate apparently | |
| Third-person | /ɐ-fɨ-jɬ(ɜ)/ | they ate apparently |
Present
The verbs in the present tense are conjugated with -/n/ in the singular and -/ɐ-n/ in the plural.
Examples:
- /qʼɜ/ - to say → /ɐ-qʼɜ-n/ (s)he says
- /fɨ/ - to eat → /ɐ-fɨ-n/ (s)he eats
- /tɕʼɜ/ - to know → /ɐ-tɕʼɜ-n/ (s)he knows
- /kʲʼɜ/ - to go → /ɐ-kʲʼɜ-n/ (s)he goes
| Plurality | Person | Ubykh | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| Singular | First-person | /s(ɨ)-fɨ-n/ | I eat |
| Second-person | /wɨ-fɨ-n/ | you eat | |
| Third-person | /ɐ-fɨ-n/ | (s)he eats | |
| Plural | First-person | /ʃ(ɨ)-f-ɐ-n/ | we eat |
| Second-person | /ɕʷ(ɨ)-f-ɐ-n/ | you (all) eat | |
| Third-person | /ɐ-f-ɐ-n/ | they eat |
Future I
The verbs in the present tense are conjugated with -/ɜw/ in the singular and -/n[ɜ]-ɜw/ in the plural. It conveys a sense of certainty, immediacy, obligation, or intentionality.
Examples:
- /qʼɜ/ - to say → /ɐ-qʼ-ɜw/ (s)he certainly will say
- /fɨ/ - to eat → /ɐ-f-ɜw/ (s)he certainly will eat
- /tɕʼɜ/ - to know → /ɐ-tɕʼ-ɜw/ (s)he certainly will know
- /kʲʼɜ/ - to go → /ɐ-kʲʼ-ɜw/ (s)he certainly will go
| Plurality | Person | Ubykh | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| Singular | First-person | /s(ɨ)-fɨ-n[ɜ]-ɜw/ | I certainly will eat |
| Second-person | /wɨ-fɨ-n[ɜ]-ɜw/ | you certainly will eat | |
| Third-person | /ɐ-fɨ-n[ɜ]-ɜw/ | (s)he certainly will eat | |
| Plural | First-person | /ʃ(ɨ)-fɨ-n[ɜ]-ɜw/ | we certainly will eat |
| Second-person | /ɕʷ(ɨ)-fɨ-n[ɜ]-ɜw/ | you (all) certainly will eat | |
| Third-person | /ɐ-fɨ-n[ɜ]-ɜw/ | they certainly will eat |
Future II
The verbs in the present tense are conjugated with -/ɜw:t/ in the singular and -/n[ɜ]-ɜw:t/ in the plural. It conveys a generic sense of the future as well as an exhortative sense such as: /ʃɨ-kʲʼɜ-n[ɜ]-ɜw/ (let's go!).
Examples:
- /qʼɜ/ - to say → /ɐ-qʼ-ɜw:t/ (s)he will say
- /fɨ/ - to eat → /ɐ-f-ɜw:t/ (s)he will eat
- /tɕʼɜ/ - to know → /ɐ-tɕʼ-ɜw:t/ (s)he will know
- /kʲʼɜ/ - to go → /ɐ-kʲʼ-ɜw:t/ (s)he will go
| Plurality | Person | Ubykh | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| Singular | First-person | /s(ɨ)-f-ɜw:t/ | I will eat |
| Second-person | /wɨ-f-ɜw:t/ | you will eat | |
| Third-person | /ɐ-f-ɜw:t/ | (s)he will eat | |
| Plural | First-person | /ʃ(ɨ)-fɨ-n[ɜ]-ɜw:t/ | we will eat |
| Second-person | /ɕʷ(ɨ)-fɨ-n[ɜ]-ɜw:t/ | you (all) will eat | |
| Third-person | /ɐ-fɨ-n[ɜ]-ɜw:t/ | they will eat |
Static Verb Conjugation
In all dialects and speakers, only two static tenses exist: present and past.
| Singular | Plural | |
|---|---|---|
| Present | -/Ø/ | -/n(ɜ)/ |
| Past | -/jtʼ/ | -/jɬ(ɜ)/ |
Aspect
There are five basic aspects that exist besides the aspects that exist within the Ubykh tense system. They are: habitual, iterative, exhaustive, excessive, and potential.
A speaker may combine one of these aspects with another to convey more complex aspects in conjunction with the tenses. [3]
| habitual | -/gʲɜ/ |
|---|---|
| iterative | -/ɐj(ɨ)/ |
| exhaustive | -/lɜ/ |
| excessive | -/tɕʷɜ/ |
| potential | -/fɜ/ |
A few meanings covered in English by adverbs or auxiliary verbs are given in Ubykh by verb suffixes:
- /ɐsfɨfɜn/ ('I can eat it') - /ɐzdʑʷɜfɜn/ ('I can drink it')
- /ɐsfɨɡʲɜn/ ('I eat it all the time') - /ɐzdʑʷɜɡʲɜn/ ('I drink it all the time')
- /ɐsfɨlɜn/ ('I am eating it all up') - /ɐzdʑʷɜlɜn/ ('I am drinking it all up')
- /ɐsfɨtɕʷɜn/ ('I eat it too much') - /ɐzdʑʷɜtɕʷɜn/ ('I drink it too much')
- /ɐsfɐjɨn/ ('I eat it again') - /ɐzdʑʷɐjɨn/ ('I drink it again')
| simple | habitual | iterative | exhaustive | excessive | potential | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Singular | First-person | /s(ɨ)-fɨ-n/ | /s(ɨ)-fɨ-gʲɜ-n/ | /s(ɨ)-f-ɐj(ɨ)-n/ | /s(ɨ)-fɨ-lɜ-n/ | /s(ɨ)-fɨ-tɕʷɜ-n/ | /s(ɨ)-fɨ-fɜ-n/ |
| Second-person | /wɨ-fɨ-n/ | /wɨ-fɨ-gʲɜ-n/ | /wɨ-f-ɐj(ɨ)-n/ | /wɨ-fɨ-lɜ-n/ | /wɨ-fɨ-tɕʷɜ-n/ | /wɨ-fɨ-fɜ-n/ | |
| Third-person | /ɐ-fɨ-n/ | /ɐ-fɨ-gʲɜ-n/ | /ɐ-f-ɐj(ɨ)-n/ | /ɐ-fɨ-lɜ-n/ | /ɐ-fɨ-tɕʷɜ-n/ | /ɐ-fɨ-fɜ-n/ | |
| Plural | First-person | /ʃ(ɨ)-f-ɐ-n/ | /ʃ(ɨ)-f-gʲ[ɜ]-ɐ-n/ | /ʃ(ɨ)-f-ɐj(ɨ)-ɐ-n/ | /ʃ(ɨ)-fɨ-l[ɜ]-ɐ-n/ | /ʃ(ɨ)-fɨ-tɕʷ[ɜ]-ɐ-n/ | /ʃ(ɨ)-fɨ-f[ɜ]-ɐ-n/ |
| Second-person | /ɕʷ(ɨ)-f-ɐ-n/ | /ɕʷ(ɨ)-fɨ-gʲ[ɜ]-ɐ-n/ | /ɕʷ(ɨ)-f-ɐj(ɨ)-ɐ-n/ | /ɕʷ(ɨ)-fɨ-l[ɜ]-ɐ-n/ | /ɕʷ(ɨ)-fɨ-tɕʷ[ɜ]-ɐ-n/ | /ɕʷ(ɨ)-fɨ-f[ɜ]-ɐ-n/ | |
| Third-person | /ɐ-f-ɐ-n/ | /ɐ-fɨ-gʲ[ɜ]-ɐ-n/ | /ɐ-f-ɐj(ɨ)-ɐ-n/ | /ɐ-fɨ-l[ɜ]-ɐ-n/ | /ɐ-fɨ-tɕʷ[ɜ]-ɐ-n/ | /ɐ-fɨ-f[ɜ]-ɐ-n/ | |
Questions
Questions may be marked grammatically, using verb suffixes or prefixes:
- Yes–no questions with -/ɕ/: /wɜnɜ ɐwbjɜqʼɜɕ/? ('did you see that?')
- Complex questions with -/j/: /sɐkʲʼɜ wɨpʼtsʼɜj/? ('what is your name?')
Other types of questions, involving the pronouns 'where' and 'what', may also be marked only in the verbal complex: /mɐwkʲʼɜnɨj/ ('where are you going?'), /sɐwqʼɜqʼɜjtʼɨj/ ('what had you said?').
Preverbs and determinants
Many local, prepositional, and other functions are provided by preverbal elements providing a large series of applicatives, and here Ubykh shows remarkable complexity. Two main types of preverbal elements exist: determinants and preverbs. The number of preverbs is limited, and mainly show location and direction. The number of determinants is also limited, but the class is more open; some determinant prefixes include /tʃɜ/- ('with regard to a horse') and /ɬɜ/- ('with regard to the foot or base of an object').
For simple locations, there are a number of possibilities that can be encoded with preverbs, including (but not limited to):
- above and touching
- above and not touching
- below and touching
- below and not touching
- at the side of
- through a space
- through solid matter
- on a flat horizontal surface
- on a non-horizontal or vertical surface
- in a homogeneous mass
- towards
- in an upward direction
- in a downward direction
- into a tubular space
- into an enclosed space
There is also a separate directional preverb meaning 'towards the speaker': /j/-, which occupies a separate slot in the verbal complex. However, preverbs can have meanings that would take up entire phrases in English. The preverb /jtɕʷʼɐ/- signifies 'on the earth' or 'in the earth', for instance: /ʁɜdjɜ ɐjtɕʷʼɐnɐɬqʼɜ/ ('they buried his body'; literally, "they put his body in the earth"). Even more narrowly, the preverb /fɐ/- signifies that an action is done out of, into or with regard to a fire: /ɐmdʒɜn zɜtʃɨtʃɜqʲɜ fɐstχʷɨn/ ('I take a brand out of the fire').
Orthography
Writing systems for the Ubykh language have been proposed,[3] but there has never been a standard written form.
Lexicon
Native vocabulary
Ubykh syllables have a strong tendency to be CV, although VC and CVC also exist. Consonant clusters are not as large as in Abzhywa Abkhaz or in Georgian, rarely being larger than two terms. Three-term clusters exist in two words - /ndʁɜ/ ('sun') and /pstɜ/ ('to swell up'), but the latter is a loan from Adyghe, and the former more often pronounced /nədʁa/ when it appears alone. Compounding plays a large part in Ubykh and, indeed, in all Northwest Caucasian semantics. There is no verb equivalent to English to love, for instance; one says "I love you" as /tʂʼɜnɨ wɨzbjɜn/ ('I see you well').
Reduplication occurs in some roots, often those with onomatopoeic values (/χˤɜχˤɜ/, 'to curry[comb]' from /χˤɜ/ 'to scrape'; /kʼɨrkʼɨr/, 'to cluck like a chicken' [a loan from Adyghe]); and /wɜrqwɜrq/, 'to croak like a frog').
Roots and affixes can be as small as one phoneme. The word /wɜntʷɐn/, 'they give you to him', for instance, contains six phonemes, each a separate morpheme:
- /w/ - 2nd singular absolutive
- /ɜ/ - 3rd singular dative
- /n/ - 3rd ergative
- /tʷ/ - to give a
- /ɐ/ - ergative plural
- /n/ - present tense
However, some words may be as long as seven syllables (although these are usually compounds): /ʂɨqʷʼɜwɨɕɜɬɐdɨtʃɜ/ ('staircase').
Slang and idioms
As with all other languages, Ubykh is replete with idioms. The word /ntʷɜ/ ('door'), for instance, is an idiom meaning either "magistrate", "court", or "government." However, idiomatic constructions are even more common in Ubykh than in most other languages; the representation of abstract ideas with series of concrete elements is a characteristic of the Northwest Caucasian family. As mentioned above, the phrase meaning "I love you" translates literally as 'I see you well'; similarly, "you please me" is literally 'you cut my heart'. The term /wɨrɨs/ ('Russian'), an Arabic loan, has come to be a slang term meaning "infidel", "non-Muslim" or "enemy" (see History below).
Foreign loans
The majority of loanwords in Ubykh are derived from either Adyghe or Arabic, with smaller numbers from Persian, Abkhaz, and the South Caucasian languages. Towards the end of Ubykh's life, a large influx of Adyghe words was noted; Vogt (1963) notes a few hundred examples. The phonemes /ɡ/ /k/ /kʼ/ were borrowed from Arabic and Adyghe. /ɬʼ/ also appears to come from Adyghe, although it seems to have arrived earlier on. It is possible, too, that /ɣ/ is a loan from Adyghe, since most of the few words with this phoneme are obvious Adyghe loans: /pɐɣɜ/ ('proud'), /ɣɜ/ ('testis').
Many loanwords have Ubykh equivalents, but were dwindling in usage under the influence of Arabic, Circassian, and Russian equivalents:
- /bɨrwɨ/ ('to make a hole in, to perforate' from Iranic languages) = /pɕɐtχʷ/
- /tʃɐj/ ('tea' from Chinese) = /bzɨpɕɨ/
- /wɨrɨs/ ('enemy' from Persian) = /bˤɜqˤʼɜ/
Some words, usually much older ones, are borrowed from less influential stock: Colarusso (1994) sees /χˤʷɜ/ ('pig') as a borrowing from a proto-Semitic *huka, and /ɜɡʲɜrɨ/ ('slave') from an Iranian root; however, Chirikba (1986) regards the latter as being of Abkhaz origin ( ← Abkhaz agər-wa 'lower cast of peasants; slave', literally 'Megrelian').
Evolution
In the scheme of Northwest Caucasian evolution, despite its parallels with Adyghe and Abkhaz, Ubykh forms a separate third branch of the family. It has fossilised palatal class markers where all other Northwest Caucasian languages preserve traces of an original labial class: the Ubykh word for 'heart', /ɡʲɨ/, corresponds to the reflex /ɡʷə/ in Abkhaz, Abaza, Adyghe, and Kabardian. Ubykh also possesses groups of pharyngealised consonants. All other NWC languages possess true pharyngeal consonants, but Ubykh is the only language to use pharyngealisation as a feature of secondary articulation.
With regard to the other languages of the family, Ubykh is closer to Adyghe and Kabardian but shares many features with Abkhaz due to geographic influence; many later Ubykh speakers were bilingual in Ubykh and Adyghe.
Dialects
While not many dialects of Ubykh existed, one divergent dialect of Ubykh has been noted (in Dumézil 1965:266-269). Grammatically, it is similar to standard Ubykh (i.e. Tevfik Esenç's dialect), but has a very different sound system, which had collapsed into just 62-odd phonemes:
- /dʷ/ /tʷ/ /tʷʼ/ have collapsed into /b/ /p/ /pʼ/.
- /ɕʷ/ /ʑʷ/ are indistinguishable from /ʃʷ/ /ʒʷ/.
- /ɣ/ seems to have disappeared.
- Pharyngealisation is no longer distinctive, having been replaced in many cases by geminate consonants.
- Palatalisation of the uvular consonants is no longer phonemic.
History
Ubykh was spoken in the eastern coast of the Black Sea around Sochi until 1864, when the Ubykhs were driven out of the region by the Russians. They eventually came to settle in Turkey, founding the villages of Hacı Osman, Kırkpınar, Masukiye and Hacı Yakup. Arabic and Circassian eventually became the preferred languages for everyday communication, and many words from these languages entered Ubykh in that period.
The Ubykh language died out on 7 October 1992, when its last fluent speaker, Tevfik Esenç, died.[1] Before his death, thousands of pages of material and many audio recordings had been collected and collated by a number of linguists, including Georges Charachidzé, Georges Dumézil, Hans Vogt, George Hewitt and A. Sumru Özsoy, with the help of some of its last speakers, particularly Tevfik Esenç and Huseyin Kozan.[1] Ubykh was never written by its speech community, but a few phrases were transcribed by Evliya Celebi in his Seyahatname and a substantial portion of the oral literature, along with some cycles of the Nart saga, was transcribed. Tevfik Esenç also eventually learned to write Ubykh in the transcription that Dumézil devised.
Julius von Mészáros, a Hungarian linguist, visited Turkey in 1930 and took down some notes on Ubykh. His work Die Päkhy-Sprache was extensive and accurate to the extent allowed by his transcription system (which could not represent all the phonemes of Ubykh) and marked the foundation of Ubykh linguistics.
The Frenchman Georges Dumézil also visited Turkey in 1930 to record some Ubykh and would eventually become the most celebrated Ubykh linguist. He published a collection of Ubykh folktales in the late 1950s, and the language soon attracted the attention of linguists for its small number of phonemic vowels. Hans Vogt, a Norwegian, produced a monumental dictionary that, in spite of its many errors (later corrected by Dumézil), is still one of the masterpieces and essential tools of Ubykh linguistics.
Later in the 1960s and into the early 1970s, Dumézil published a series of papers on Ubykh etymology in particular and Northwest Caucasian etymology in general. Dumézil's book Le Verbe Oubykh (1975), a comprehensive account of the verbal and nominal morphology of the language, is another cornerstone of Ubykh linguistics.
Since the 1980s, Ubykh linguistics has slowed drastically with the most recent treatise being Fenwick's A Grammar of Ubykh (2011), who was also working on a dictionary.[6] The Ubykh themselves have shown interest in relearning their language.
The Abkhaz writer Bagrat Shinkuba's historical novel Bagrat Shinkuba. The Last of the Departed treats the fate of the Ubykh people.
People who have published literature on Ubykh include
- Brian George Hewitt
- Brian Fell
- Catherine Paris
- Christine Leroy
- Georg Bossong
- Georges Dumézil
- Hans Vogt
- John Colarusso
- Julius von Mészáros
- Rieks Smeets
- Rhona (formerly Rohan) Fenwick
- Tevfik Esenç
- Viacheslav Chirikba
- Wim Lucassen
Notable characteristics
Ubykh had been cited in the Guinness Book of Records (1996 ed.) as the language with the most consonant phonemes, but since 2017 the !Xóõ language (a member of the Tuu languages) has been considered by the book to have broken that record, with 130 consonants.[7] Ubykh has 20 uvular and 29 pure fricative phonemes, more than any other known language.
Samples
All examples from Dumézil 1968.[8]
Faːχe
faaχʲa
once
tʼqʼokobʒe
tʼqʷʼa-kʷabʒa
two-man
kʼeʁən
kʲʼaʁə-n
friend-ADV
azaχeʃinan
a-za-χʲa-ʃə-na-n
they-each.other-BEN-become-PL-ADV
amʁen
a-mʁʲa-n
the-road-OBL
Once, two men set out together on the road.
Afoːtənə
a-f-awtə-nə
they-eat-FUT-ADV
mʁøːuf
mʁʲawəf
provisions
aχodoːtən
a-χʷada-awtə-n
they-buy-FUT-ADV
akʼenan,
a-kʲʼa-na-n
they-go-PL-ADV
azan
a-za-n
the-one-ERG
fatɕʼaːla
fatɕʼ-aala
cheese-and
ɕybˤaːla
ɕʷəbˤa-aala
bread-and
χodaqʼa;
χʷada-qʼa
buy-PAST
They went to buy some provisions for the journey; the one bought cheese and bread
Aːjdəχəŋɡi
aajdə-χə-n-ɡʲə
other-of-ERG-and
ɕybˤaːla
ɕʷəbˤa-aala
bread-and
psaːla
psa-aala
fish-and
χodan
χʷada-n
buy-ADV
eːnuːqʼa.
a-j-nə-w-qʼa
it-hither-he-bring-past
and the other bought bread and fish.
Amʁen
a-mʁʲa-n
the-road-OBL
ɡikenan
ɡʲə-kʲa-na-n
on-enter(PL)-PL-GER
akʼenaɡi
a-kʲ'a-na-gʲə
they-go-PL-ADV
wofatɕʼ
wa-fatɕʼ
that-cheese
dəχodaqʼeːtʼə
də-χʷada-qʼajtʼ-ə
REL-buy-PLUP-GER
ʁakʼeʁʁaːfa
ʁa-kʲʼaʁ-ʁaafa
his-friend-towards
While they were on the road, the one who had bought the cheese asked the other
"ɕoɬa
ɕʷaɬa
you.all
psa
psa
fish
jeda
jada
much
"You people eat a lot of fish;"
"Saːba
saaba
why
wanaŋɡʲaːfə
wana-n-ɡʲaafə
that-OBL-as.much.as
psa
psa
fish
ɕʷfaːniː?"
ɕʷ-f-aa-nə-j
you.all-eat-PL-PRES-Q
qʼan
qʼa-n
say-ADV
ʁaːdzʁaqʼa.
ʁa-aa-dzʁa-qʼa
him-to-ask-past
"why do you eat fish as much as that?"
"Psa
psa
fish
ufəba
wə-fə-ba
you-eat-if
utɕʼe
wə-tɕʼa
your-knowledge
jeda
jada
much
ʃoːt,"
ʃ-awt
become-FUT
"If you eat fish, you get smarter,"
"Wonaʁaːfa
wana-ʁaafa
that-for
ʃaɬa
ʃaɬa
we
psa
psa
fish
jeda
jada
much
ʃfən,"
ʃ-fə-n
we-eat-PRES
"so we eat a lot of fish," he answered.
- Notes
- ɡʲə-w-qʼa. (on-enter(SG)-past) vs ɡʲə-kʲa-qʼa-n.(on-enter(PL)-past-PL)
- ɡʲə-w-qʼa. (on-enter(SG)-past) vs ɡʲə-kʲa-qʼa-n.(on-enter(PL)-past-PL)
- Only Tevfik Esenç pronounced "ɕʷəʁʷa(ɬa)" (Karacalar dialect:"ɕʷəʁʷa") as "ɕʷaɬa".[3]
- Only Tevfik Esenç pronounced "ɕʷəʁʷa(ɬa)" (Karacalar dialect:"ɕʷəʁʷa") as "ɕʷaɬa".[3]
- Only Tevfik Esenç pronounced "ʃəʁʷa(ɬa)" (Karacalar dialect:"ʃəʁʷa") as "ʃaɬa".[3]
- Only Tevfik Esenç pronounced "ʃəʁʷa(ɬa)" (Karacalar dialect:"ʃəʁʷa") as "ʃaɬa".[3]
Notes
- ^a Fenwick lists a plural form for /tʷ/ ('to give') but it is never used in the grammar even when a plural form is expected.
See also
- North Caucasian languages
References
- Koerner, E. F. K. (1 January 1998). First Person Singular III: Autobiographies by North American Scholars in the Language Sciences. John Benjamins Publishing. p. 33. ISBN 978-90-272-4576-2.
- King, Charles (2008). The Ghost of Freedom. p. 15.
- Fenwick, R. S. H. (2011). A Grammar of Ubykh. Munich: Lincom Europa.
- Dumézil, G. 1975 Le verbe oubykh: études descriptives et comparatives (The Ubykh Verb: Descriptive and Comparative Studies). Paris: Imprimerie Nationale
- Hewitt, B. G. 2005 North-West Caucasian. Lingua 115: 91-145.
- Fenwick, Rhona S. H. (2018). "Ubykh Dictionary Draft - M". zenodo.org. doi:10.5281/zenodo.1189012. Retrieved 30 July 2022.
- "Language with most consonants". Guinness World Records. Retrieved 2021-07-29.
- "Ressource". Archived from the original on 2010-12-28. Retrieved 2009-12-23.
Bibliography
- Viacheslav Chirikba (1986). Abxazskie leksicheskie zaimstvovanija v ubyxskom jazyke (Abkhaz Lexical Loans in Ubykh). Problemy leksiki i grammatiki jazykov narodov Karachaevo-Cherkesii: Sbornik nauchnyx trudov (Lexical and Grammatical Problems of the Karachay-Cherkessian National Languages: A Scientific Compilation). Cherkessk, 112–124.
- Viacheslav Chirikba (1996). Common West Caucasian. The Reconstruction of its Phonological System and Parts of its Lexicon and Morphology. Leiden: CNWS Publications.
- Colarusso, J. (1994). Proto-Northwest Caucasian (Or How To Crack a Very Hard Nut). Journal of Indo-European Studies 22, 1-17.
- Dumézil, G. (1961). Etudes oubykhs (Ubykh Studies). Paris: Librairie A. Maisonneuve.
- Dumézil, G. (1965). Documents anatoliens sur les langues et les traditions du Caucase (Anatolian Documents on the Languages and Traditions of the Caucasus), III: Nouvelles études oubykhs (New Ubykh Studies). Paris: Librairie A. Maisonneuve.
- Dumézil, G. (1968). Eating Fish Makes You Clever. Annotated recording available via Archived 2010-12-28 at the Wayback Machine.
- Dumézil, G. (1975). Le verbe oubykh: études descriptives et comparatives (The Ubykh Verb: Descriptive and Comparative Studies). Paris: Imprimerie Nationale.
- Hewitt, B. G. (2005). North-West Caucasian. Lingua. 115, 91-145.
- Mészáros, J. von. (1930). Die Päkhy-Sprache (The Ubykh Language). Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- Vogt, H. (1963). Dictionnaire de la langue oubykh (Dictionary of the Ubykh Language). Oslo: Universitetsforlaget.
- Fenwick, R. (2011). A Grammar of Ubykh. Munich: Lincom Europa.