Blagoevgrad Province
Blagoevgrad Province (Bulgarian: област Благоевград, oblast Blagoevgrad or Благоевградска област, Blagoevgradska oblast), also known as Pirin Macedonia or Bulgarian Macedonia (Bulgarian: Пиринска Македония; Българска Македония), (Pirinska Makedoniya or Bulgarska Makedoniya) is a province (oblast) of southwestern Bulgaria. It borders four other Bulgarian provinces to the north and east, the Greek region of Macedonia to the south, and North Macedonia to the west. The province has 14 municipalities with 12 towns. Its principal city is Blagoevgrad, while other significant towns include Bansko, Gotse Delchev, Melnik, Petrich, Razlog, Sandanski, and Simitli.
Blagoevgrad Province
Област Благоевград | |
|---|---|
 Location of Blagoevgrad Province in Bulgaria | |
| Country | Bulgaria |
| Capital | Blagoevgrad |
| Municipalities | 14 |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Biser Mihaylov |
| Area | |
| • Total | 6,449.47 km2 (2,490.15 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 555 m (1,821 ft) |
| Population (Census February 2011)[1] | |
| • Total | 323,552 |
| • Density | 50/km2 (130/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (EET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+3 (EEST) |
| License plate | E |
| Website | www |
Geography and climate
Geography
The province has a territory of 6,449.5 km2 (2,490.2 sq mi) and a population of 323,552[1] (as of 2011). It is the third largest in Bulgaria after Burgas and Sofia Provinces and comprises 5.8% of the country's territory. Blagoevgrad Province includes the mountains, or parts of, Rila (highest point of the Balkans — Musala summit, 2925 m), Pirin (highest point — Vihren summit, 2914 m), the Rhodopes, Slavyanka, Belasitsa, Vlahina, Maleshevo, Ograzhden and Stargach. There are two major rivers — Struma River and Mesta River — with population concentrations along their valleys, which are also the main transport corridors.
Climate
The climate varies from temperate continental to Mediterranean in the southernmost parts. Natural resources are timber, mineral springs, coal, construction materials, including marble and granite. The beautiful and preserved environment is widely considered an important resource. A number of national parks and protected territories care for the biodiversity. Arable land is 38.8% and forests constitute 52% of the province's territory.
History
The Balkan Wars of 1912–1913 saw the annexation of the area to the Bulgarian state. Before the wars, it had been under Ottoman rule for over five centuries.
Municipalities
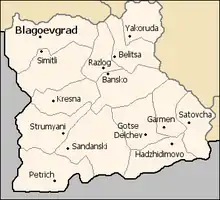
The Blagoevgrad province (област, oblast) contains 14 municipalities (singular: община, obshtina - plural: общини, obshtini). The following table shows the names of each municipality in English and Cyrillic, the main town (in bold) or village, and the population of each as of 2011.
| Municipality | Cyrillic | Pop.[1] census 2011 |
Town/Village | Pop.[1] census 2011 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bansko | Банско | 13,125 | Bansko | 8,562 |
| Belitsa | Белица | 9,927 | Belitsa | 3,362 |
| Blagoevgrad | Благоевград | 77,441 | Blagoevgrad | 70,881 |
| Garmen | Гърмен | 14,981 | Garmen | 1,982 |
| Gotse Delchev | Гоце Делчев | 31,236 | Gotse Delchev | 19,219 |
| Hadzhidimovo | Хаджидимово | 10,091 | Hadzhidimovo | 2,730 |
| Kresna | Кресна | 5,441 | Kresna | 3,470 |
| Petrich | Петрич | 54,006 | Petrich | 28,902 |
| Razlog | Разлог | 20,598 | Razlog | 11,960 |
| Sandanski | Сандански | 40,470 | Sandanski | 26,472 |
| Satovcha | Сатовча | 15,444 | Satovcha | 2,434 |
| Simitli | Симитли | 14,283 | Simitli | 6,674 |
| Strumyani | Струмяни | 5,778 | Strumyani | 998 |
| Yakoruda | Якоруда | 10,731 | Yakoruda | 5,792 |
Economy
The region is characterized with diversified economic branch structure: food and tobacco processing industries, agriculture, tourism, transport and communications, textile industry, timber and furniture industries, iron processing and machinery industry, construction materials industry, as well as pharmaceuticals, plastics, paper and shoes production. Approximately 10% of the population is unemployed (close to the national average). There are 4 major hospitals in the province.
With its railway line and road connection, the region forms the heart of the land-based trading route between northern Greece, Bulgaria and Romania. Since the early 2000s the province enjoys a mini boom in trade from thousands Greek day-trippers from across the border, purchasing cheaper goods and services (dental, opticians, etc.). Since the early 1990s, the region has also attracted Greek manufacturers who moved their production line from Greece, especially to Petrich. It was an important tourist destination during the communist years for East Germans and is slowly picking up again. The unique town of Melnik was once a wealthy centre built on the back of exiled phanariots from Constantinople. Now it is a centre for wine production and offers eco-tourism.
Infrastructure remains relatively underdeveloped, especially regarding road and rail communications. It remains an important target for potential EU funding. There are two major infrastructural projects in the region. The Struma motorway, which is planned to connect the capital Sofia with the Greek border and the port of Thessaloniki, is going to run through the valley of the Sruma River, and will be ready in a few years. The second project is the airport of Bansko. The cost is currently estimated at around €30,000,000.
Culture, education and monuments
Historical and archaeological monuments include the ruins of antique Thracian and Roman settlements, Early Christian basilicas, medieval Byzantine and Bulgarian towns, monasteries and fortresses, as well as many preserved buildings and whole villages — examples of the architecture from the Ottoman period (like Melnik, the Rozhen Monastery and Bansko).
A theatre, a library with 345,000 tomes, and an opera house are situated in the provincial centre, Blagoevgrad. There are art galleries in Bansko, Blagoevgrad and Sandanski. Many small cultural institutions, chitalishta, are dispersed around the province. The Pirin State Ensemble is the most prominent among the numerous folklore and music bands. There are 10 museums in the province that preserve the rich historical, ethnographic and archaeological heritage. Cultural events include the Theatre Festival in Blagoevgrad, the Jazz Festival in Bansko and the Melnik Evenings of Poetry.
The Southwestern University and the American University in Bulgaria are situated in Blagoevgrad; the latter is the second largest American university campus in Europe and is located in the former headquarters of the communist party. Annually the city draws around 10,000 students from the country and abroad. The number of schools in the province is 182.
Notable people from Blagoevgrad Province
A number of the province's towns were renamed in honor of major figures such as Sandanski (after Yane Sandanski).
- Paisiy Hilendarski (1722–1773)
- Neofit Rilski (1793–1881)
- Georgi Izmirliev (1851–1876)
- Boris Sarafov (1872–1907)
- Yane Sandanski (1872–1915)
- Nikola Vaptsarov (1909–1942)
- Georgi Pirinski (1948)
- Rosen Plevneliev (1964)
Demographics
The province had a population of 323,552 according to the 2011 census, of which 49.3% were male and 50.9% were female.[2][3][4][5]
The following table represents the change of the population in the province after World War II:
| Blagoevgrad Province | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | 1946 | 1956 | 1965 | 1975 | 1985 | 1992 | 2001 | 2005 | 2007 | 2009 | 2011 |
| Population | 252,908 | 281,015 | 302,503 | 322,974 | 345,942 | 351,637 | 341,173 | 333,577 | 329,309 | 327,885 | 323,552 |
| Sources: National Statistical Institute,[2] „Census 2001“,[3] „Census 2011“,[4] „pop-stat.mashke.org“,?? | |||||||||||
Ethnic groups
Total population (2011 census): 323 552
Ethnic groups (2011 census):[6]
Identified themselves: 283,556 persons:
- Bulgarians: 251,097 (88,55%)
- Turks: 17,027 (6,0%)
- Romani: 9,739 (3,43%)
- Others and indefinable: 5,693 (2,01%)
- Unspecified: 40,524 (this figure is not included in the percentage.)
The issue of the current number of ethnic Macedonians in the province is complicated. In 2008, the local ethnic Macedonian political activist Stojko Stojkov, head of the United Macedonian Organization Ilinden–Pirin, claimed the number of the native ethnic Macedonians to be between 5,000 and 10,000 in the whole of Bulgaria.[7] However, in 2017 there were 18,000 ethnic Macedonian nationals registered as residents only in the Blagoevgrad Municipality. Their number in the whole of the province is higher.[8] They are citizens of the Republic of North Macedonia, but have also Bulgarian citizenship, based on declared Bulgarian ethnic origin.[9] The ethnic Bulgarian population in the province, has on the other hand, also a regional Macedonian identity.[10] Indeed it is said there is no clear ethnic difference between both groups.[11] According to the 2011 census only 561 persons (0.2%) declared themselves as ethnic Macedonians in Blagoevgrad Province.
Languages
Mother tongues in the province according to 2001 census:[12]
306,118 Bulgarian (89.7%),
19,819 Turkish (5.8%),
9,232 Romani (2.7%) and 6004 others and unspecified (1.6%).
Religion
Religious adherence in the province according to 2001 census:[14]
| Census 2001 | ||
|---|---|---|
| religious adherence | population | % |
| Orthodox Christians | 268,968 | 78.84% |
| Muslims | 62,431 | 18.30% |
| Protestants | 1,546 | 0.45% |
| Roman Catholics | 277 | 0.08% |
| Other | 933 | 0.27% |
| Religion not mentioned | 7,018 | 2.06% |
| total | 341,173 | 100% |
Most Muslims in the province are Bulgarian Muslims, also called Pomaks. That makes Blagoevgrad Province together with Smolyan Province and the area around Velingrad one of the few places where Bulgarian Muslims make up the majority of the Muslims while in Bulgaria general most Muslims are from Turkish background.
Sport
Blagoevgrad Province is currently one of the best-represented provinces in Bulgarian football, with 3 teams playing in the Bulgarian A PFG (second only to Sofia with 4) — FC Vihren Sandanski, PFC Belasitsa Petrich and PFC Pirin 1922 Blagoevgrad. One more team from the province, PFC Pirin Blagoevgrad (as distinct from Pirin 1922), began the 2005/06 season in the highest Bulgarian division, but disbanded shortly afterwards due to financial problems.
Owing to the alpine features and accessible location, the northern and eastern regionof Blagoevgrad Province is also a centre of winter sports. The main centre is Bansko which is becoming a leading skiing resort at European level with rapidly rising property prices.
Gallery
 Tevno Vasilashko Lake in Pirin
Tevno Vasilashko Lake in Pirin Kamenitsa Peak and lake Tevno ezero in Pirin
Kamenitsa Peak and lake Tevno ezero in Pirin Sinanitsa Peak in Pirin
Sinanitsa Peak in Pirin Edelweisses under the Koncheto ridge in Pirin
Edelweisses under the Koncheto ridge in Pirin Dzhengal Peak in Pirin up-close in late April
Dzhengal Peak in Pirin up-close in late April Vihren Peak in Pirin mountain
Vihren Peak in Pirin mountain The defeat of the army of Tsar Samuil of Bulgaria in the medieval Battle of Kleidion
The defeat of the army of Tsar Samuil of Bulgaria in the medieval Battle of Kleidion The Rozhen Monastery from the outside
The Rozhen Monastery from the outside The Church of the Holy Trinity in Bansko
The Church of the Holy Trinity in Bansko Genеral Ivan Tsonchev's revolutionary band
Genеral Ivan Tsonchev's revolutionary band Lieutenant Boris Sarafov's revolutionary band
Lieutenant Boris Sarafov's revolutionary band Monument to the perished Bulgarian soldiers during World War I in Petrich
Monument to the perished Bulgarian soldiers during World War I in Petrich Bansko Ski Zone as seen from Razlog
Bansko Ski Zone as seen from Razlog Petrich at night
Petrich at night
See also
- Provinces of Bulgaria
- Municipalities of Bulgaria
- List of cities and towns in Bulgaria
- List of villages in Blagoevgrad Province
References
- Census 2011
- (in Bulgarian) Bulgarian National Statistical Institute - 2011 census Archived 2011-07-14 at the Wayback Machine
- „WorldCityPopulation“
- „pop-stat.mashke.org“
- (in Bulgarian) Population by 01.02.2011 by Area and Sex Archived 2011-04-08 at the Wayback Machine from Bulgarian National Statistical Institute: Preliminary results of Census 2011
- Population by province, municipality, settlement and ethnic identification, by 01.02.2011; Bulgarian National Statistical Institute Archived 2013-05-21 at the Wayback Machine (in Bulgarian)
- source
- Over 70,000 Macedonian nationals have received Bulgarian citizenship between 2001 and 2018, or roughly 3.5% of the population.
- в-к Труд, Март 26, 2017, В Благоевградска община има регистрирани 18 хиляди македонци.
- Center for Documentation and Information on Minorities in Europe - Southeast Europe (CEDIME-SE) - Macedonians of Bulgaria
- Day, Alan John; East, Roger; Thomas, Richard (2002). Political and economic dictionary of Eastern Europe. Routledge. p. 94. ISBN 1-85743-063-8.
- (in Bulgarian) Population to 01.03.2001 by District and Mother Tongue from Bulgarian National Statistical Institute: Census 2001 Archived 2017-11-10 at the Wayback Machine
- ""Religious composition: 2011 census"". pop-stat.mashke.org. Retrieved 29 June 2018.
- (in Bulgarian) Religious adherence in Bulgaria - census 2001 Archived 2010-09-07 at the Wayback Machine
Sources
- Who are the Macedonians? by Hugh Poulton. London: 1995.
External links
- Blagoevgrad Province — information on all of cities and villages
- Provincial administration of Blagoevgrad Province
- Municipality of Blagoevgrad
- Municipality of Gotse Delchev Archived 2008-10-04 at the Wayback Machine
- Municipality of Sandanski Archived 2011-08-09 at the Wayback Machine
- Municipality of Petrich
- Official website of Bansko
- Pirin National Park
- Rila National Park
- Neofit Rilski Southwestern University
- American University in Bulgaria
- Pirin Folk song and dances State Ensemble
- Historical and Architectural Reserve Village Kovachevitsa Archived 2008-01-11 at the Wayback Machine
- Rozhen Monastery St. Nativity of Virgin Mary
- Bansko Ski Zone
- Beautiful Blagoevgrad Online
- Kordopulova House in Melnik Archived 2019-05-08 at the Wayback Machine
- Radio Blagoevgrad online, regional station of the Bulgarian National Radio (in Bulgarian)
- Informative site about South-Western Bulgaria (in Bulgarian)
- Struma Daily newspaper of South-Western Bulgaria (in Bulgarian)
- Village Dabrava - Blagoevgrad
.svg.png.webp)