532
Year 532 (DXXXII) was a leap year starting on Thursday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Second year after the Consulship of Lampadius and Probus (or, less frequently, year 1285 Ab urbe condita). The denomination 532 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
| Millennium: | 1st millennium |
|---|---|
| Centuries: | |
| Decades: | |
| Years: |
| 532 by topic |
|---|
| Leaders |
|
| Categories |
|
| Gregorian calendar | 532 DXXXII |
| Ab urbe condita | 1285 |
| Assyrian calendar | 5282 |
| Balinese saka calendar | 453–454 |
| Bengali calendar | −61 |
| Berber calendar | 1482 |
| Buddhist calendar | 1076 |
| Burmese calendar | −106 |
| Byzantine calendar | 6040–6041 |
| Chinese calendar | 辛亥年 (Metal Pig) 3228 or 3168 — to — 壬子年 (Water Rat) 3229 or 3169 |
| Coptic calendar | 248–249 |
| Discordian calendar | 1698 |
| Ethiopian calendar | 524–525 |
| Hebrew calendar | 4292–4293 |
| Hindu calendars | |
| - Vikram Samvat | 588–589 |
| - Shaka Samvat | 453–454 |
| - Kali Yuga | 3632–3633 |
| Holocene calendar | 10532 |
| Iranian calendar | 90 BP – 89 BP |
| Islamic calendar | 93 BH – 92 BH |
| Javanese calendar | 419–420 |
| Julian calendar | 532 DXXXII |
| Korean calendar | 2865 |
| Minguo calendar | 1380 before ROC 民前1380年 |
| Nanakshahi calendar | −936 |
| Seleucid era | 843/844 AG |
| Thai solar calendar | 1074–1075 |
| Tibetan calendar | 阴金猪年 (female Iron-Pig) 658 or 277 or −495 — to — 阳水鼠年 (male Water-Rat) 659 or 278 or −494 |
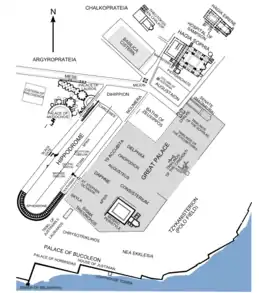
Nika riots in the Hippodrome of Constantinople
Events
Byzantine Empire
- January 11 – Nika riots in Constantinople: Anger among the supporters of the most important chariot teams—the Blues and the Greens—escalates into violence towards the emperor. For the next five days the capital is in chaos. The fires that start during the tumult result in the destruction of much of the city. The insurrection is put down a week later by Belisarius and Mundus; 30,000 people are killed in the Hippodrome.
- February 23 – Emperor Justinian I orders the building of a new Orthodox Christian basilica in Constantinople – the Hagia Sophia. He chooses Isidore of Miletus and Anthemius of Tralles as architects. The material for the construction is brought from all over the empire, such as large stones from quarries in Porphyry, Egypt. More than 10,000 people are employed.
- September – Justinian I signs a peace treaty, the "Eternal Peace", with the Persian king Khosrau I, ending the Iberian War (527-531). Both sides agree to return all occupied territories, and Justinian makes a one-off payment of 110 centenaria (11,000 pounds of gold), as a contribution to the defense of the Caucasus passes.
Europe
- Battle of Autun - The Franks, under command of King Childebert I and his brother Chlothar I, invade the Kingdom of Burgundy. They defeat the Burgundians under King Godomar near Autun (modern France).
Asia
- An Ding Wang commits suicide, and is succeeded by Xiao Wu Di as Chinese emperor of Northern Wei.
- Silla conquers the city-state of Geumgwan Gaya (Korea) during the Three Kingdoms Period.
Arts and sciences
- First year in which the Anno Domini calendar is used for numbering the years.
Religion
- October 17 – Pope Boniface II dies in Rome after a 2-year reign.
Births
- Áedán mac Gabráin, king of Dál Riata (Scotland) (approximate date)
- Guntram, king of Burgundy (approximate date)
- Marius Aventicensis, bishop of Aventicum (d. 596)
- Xiao Mohe, general of the Chen Dynasty and Sui Dynasty (d. 604)
Deaths
- March 3 – Winwaloe, saint and founder of Landévennec Abbey (b.c. 460)
- October 17 – Pope Boniface II
- An Ding Wang, emperor of Northern Wei (b. 513)
- Chang Guang Wang, emperor of Northern Wei
- Ecclesio, bishop of Ravenna (approximate date)
- Erzhu Shilong, official of Northern Wei (b. 500)
- Erzhu Tianguang, general of Northern Wei (b. 496)
- Guntheuc, princess of Burgundy (approximate date)
- Hypatius, Byzantine nobleman (executed)
- Jie Min Di, emperor of Northern Wei (b. 498)
- Pompeius, Byzantine politician (executed)
- Sabbas the Sanctified, monk and saint (b. 439)
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.