Sea Islands
The Sea Islands are a chain of tidal and barrier islands on the Atlantic Ocean coast of the Southeastern United States. Numbering over 100, they are located between the mouths of the Santee and St. Johns Rivers along the coast of South Carolina, Georgia, and Florida. The largest of these is Johns Island in South Carolina. The Sea Islands, particularly Sapelo Island, are home to the Gullah people. The islands are very acutely threatened by sea level rise due to Climate Change.[1]
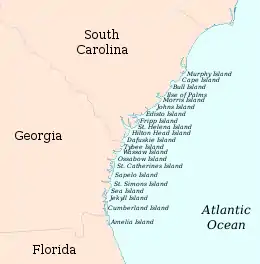 Map of the Sea islands | |
 Sea Islands | |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | Atlantic Ocean |
| Total islands | Over 100 |
| Administration | |
United States | |
History
Settled by indigenous cultures over thousands of years, the islands were selected by Spanish colonists as sites for founding of colonial missions. Historically the Spanish influenced the Guale and Mocama chiefdoms by establishing Christian missions in their major settlements, from St. Catherine's Island south to Fort George Island (at present-day Jacksonville, Florida).[2] The area was home to multiple plantations; in 1863 Fanny Kemble published Journal of a Residence on a Georgian Plantation in 1838–1839 about her experience on her husband's plantations in St. Simon's Island and Butler Island.[3]
After President Abraham Lincoln's Emancipation Proclamation became effective on January 1, 1863, more than 5,000 slaves on Union-occupied islands obtained their freedom.[4]
Major Sea Islands
Charleston County
- Bull Island
- Dewees Island
- Edisto Island (also in Colleton County)
- Folly Island
- Isle of Palms
- James Island
- Johns Island
- Kiawah Island
- Morris Island
- Seabrook Island
- Sullivan's Island
- Wadmalaw Island
- Yonges Island
Colleton County
- Bear Island
Beaufort County
- Bay Point Island
- Cane Island
- Cat Island
- Coosaw Island
- Dataw Island
- Daufuskie Island
- Distant Island
- Fripp Island
- Gibbes Island
- Harbor Island
- Hilton Head Island
- Horse Island
- Hunting Island
- Lady's Island
- Morgan Island
- Parris Island
- Port Royal Island
- Pritchards Island[5]
- St. Helena Island
- St. Phillips Island
- Spring Island
Chatham County
- Tybee Island
- Little Tybee Island
- Cockspur Island
- Wilmington Island
- Talahi Island
- Whitemarsh Island
- Oatland Island
- Skidaway Island
- Isle of Hope
- Williamson Island
- Dutch Island
- Burnside Island
- Wassaw Island
- Ossabaw Island
Liberty County
- St. Catherine's Island
- Isle of Wight
- Hampton Island
McIntosh County
- Blackbeard Island
- Sapelo Island
Glynn County
- Jekyll Island
- Little St. Simons Island
- St. Simons Island
- Sea Island
Camden County
- Cumberland Island
Nassau County
- Amelia Island
Duval County
- Big Talbot Island
- Little Talbot Island
St. Johns County
- Anastasia Island
See also
- Sea Island cotton
- Carolina Gold rice
- Sea Island red peas
References
- https://www.nationalgeographic.com/environment/article/rising-seas-threaten-the-gullah-geechee-culture-heres-how-theyre-fighting-back
- "Mission Santa Catalina de Guale", New Georgia Encyclopedia, 2008, accessed 13 May 2010
- "Journal of a Residence on a Georgian Plantation in 1838–1839". Encyclopedia.com. Retrieved 2022-07-05.
- William Klingaman, Abraham Lincoln and the Road to Emancipation, 1861-1865 (NY: Viking Press, 2001), p. 234
- "University of South Carolina Beaufort - Pritchards Island". www.uscb.edu. Archived from the original on 2 September 2006. Retrieved 12 January 2022.
Further reading
- Gibson, Count D. (1948). Sea Islands of Georgia—Their Geologic History. Athens, Georgia: University of Georgia Press. ISBN 9780820334943. Retrieved 3 July 2019.
