Research Triangle
The Research Triangle, or simply The Triangle, are both common nicknames for a metropolitan area in the Piedmont region of North Carolina in the United States, anchored by the cities of Raleigh and Durham and the town of Chapel Hill, home to three major research universities: North Carolina State University, Duke University, and University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, respectively. The nine-county region, officially named the Raleigh–Durham–Cary combined statistical area (CSA), comprises the Raleigh–Cary and Durham–Chapel Hill Metropolitan Statistical Areas and the Henderson Micropolitan Statistical Area. The "Triangle" name originated in the 1950s with the creation of Research Triangle Park, located between the three anchor cities and home to numerous high tech companies.
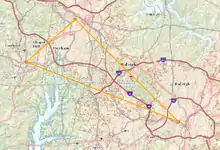
A 2019 Census estimate put the population at 2,079,687, making it the second largest combined statistical area in the state of North Carolina behind Charlotte CSA.[1] The Raleigh–Durham television market includes a broader 24-county area which includes Fayetteville, North Carolina, and has a population of 2,726,000 persons.[2]
Most of the Triangle is part of North Carolina's first, second, fourth, ninth, and thirteenth congressional districts.[3]
The region is sometimes confused with The Triad, which is a North Carolina region adjacent to and directly west of the Triangle comprising Greensboro, Winston-Salem, and High Point, among other cities.
Counties
Depending on which definition of the Research Triangle region is used, as few as three or as many as 16 counties are included as part of the region. All of these counties when included hold a population of over 2,167,000 people.
The three core counties of Wake, Durham and Orange are the homes of the three research universities for which the area is named.
The 2020 members of the Research Triangle Regional Partnership are:[4]
- Chatham
- Durham
- Franklin
- Granville
- Johnston
- Lee
- Person
- Wake
- Vance
NC Regional Councils of Governments Definition
All counties in the State of North Carolina are in one of 16 regional councils which provide programs and services to local governments. The Triangle J Council of Governments includes Chatham, Durham, Johnston, Lee, Moore, Orange, and Wake Counties.[5] The northern Triangle counties of Person, Granville, Franklin, Vance and Warren are part of the Kerr-Tar Regional Council of Governments.
Office of Management and Budget Definition
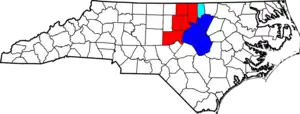
As of September 14, 2018, the US Office of Management and Budget (OMB) delineated the Raleigh-Durham-Cary Combined Statistical Area as consisting of two metropolitan and one micropolitan statistical areas.[6] Those three statistical areas in turn are defined as consisting of a total of nine counties. The MSAs and their constituent counties are:
- Durham-Chapel Hill Metropolitan SA
- Chatham County
- Durham County
- Granville County
- Orange County
- Person County
- Henderson Micropolitan SA
- Vance County
- Raleigh-Cary Metropolitan SA
- Franklin County
- Johnston County
- Wake County
Prior to September 2018, the OMB had used the name Raleigh-Durham-Chapel Hill Combined Statistical Area and it included several additional counties.[7] The Dunn Micropolitan Statistical Area (Harnett County) and Sanford Micropolitan Statistical Area (Lee County) were moved to the Fayetteville-Sanford-Lumberton Combined Statistical Area, while the Oxford Micropolitan Statistical Area (Granville County) was folded into the Durham-Chapel Hill Metropolitan Statistical Area. The Raleigh Metropolitan Statistical Area was also renamed the Raleigh-Cary Metropolitan Statistical Area.
The table below outlines the populations of the constituent counties of the Raleigh–Durham-Cary Combined Statistical Area as of the 2020 Census.[8]
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1950 | 483,418 | — | |
| 1960 | 534,029 | 10.5% | |
| 1970 | 628,319 | 17.7% | |
| 1980 | 765,191 | 21.8% | |
| 1990 | 962,962 | 25.8% | |
| 2000 | 1,315,016 | 36.6% | |
| 2010 | 1,740,185 | 32.3% | |
| 2020 | 2,043,867 | 17.5% | |
| 2020[9] | |||
| County | 2021 Estimate | 2020 Census | Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wake County | 1,150,204 | 1,129,410 | +1.84% |
| Durham County | 326,126 | 324,833 | +0.40% |
| Johnston County | 226,504 | 215,999 | +4.86% |
| Orange County | 148,884 | 148,696 | +0.13% |
| Chatham County | 77,889 | 76,285 | +2.10% |
| Franklin County | 71,703 | 68,573 | +4.56% |
| Granville County | 61,986 | 60,992 | +1.63% |
| Vance County | 42,185 | 42,578 | −0.92% |
| Person County | 39,127 | 39,097 | +0.08% |
| Total | 2,144,608 | 2,106,463 | +1.81% |
Cities


The Triangle region, as defined for statistical purposes as the Raleigh–Durham–Cary CSA, comprises nine counties, although the U.S. Census Bureau divided the region into two metropolitan statistical areas and one micropolitan area in 2003. The Raleigh-Cary metropolitan area comprises Wake, Franklin, and Johnston Counties; the Durham-Chapel Hill metropolitan area comprises Durham, Orange, Chatham, Granville, and Person Counties; and the Henderson micropolitan area comprises Vance County.
Some area television stations define the region as Raleigh–Durham–Fayetteville. Fayetteville is more than 50 miles (80 km) from Raleigh, but is part of the Triangle television market.
15 largest municipalities
| Rank | City / town | County | 2020 Census | 2010 Census | Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Raleigh | Wake County / Durham County | 467,665 | 403,892 | +15.79% |
| 2 | Durham | Durham County / Wake County | 283,506 | 228,330 | +24.17% |
| 3 | Cary | Wake County / Chatham County | 174,721 | 135,234 | +29.20% |
| 4 | Chapel Hill | Orange County / Durham County / Chatham County | 61,960 | 57,233 | +8.26% |
| 5 | Apex | Wake County | 58,780 | 37,476 | +56.85% |
| 6 | Wake Forest | Wake County / Franklin County | 47,601 | 30,117 | +58.05% |
| 7 | Holly Springs | Wake County | 41,239 | 24,661 | +67.22% |
| 8 | Fuquay-Varina | Wake County | 34,152 | 17,937 | +90.40% |
| 9 | Garner | Wake County | 31,159 | 25,745 | +21.03% |
| 10 | Morrisville | Wake County / Durham County | 29,630 | 18,576 | +59.51% |
| 11 | Clayton | Johnston County / Wake County | 26,307 | 16,116 | +63.24% |
| 12 | Carrboro | Orange County | 21,295 | 19,582 | +8.75% |
| 13 | Knightdale | Wake County | 19,632 | 11,401 | +72.20% |
| 14 | Mebane | Alamance County / Orange County | 17,797 | 11,393 | +56.21% |
| 15 | Henderson | Vance County | 15,060 | 15,368 | −2.00% |
Education
Public secondary education in the Triangle is similar to that of the majority of the state of North Carolina, in which there are county-wide school systems (the exception is Chapel Hill-Carrboro City Schools within Orange County but apart from Orange County Schools). Based in Cary, the Wake County Public School System, which includes the cities of Raleigh and Cary, is the largest school system in the state of North Carolina and the 15th-largest in the United States, with average daily enrollment of 159,949 as of the second month of the 2016–17 school year.[10] Other larger systems in the region include Durham Public Schools (about 33,000 students) and rapidly growing Johnston County Schools (about 31,000 students).
Institutions of higher education



- Campbell University
- Central Carolina Community College
- Duke University
- Durham Technical Community College
- Louisburg College
- Meredith College
- North Carolina Central University
- North Carolina State University
- Piedmont Community College
- Shaw University
- Southeastern Baptist Theological Seminary and The College at Southeastern
- St. Augustine's College
- University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
- Vance-Granville Community College
- Wake Technical Community College
- William Peace University
Sports
College sports
With the significant number of universities and colleges in the area and the relative absence of major league professional sports, NCAA sports are very popular, particularly those sports in which the Atlantic Coast Conference participates, most notably basketball.
The Duke Blue Devils (representing Duke University in Durham), NC State Wolfpack (representing North Carolina State University in Raleigh), and North Carolina Tar Heels (representing the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill) are all members of the ACC. Rivalries among these schools are very strong, fueled by proximity to each other, with annual competitions in every sport. Adding to the rivalries is the large number of graduates the high schools in the region send to each of the local universities. It is very common for students at one university to know many students attending the other local universities, which increases the opportunities for "bragging" among the schools. The four ACC schools in the state, Duke, North Carolina, North Carolina State, and Wake Forest University (the last of which was originally located in the town of Wake Forest before moving to Winston-Salem in 1956), are referred to as Tobacco Road by sportscasters, particularly in basketball. All four teams consistently produce high-caliber teams . Each of the Triangle-based universities listed has won at least two NCAA Basketball national championships.
Three historically black colleges, including recent Division I arrival North Carolina Central University and Division II members St. Augustine College and Shaw University also boost the popularity of college sports in the region.
Other colleges in the Triangle that field intercollegiate teams include Campbell University, Meredith College, and William Peace University.
Professional sports

The region has only one professional team of the four major sports, the Carolina Hurricanes of the NHL, based in Raleigh. Since moving to the Research Triangle region from Hartford, Connecticut, they have enjoyed great success, including winning a Stanley Cup. With only one top-level professional sports option, minor league sports are quite popular in the region. The Durham Bulls in downtown Durham are a AAA Minor League baseball affiliate of the Tampa Bay Rays, and the Carolina Mudcats, based in Zebulon, 10 miles east of Raleigh, are the Advanced-A affiliate of the Milwaukee Brewers. In Cary, North Carolina FC plays in the second-level United Soccer League, and the North Carolina Courage began play in the National Women's Soccer League in 2017 after the owner of North Carolina FC bought the NWSL franchise rights of the Western New York Flash and relocated the NWSL franchise to the Triangle.
| Team | League | Sport | Venue (capacity) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carolina Hurricanes | NHL | Hockey | PNC Arena (18,680) |
| Durham Bulls | IL (AAA) | Baseball | DBAP (10,000) |
| Carolina Mudcats | CL (A) | Baseball | Five County Stadium (6,500) |
| North Carolina Courage | NWSL (D1) | Soccer | WakeMed Soccer Park (10,000) |
| North Carolina FC | USLC (D2) | Soccer | WakeMed Soccer Park (10,000) |
| Carolina Flyers | AUDL | Ultimate | WakeMed Soccer Park (10,000) / Cardinal Gibbons High School |
The area also had a team in the fledgling World League of American Football – however, the Raleigh–Durham Skyhawks, coached by Roman Gabriel, did not exactly cover themselves in glory; they lost all 10 games of their inaugural (and only) season in 1991. The team folded after that, being replaced in the league by the Ohio Glory, which fared little better at 1–9, ultimately suffering the same fate – along with the other six teams based in North America – when the league took a two-year hiatus, returning as a six-team all-European league in 1995.
Commerce

The region's growing high-technology community includes such companies as IBM, Lenovo, SAS Institute, Cisco Systems, NetApp, Red Hat, EMC Corporation, and Credit Suisse First Boston. In addition to high-tech, the region is consistently ranked in the top three in the U.S. with concentration in life science companies. Some of these companies include GlaxoSmithKline, Biogen Idec, BASF, Merck & Co., Novo Nordisk, Novozymes, and Pfizer. Research Triangle Park and North Carolina State University's Centennial Campus in Raleigh support innovation through R&D and technology transfer among the region's companies and research universities (including Duke University and the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill).
The area fared relatively well during the late-2000s recession, ranked as the strongest region in North Carolina by the Brookings Institution and among the top 40 in the country. The change in unemployment during 2008 to 2009 was 4.6% and home prices was 2%. The Greensboro metropolitan area was listed among the second-weakest and the Charlotte area among the middle in the country.[11]
Major employers
- ABB
- Ajinomoto
- American Airlines
- BASF
- Bank of America
- Bayer
- BB&T
- Blue Cross Blue Shield of North Carolina
- Biogen
- bioMérieux
- The Body Shop
- Burt's Bees
- Caterpillar Inc.
- Cisco Systems
- Credit Suisse Group
- Cree Inc.
- Cengage
- Dell EMC
- Delta Electronics
- Deutsche Bank
- Duke University
- Durham Public Schools
- DuPont
- Eaton
- Fidelity Investments
- Fujifilm
- Environmental Protection Agency
- General Electric
- GKN
- GlaxoSmithKline
- IBM
- Intel
- IQVIA
- John Deere
- LabCorp
- Lenovo
- MetLife
- National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, part of the National Institutes of Health
- Netapp
- North Carolina state government (including University of NC system)
- Novo Nordisk
- Nvidia
- Oracle Corporation
- Pfizer (Pfizer Poultry Health)
- Progress Energy
- PNC (PNC Financial Services Group, Inc.)
- Qualcomm
- Railinc Corporation
- Red Hat
- Research Triangle Institute
- SAS Institute
- Sony Ericsson
- Syngenta
- Teleflex Medical
- Toshiba Global Commerce Solutions
- Toyota
- Truist Financial
- United States Forest Service
- Verizon
- Wake County Public School System
- WakeMed Hospital
Major hospitals, medical centers and medical schools


The Research Triangle region is served by these hospitals and medical centers:[12]
- Hospitals of the Duke University Health System
- Duke Ambulatory Surgery Center (Durham)
- Duke Children's Hospital and Health Center (Durham)
- Duke Raleigh Hospital (formerly Raleigh Community Hospital)
- Duke University Medical Center (Durham)
- Duke Regional Hospital (formerly Durham Regional Hospital)
- Person Memorial Hospital (Roxboro)
- Hospitals of the UNC Health Care system
- Chatham Hospital (Siler City)
- North Carolina Cancer Hospital (Chapel Hill)
- North Carolina Children's Hospital (Chapel Hill)
- North Carolina Memorial Hospital (Chapel Hill)
- North Carolina Neurosciences Hospital (Chapel Hill)
- North Carolina Women's Hospital (Chapel Hill)
- Rex Hospital (Raleigh)
- Johnston Medical Center (Smithfield)
- Hospitals of the WakeMed system
- WakeMed Raleigh Campus (formerly Wake Memorial Hospital and Wake Medical Center)
- WakeMed Cary Hospital (formerly Western Wake Medical Center)
- Other hospitals and medical centers
- Central Regional Hospital,(Butner)
- Durham VA Medical Center (Durham)
- Franklin Regional Medical Center (Louisburg)
- Harnett Health System (Dunn)
- Betsy Johnson Regional Hospital
- Angier Medical Services
- Good Hope Hospital
- Betsy Johnson Cancer Research Clinic
- Central Harnett Hospital
- Medical Schools
- Duke University School of Medicine
- University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill School of Medicine
- Campbell University School of Osteopathic Medicine
Transportation
Freeways and primary designated routes


The Triangle proper is served by three major interstate highways: I-40, I-85, and I-87 along with their spurs: I-440 and I-540, and seven U.S. Routes: 1, 15, 64, 70, 264, 401, and 501. US Highways 15 and 501 are multiplexed through much of the region as US 15-501. I-95 passes 30 miles east of Raleigh through Johnston County, with I-87 connecting I-95 at Rocky Mount, NC to Raleigh via the US 64–264 Bypass.
The two interstates diverge from one another in Orange County, with I-85 heading northeast through northern Durham County toward Virginia, while I-40 travels southeast through southern Durham, through the center of the region, and serves as the primary freeway through Raleigh. The related loop freeways I-440 and I-540 are primarily located in Wake County around Raleigh. I-440 begins at the interchange of US 1 and I-40 southwest of downtown Raleigh and arcs as a multiplex with US 1 northward around downtown with the formal designation as the Cliff Benson/Raleigh Beltline (cosigned with US 1 on three-fourths of its northern route) and ends at its junction with I-40 in southeast Raleigh. I-540, sometimes known as the Raleigh Outer Loop, extends from the US 64–264 Bypass to I-40 just inside Durham County, where it continues across the interstate as a state route (NC 540), prior to its becoming a toll road from the NC 54 interchange to the current terminus at NC Highway 55 near Holly Springs. I-95 serves the extreme eastern edge of the region, crossing north–south through suburban Johnston County.
U.S. Routes 1, 15, and 64 primarily serve the region as limited-access freeways or multilane highways with access roads. US 1 enters the region from the southwest as the Claude E. Pope Memorial Highway and travels through suburban Apex where it merges with US 64 and continues northeast through Cary. The two highways are codesignated for about 2 miles (3.2 km) until US 1 joins I-440 and US 64 with I-40 along the Raleigh–Cary border. Capital Boulevard, which is designated US 1 for half of its route and US 401 the other is not a limited-access freeway, although it is a major thoroughfare through northeast Raleigh and into the northern downtown area.
North Carolina Highway 147 is a limited-access freeway that connects I-85 with Toll Route NC 540 in northwestern Wake County. The older, toll-free portion of the four-lane route—known as the Durham Freeway or the I.L. "Buck" Dean Expressway—traverses downtown Durham and extends through Research Triangle Park to I-40. The Durham Freeway is often used as a detour or alternate route for I-40 through southwestern Durham the Chapel Hill area in cases of traffic accident, congestion or road construction delays. The tolled portion of NC 147, called the Triangle Expressway—North Carolina's first modern toll road when it opened to traffic in late 2011—continues past I-40 to Toll NC 540. Both Toll NC 147 and Toll NC 540 are modern facilities which collect tolls using transponders and license plate photo-capture technology.
Public transit


A partnering system of multiple public transportation agencies currently serves the Triangle region under the joint GoTransit branding. Raleigh is served by GoRaleigh (formerly Capital Area Transit) municipal transit system, while Durham has GoDurham (formerly the Durham Area Transit Authority). Chapel Hill is served by Chapel Hill Transit, and Cary is served by GoCary (formerly C-Tran) public transit systems. However, GoTriangle, formerly called Triangle Transit, works in cooperation with all area transit systems by offering transfers between its own routes and those of the other systems. Triangle Transit also coordinates an extensive vanpool and rideshare program that serves the region's larger employers and commute destinations.
Plans have been made to merge all of the area's municipal systems into Triangle Transit, and Triangle Transit also has proposed a regional rail system to connect downtown Durham, downtown Cary and downtown Raleigh with multiple suburban stops, as well as stops in the Research Triangle Park area. The agency's initial proposal was effectively cancelled in 2006, however, when the agency could not procure adequate federal funding. A committee of local business, transportation and government leaders currently are working with Triangle Transit to develop a new transit blueprint for the region, with various modes of rail transit, as well as bus rapid transit, open as options for consideration.[13]
Raleigh–Durham International Airport (RDU)
(IATA: RDU, ICAO: KRDU, FAA LID: RDU)



Raleigh–Durham International Airport (RDU) has nonstop passenger service to 68 destinations with over 450 average daily departures, including nonstop international service to Canada, Europe, and Mexico.[14] It is located near the geographic center of The Triangle, 4+1⁄2 miles (7.2 km) northeast of the town of Morrisville in Wake County. The airport covers 5,000 acres (2,023 ha) and has three runways.[15]
In 1939 the General Assembly of North Carolina chartered the Raleigh–Durham Aeronautical Authority, which was changed in 1945 to the Raleigh–Durham Airport Authority. The first new terminal opened in 1955. Terminal A (now Terminal 1) opened in 1981. American Airlines began service to RDU in 1985.
RDU opened the 10,000-foot (3,000 m) runway, 5L-23R, in 1986. American Airlines opened its north–south hub operation at RDU in the new Terminal C in June 1987, greatly increasing the size of RDU's operations with a new terminal including a new apron and runway. American brought RDU its first international flights to Bermuda, Cancun, Paris and London.
In 1996, American Airlines ceased its hub operations at RDU due to Pan Am and Eastern Airlines. Pan Am and Eastern were Miami's main tenants until 1991, when both carriers went bankrupt. Their hubs at MIA were taken over by United Airlines and American Airlines. This created a difficulty in competing with US Airways' hub in Charlotte and Delta Air Lines' hub in Atlanta, Georgia for passengers traveling between smaller cities in the North and South. Midway Airlines entered the market, starting service in 1995 with the then somewhat novel concept of 50-seat Canadair Regional Jets providing service from its RDU hub primarily along the East Coast. Midway, originally incorporated in Chicago, had some success after moving its operations to the midpoint of the eastern United States at RDU and its headquarters to Morrisville, NC. The carrier ultimately could not overcome three weighty challenges: the arrival of Southwest Airlines, the refusal of American Airlines to renew the frequent flyer affiliation it had with Midway (thus dispatching numerous higher fare-paying businesspeople to airlines with better reward destinations), and the significant blow of September 11, 2001. Midway Airlines filed Chapter 11 bankruptcy on August 13, 2001, and ceased operations entirely on October 30, 2003.
In February 2000, RDU was ranked as the nation's second fastest-growing major airport in the United States, by Airports Council International, based on 1999 statistics. Passenger growth hit 24% over the previous year, ranking RDU second only to Washington Dulles International Airport. RDU opened Terminal A south concourse for use by Northwest and Continental Airlines in 2001. The addition added 46,000 square feet (4,300 m2) and five aircraft gates to the terminal. Terminal A became designated as Terminal 1 on October 26, 2008. In 2003, RDU also dedicated a new general aviation terminal. RDU continues to keep pace with its growth by redeveloping Terminal C into a new state-of-the-art terminal, now known as Terminal 2, which opened in October 2008.[16]
As of June 2022, the airport will have international flights to Cancun, London, Montreal, Paris, Reykjavik and Toronto. Cancun service is provided by American, Frontier and JetBlue, while the Canada flights are provided by Air Canada, Paris by Delta, Reykjavik by new to the market Icelandair, and London by American. Icelandair is the first international carrier outside of Air Canada to service the airport. Delta Air Lines currently considers the airport to be a "focus city", or an airport that is not a hub, but is of importance to the carrier. The COVID-19 pandemic significantly shrunk the operation, but by September 2022, Delta will be serving 21 destinations on aircraft ranging from the CRJ700 to the 767.
Public general-aviation airports
In addition to RDU, several smaller publicly owned general-aviation airports also operate in the metropolitan region:
- Triangle North Executive Airport (IATA: LFN, ICAO: KLHZ, FAA LID: LHZ), Louisburg
- Raleigh Exec (ICAO: KTTA, FAA LID: TTA), Sanford
- Johnston County Airport (IATA: JNX, ICAO: KJNX, FAA LID: JNX), Smithfield
- Horace Williams Airport (IATA: IGX, ICAO: KIGX, FAA LID: IGX), Chapel Hill (Closed)
- Harnett Regional Jetport (IATA: HRJ, ICAO: KHRJ, FAA LID: HRJ), Erwin
- Person County Airport (ICAO: KTDF, FAA LID: TDF), Roxboro
- Siler City Municipal Airport (ICAO: K5W8, FAA LID: 5W8), Siler City
Private airfields
Several licensed private general-aviation and agricultural airfields are located in the region's suburban areas and nearby rural communities:

- Bagwell Airport (FAA LID: NC99), Garner
- Ball Airport (FAA LID: 79NC), Louisburg
- Barclaysville Field Airport (FAA LID: NC44), Angier
- Brooks Field Airport (FAA LID: 8NC6), Siler City
- CAG Farms Airport (FAA LID: 87NC), Angier
- Charles Field Airport (FAA LID: NC22), Dunn
- Cox Airport (FAA LID: NC81), Apex
- Crooked Creek Airport (FAA LID: 7NC5), Bunn
- Dead Dog Airport (FAA LID: 8NC4), Pittsboro
- Deck Airpark Airport (FAA LID: NC11), Apex
- Dutchy Airport (FAA LID: 5NC5), Chapel Hill
- Eagle's Landing Airport (FAA LID: 9NC8), Pittsboro
- Field of Dreams Airport (FAA LID: 51NC), Zebulon
- Fuquay/Angier Field Airport (FAA LID: 78NC), Fuquay-Varina
- Hinton Field Airport (FAA LID: NC72), Princeton
- Kenly Airport (FAA LID: 7NC3), Kenly
- Lake Ridge Aero Park Airport (FAA LID: 8NC8), Durham
- Miles Airport (FAA LID: NC34), Chapel Hill
- North Raleigh Airport (FAA LID: 00NC), Louisburg
- Peacock Stolport Airport (FAA LID: 4NC7), Garner
- Raleigh East Airport (FAA LID: 9NC0), Knightdale
- Riley Field Airport (FAA LID: 1NC5), Bunn
- Ron's Field Ultralight Airport (FAA LID: 1NC1), Pittsboro
- Triple W Airport (ICAO: K5W5, FAA LID: 5W5), Raleigh
- Womble Field Airport (FAA LID: 3NC9), Chapel Hill
Heliports
These licensed heliports serve the Research Triangle region:

- Betsy Johnson Memorial Hospital Heliport (FAA LID: NC96), Dunn—publicly owned; medical service
- Duke University North Heliport (ICAO: NC92, FAA LID: NC92), Durham—privately owned; public medical service
- Garner Road Heliport (FAA LID: 3NC2), Raleigh—publicly owned; state government service
- Holly Green Heliport (FAA LID: 83NC), Durham—private
- Sky-5 Heliport (FAA LID: 2NC3), Raleigh—private, owned by Sky-5 Inc. (WRAL-TV)
- Sprint MidAtlantic Telecom Heliport (FAA LID: 11NC), Youngsville—private; corporate service
- Wake Medical Center Heliport (FAA LID: 0NC4), Raleigh—publicly owned; medical service
- Western Wake Medical Center Heliport (FAA LID: 04NC), Cary—publicly owned; medical service
A number of helipads (i.e. marked landing sites not classified under the FAA LID system) also serve a variety of additional medical facilities (such as UNC Hospitals in Chapel Hill), as well as private, corporate and governmental interests, throughout the region.
Rail
Amtrak serves the region with the Silver Meteor, Silver Star, Palmetto, Carolinian, and Piedmont routes.
| Station\Route | Silver Meteor | Silver Star | Palmetto | Carolinian | Piedmont |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Selma (SSM) | X | X | |||
| Fayetteville (FAY) | X | X | |||
| Southern Pines (SOP) | X | ||||
| Raleigh (RGH) | X | X | X | ||
| Cary (CYN) | X | X | X | ||
| Durham (DNC) | X | X |
Shopping
Notable shopping centers and malls:

Super-regional enclosed malls
- Triangle Town Center and Commons (Raleigh; 1,431,091 ft²) (opened 2002)
- The Streets at Southpoint (Durham; 1,336,000 ft²) (opened 2002)
- Crabtree Valley Mall (Raleigh; 1,326,000 ft²) (opened 1972)
- Cary Towne Center (Cary; 914,252 ft²) (opened 1979, closed 2021)
- Northgate Mall (Durham; 857,099 ft²) (opened 1960, enclosed 1972, closed 2020)
Major shopping centers
- Crossroads Plaza (Cary; 1,300,000 ft²)
- Village District (Raleigh; 656,000 ft²)
- Carolina Premium Outlets (Smithfield; 440,000 ft²)
- University Place (Chapel Hill; 366,000 ft²)
- Carr Mill Mall (Carrboro; 86,000 ft²)
- Tanger Outlet Center (Mebane; 317,000 ft²)
- North Hills Mall & Plaza (Raleigh)
Entertainment
Film festivals and events:
- Full Frame Documentary Film Festival – Durham
- North Carolina Gay & Lesbian Film Festival – Durham
Notable performing arts and music venues:
- The Time Warner Cable Music Pavilion at Walnut Creek – Raleigh
- Red Hat Amphitheater – downtown Raleigh
- Koka Booth Amphitheatre at Regency Park – Cary
- Progress Energy Center for the Performing Arts – downtown Raleigh
- PNC Arena – Raleigh
- Durham Performing Arts Center – Durham
- Carolina Theatre – Durham
Theatre and dance events:
- American Dance Festival – Durham
Music festivals:
- Hopscotch Music Festival – Raleigh
- Moogfest – Durham
- ProgDay – Chapel Hill
Movie theatres:
- Alamo Drafthouse Cinema
Museums
| Greater Raleigh metropolitan area, North Carolina museums | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Museum name | Image | City | Type | Notes |
| Ackland Art Museum |  | Chapel Hill | Art | |
| Artspace | Raleigh | Art | ||
| Ayr Mount | .jpg.webp) | Hillsborough | History | |
| Bennett Place State Historic Site | Durham | History | ||
| Carolina Basketball Museum | Chapel Hill | Sports | ||
| Carolina Tiger Rescue | Pittsboro | Science | ||
| Contemporary Art Museum of Raleigh |  | Raleigh | Art | |
| Duke Homestead | Durham | History | ||
| Joel Lane Museum House | Raleigh | History | ||
| Kidzu Children's Museum | Chapel Hill | Children | ||
| Legends of Harley Drag Racing Museum | Raleigh | Sports | ||
| Marbles Kids Museum |  | Raleigh | Children | formerly Exploris |
| Meredith College Galleries | Raleigh | Art | ||
| Mordecai Mansion |  | Raleigh | History | |
| Morehead Planetarium and Science Center |  | Chapel Hill | Science | home to astronaut training for years |
| Museum of Life and Science | Durham | Science | includes small outdoor zoo | |
| North Carolina Museum of Art |  | Raleigh | Art | expanded in 2010 |
| North Carolina Museum of History |  | Raleigh | History | also home to North Carolina Sports Hall of Fame |
| North Carolina Museum of Natural Science |  | Raleigh | Science | annual BugFest and Astronomy Days |
| Raleigh City Museum | Raleigh | History | ||
| North Carolina State Capitol |  | Raleigh | History | |
| North Carolina State University Insect Museum | Raleigh | Science | ||
| Nasher Museum of Art |  | Durham | Art | |
| NCCU Art Museum | Raleigh | Art | ||
| Page-Walker Arts & History Center | Cary | History | ||
Media
The area is part of the Raleigh–Durham–Fayetteville television designated media area and is the 25th-largest in the country with 1,135,920 households (2014) included in that area and the second largest television market in North Carolina.[17] It is part of the Raleigh–Durham Nielsen Audio radio market (code 115) and is the 42nd-largest in the country with a population of 1,365,900.[18]
The Raleigh–Durham–Fayetteville market is defined by Nielsen as including Chatham, Cumberland, Dunn, Durham, Granville, Halifax, Harnett, Hoke, Johnston, Lee, Moore, Northampton, Orange, Robeson, Vance, Wake, Warren, Wayne, and Wilson Counties, along with parts of Franklin County.[19]
Print
Numerous newspapers and periodicals serve the Triangle market.
Paid and subscription
- The News & Observer, the major daily Raleigh newspaper and the region's largest, with a significant regional and statewide readership (especially to the east of the Triangle)
- The Herald-Sun, the major daily Durham newspaper
- Garner News, the weekly community newspaper for suburban Garner in southern Wake County
- The Apex Herald, the weekly community newspaper for suburban Apex in western Wake County
- Holly Springs Sun, the weekly community newspaper for suburban Holly Springs in southwestern Wake County
- Butner-Creedmoor News The Weekly community newspaper for southern Granville County and surrounding areas
- Cleveland Post, the weekly community newspaper for suburban Cleveland and nearby northwestern Johnston and southern Wake Counties
- Fuquay-Varina Independent, the weekly community newspaper for suburban Fuquay-Varina in southwestern Wake County
- The Wake Weekly, a weekly community newspaper serving suburban Wake Forest, northern Wake County and southern Franklin County
- The Chatham Journal, the weekly community newspaper for suburban Pittsboro and surrounding Chatham County
- The Clayton News-Star, a weekly community newspaper for suburban Clayton and western Johnston County
- The Daily Record, the daily community newspaper for suburban Dunn and surrounding Harnett County
- The Courier-Times, the semiweekly community newspaper for suburban Roxboro and Person County
- The Triangle Business Journal, a weekly regional economic journal
- Cary Magazine, a bi-monthly magazine for Cary and western Wake County
- Chapel Hill Magazine, a bi-monthly magazine that serves 12,500 households and 1,600 businesses of Chapel Hill, Carrboro, Hillsborough and northern Chatham County
Free
- The Independent Weekly, a free weekly regional independent journal published in Durham
- The Carolina Journal, a monthly free regional newspaper published in Raleigh
- The Raleigh Downtowner, a free monthly magazine for downtown Raleigh and environs
- The Raleigh Hatchet, a free monthly magazine
- The Daily Tar Heel, the free weekday (during the regular academic year) student newspaper at UNC-Chapel Hill
- Technician, the free weekday (during the regular academic year) student newspaper at NC State University in Raleigh
- The Chronicle, a free daily newspaper for (but independent of) Duke University and its surrounding community in Durham
- The Blotter, a free monthly regional literary journal
- Fifteen-501, a free magazine for the Durham–Chapel Hill area (named for nearby U.S. Route 15-501)
- Acento Latino, a free Spanish-language weekly regional newspaper published in Raleigh
Online only
- The Cary Citizen, a free daily news source for the greater Cary and western Wake County area
- The Raleigh Telegram, a free daily news source for the greater Raleigh area
- The Wake Forest Gazette, a free weekly news site for items of local Wake Forest interest
Broadcast
The Triangle is part of the Raleigh–Durham–Fayetteville Designated Market Area for broadcast television. As of 2015–16, the area was the 25th-largest in the country. This area includes these television stations:
- WUNC-TV (4, Chapel Hill), PBS member station and flagship station of the PBS North Carolina television network, owned by the University of North Carolina system
- WRAL-TV (5, Raleigh), NBC affiliate owned by Capitol Broadcasting Company
- WTVD (11, Durham), ABC O&O owned by ABC Owned Television Stations
- WNCN (17, Goldsboro), CBS affiliate owned by Nexstar Media Group
- WLFL (22, Raleigh), CW affiliate owned by Sinclair Broadcast Group
- WTNC-LD (26, Durham), UniMás O&O owned by TelevisaUnivision
- WRDC (28, Durham), MyNetworkTV affiliate owned by Sinclair Broadcast Group
- WRAY-TV (30, Wilson), TCT O&O owned by Tri-State Christian Television
- WUVC-DT (40, Fayetteville), Univision O&O owned by TelevisaUnivision
- WRPX-TV (47, Rocky Mount) and WFPX-TV (62, Fayetteville), both Ion Television O&Os owned by Scripps Networks
- WRAZ-TV (50, Raleigh), Fox affiliate owned by Capitol Broadcasting Company
Cable
Raleigh is home to the Research Triangle Region bureau of the regional cable TV news channel Spectrum News 1 North Carolina.
Radio
The Triangle is home to North Carolina Public Radio, a public radio station/NPR provider that brings in listeners around the country. Raleigh and a large part of the Triangle area is Arbitron radio market #43. Stations include:
|
FM stations:
|
AM stations:
|
Map of the Triangle
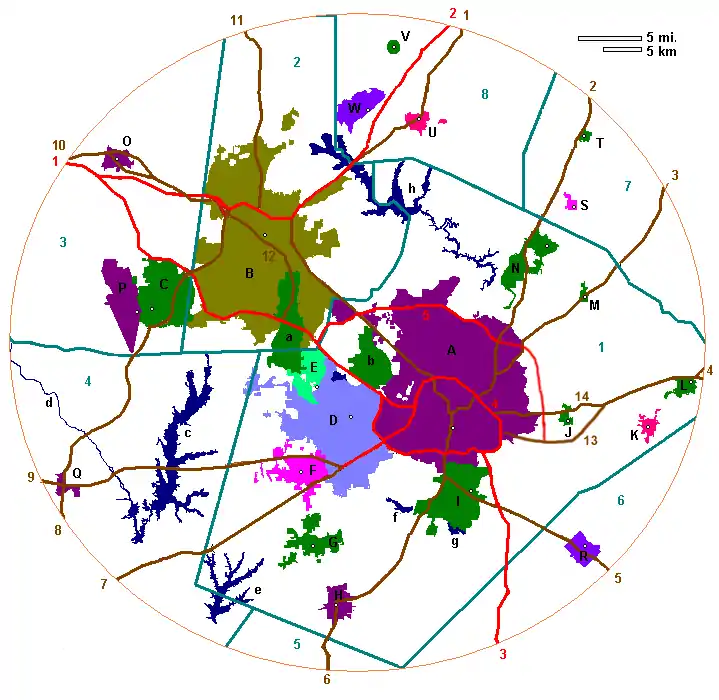
Primary cities and towns
A – Raleigh |
Counties
1 – Wake County Parks and bodies of water
a – Research Triangle Park |
Interstate highways
1 – I-40/I-85 Other major highways
1 – US 15 |
See also
- Piedmont Atlantic
- Piedmont Crescent
- Piedmont Triad
References
- "Metropolitan and Micropolitan Statistical Areas Population Totals: 2010–2019". U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved 2020-03-29.
- Nielsen Station Index, Viewers in Profile, Raleigh–Durham (Fayetteville), NC May 2010
- Rakich, Ryan Best, Aaron Bycoffe and Nathaniel (2021-08-09). "What Redistricting Looks Like In Every State - North Carolina". FiveThirtyEight. Retrieved 2022-05-23.
- "Counties - Research Triangle Regional Partnership". Retrieved 2020-08-24.
- "NC Regional Councils Map". NC Association of Regional Councils of Government. Retrieved 2019-06-24.
- OMB Bulletin No. 18-04 (PDF) (Report). Office of Management and Budget. September 14, 2018. p. 142. Retrieved 2020-02-06.
- OMB Bulletin No. 18-03 (PDF) (Report). Office of Management and Budget. April 10, 2018. p. 141. Retrieved 2020-02-06.
- "County Population Totals and Components of Change: 2010-2020". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2021-05-25.
- "Raleigh-Durham-Cary, NC CSA". censusreporter.org. Retrieved June 22, 2022.
- "District Facts / Overview". wcpss.net.
- Snipes, Cameron (June 17, 2009). "Brookings report ranks Raleigh–Cary strongest metro in N.C." Triangle Business Journal. Retrieved 2009-06-23.
- "North Carolina Hospitals and Medical Centers". The Agape Center. Retrieved 2008-05-30.
- "Regional Transit Needs: Next Steps". TTA Web Site. Retrieved 2007-07-04.
- "Nonstop Destinations Raleigh–Durham International Airport". Retrieved 19 October 2017.
- FAA Airport Form 5010 for RDU PDF, effective February 1, 2018.
- "Raleigh–Durham International Airport".
- "Local Television Market Universe Estimates" (PDF).
- "Spring 2011 Market Survey Schedule & Population Ranking". Arbitron.
- "Raleigh–Durham DMA". Time Warner. Archived from the original on 2011-10-17.
External links
- Greater Raleigh Chamber of Commerce
- Research Triangle Regional Partnership
- Triangle Wiki – Local wiki for the Triangle

