Standard-definition television
Standard-definition television (SDTV, SD, often shortened to standard definition) is a television system which uses a resolution that is not considered to be either high or enhanced definition. "Standard" refers to it being the prevailing specification for broadcast (and later, cable) television in the mid- to late-20th century, and compatible with legacy analog broadcast systems.
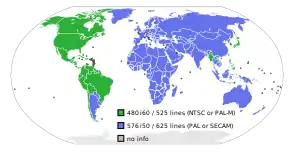
The two common SDTV signal types are 576i, with 576 interlaced lines of resolution, derived from the European-developed PAL and SECAM systems, and 480i based on the American NTSC system. Common SDTV refresh rates are 25, 29.97 and 30 frames per second.[lower-alpha 1] Both systems use a 4:3 aspect ratio.
Standards that support digital SDTV broadcast include DVB, ATSC, and ISDB. The last two were originally developed for HDTV, but are also used for their ability to deliver multiple SD video and audio streams via multiplexing. In North America, digital SDTV is broadcast in the same 4:3 aspect ratio as NTSC signals, with widescreen content often being center cut.[1] However, the aspect ratio of widescreen content may be preserved in a 4:3 frame through letterboxing. In other parts of the world that used the PAL or SECAM color systems, digital standard-definition television is now usually shown with a 16:9 aspect ratio, with the transition occurring between the mid-1990s and late-2000s depending on region. Older programs with a 4:3 aspect ratio are broadcast with a flag that switches the display to 4:3.[lower-alpha 2]
Digital SDTV eliminates the ghosting and noisy images associated with analog systems. However, if the reception has interference or is poor, where the error correction cannot compensate one will encounter various other artifacts such as image freezing, stuttering or dropouts from missing intra-frames or blockiness from missing macroblocks.[lower-alpha 3]
Pixel aspect ratio
The table below summarizes pixel aspect ratios for the scaling of various kinds of SDTV video lines.
| Video format | Display aspect ratio (DAR) | Resolution | Pixel aspect ratio (PAR) | After horizontal scaling |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 480i | 4:3 | 704 × 480 (horizontal blanking cropped) | 10:11 | 640 × 480 |
| 720 × 480 (full frame) | 655 × 480 | |||
| 480i | 16:9 | 704 × 480 (horizontal blanking cropped) | 40:33 | 854 × 480 |
| 720 × 480 (full frame) | 873 × 480 | |||
| 576i | 4:3 | 704 × 576 (horizontal blanking cropped) | 12:11 | 768 × 576 |
| 720 × 576 (full frame) | 788 × 576 | |||
| 576i | 16:9 | 704 × 576 (horizontal blanking cropped) | 16:11 | 1024 × 576 |
| 720 × 576 (full frame) | 1050 × 576 |
The pixel aspect ratio is the same for 720- and 704-pixel resolutions because the visible image (be it 4:3 or 16:9) is contained in the center 704 horizontal pixels of the digital frame. In the case of a digital video line having 720 horizontal pixels (including horizontal blanking), only the center 704 pixels contain the actual 4:3 or 16:9 image, and the 8-pixel-wide stripes on either side are called nominal analog blanking or horizontal blanking and should be discarded when displaying the image. Nominal analog blanking should not be confused with overscan, as overscan areas are part of the actual 4:3 or 16:9 image.
For SMPTE 259M-C compliance, an SDTV broadcast image is scaled to 720 pixels wide[lower-alpha 4] for every 480 NTSC (or 576 PAL) lines of the image with the amount of non-proportional line scaling dependent on either the display or pixel aspect ratio. The display ratio for broadcast widescreen is commonly 16:9,[lower-alpha 5] the display ratio for a traditional or letterboxed broadcast is 4:3.[lower-alpha 6]
An SDTV image outside the constraints of the SMPTE standards requires no non-proportional scaling with 640 pixels[lower-alpha 7] for every line of the image. The display and pixel aspect ratio is generally not required with the line height defining the aspect. For widescreen 16:9, 360 lines define a widescreen image and for traditional 4:3, 480 lines define an image.
See also
- Digital Audio Broadcasting
- Moving Picture Experts Group
- ISDB-T International
- Rec. 601 (aka CCIR 601)
Notes
- 50 and 60 rates are sometimes used as frame-doubled versions of 25 and 30 rates to mitigate interlace artifacts.
- Some broadcasters prefer to reduce the horizontal resolution by anamorphically scaling the video into a pillarbox.
- The audio encoding is the last to suffer loss due to the lower bandwidth requirements.
- Only 704 center pixels contain the actual image and 16 pixels are reserved for horizontal blanking though a number of broadcasters fill the whole 720 frame.
- Pixel aspect ratio of 40:33 for anamorphic
- Pixel aspect ratio of 10:11
- Defined by the adopted IBM VGA standard