Bibliothèque nationale de France
The Bibliothèque nationale de France (French: [biblijɔtɛk nasjɔnal də fʁɑ̃s], 'National Library of France'; BnF) is the national library of France, located in Paris. It is the national repository of all that is published in France and also holds extensive historical collections.
| National Library of France | |
|---|---|
| Bibliothèque nationale de France | |
 | |
%252C_Paris_-_Salle_Ovale.jpg.webp) | |
| Established | 1461[1] |
| Location | Paris, France |
| Collection | |
| Items collected | books, journals, newspapers, magazines, sound and music recordings, patents, databases, maps, stamps, prints, drawings and manuscripts |
| Size | 40.9M items including 15.7M books, 400,000 journals, 900,000 maps, 2M music sheets. 40M web archives equivalent to 1,400 teraoctets [2] |
| Access and use | |
| Access requirements | Open to anyone with a need to use the collections and services |
| Other information | |
| Budget | €254 million[2] |
| Director | Laurence Engel |
| Staff | 2,300 |
| Website | bnf.fr (in French) |
| Map | |
 | |
History
The National Library of France traces its origin to the royal library founded at the Louvre Palace by Charles V in 1368. Charles had received a collection of manuscripts from his predecessor, John II, and transferred them to the Louvre from the Palais de la Cité. The first librarian of record was Claude Mallet, the king's valet de chambre, who made a sort of catalogue, Inventoire des Livres du Roy nostre Seigneur estans au Chastel du Louvre. Jean Blanchet made another list in 1380 and Jean de Bégue one in 1411 and another in 1424. Charles V was a patron of learning and encouraged the making and collection of books. It is known that he employed Nicholas Oresme, Raoul de Presle and others to transcribe ancient texts. At the death of Charles VI, this first collection was unilaterally bought by the English regent of France, the Duke of Bedford, who transferred it to England in 1424. It was apparently dispersed at his death in 1435.[3][4]
Charles VII did little to repair the loss of these books, but the invention of printing resulted in the starting of another collection in the Louvre inherited by Louis XI in 1461. Charles VIII seized a part of the collection of the kings of Aragon.[5] Louis XII, who had inherited the library at Blois, incorporated the latter into the Bibliothèque du Roi and further enriched it with the Gruthuyse collection and with plunder from Milan. Francis I transferred the collection in 1534 to Fontainebleau and merged it with his private library. During his reign, fine bindings became the craze and many of the books added by him and Henry II are masterpieces of the binder's art.[4]
Under librarianship of Jacques Amyot, the collection was transferred to Paris and then relocated on several occasions, a process during which many treasures were lost. Henry IV had it moved to the Collège de Clermont in 1595, a year after the expulsion of the Jesuits from their establishment. In 1604, the Jesuits were allowed to return and the collection was moved to the Cordeliers Convent, then in 1622 to the nearby Confrérie de Saint-Côme et de Saint-Damien on the rue de la Harpe. The appointment of Jacques Auguste de Thou as librarian initiated a period of development that made it the largest and richest collection of books in the world. He was succeeded by his son who was replaced, when executed for treason, by Jérôme Bignon, the first of a line of librarians of the same name. Under de Thou, the library was enriched by the collections of Queen Catherine de Medici. The library grew rapidly during the reigns of Louis XIII and Louis XIV, due in great part to the interest of Minister Jean-Baptiste Colbert, himself a dedicated collector of books.[4]
The site in the Rue de la Harpe becoming inadequate, the library was again moved, in 1666, to two adjacent houses in Rue Vivienne. After Colbert, Louis XIV's minister Louvois also took interest in the library and employed Jean Mabillon, Melchisédech Thévenot and others to procure books from every source. In 1688, a catalogue in eight volumes was compiled.[4] Louvois considered the erection of an opulent building to host it on what would become the Place Vendôme, a project that was however left unexecuted following the minister's death in 1691.
The library opened to the public in 1692, under the administration of Abbott Camille le Tellier de Louvois, the minister's son. The Abbé Louvois was succeeded by Jean-Paul Bignon, who in 1721 seized the opportunity of the collapse of John Law's Mississippi Company. The company had been relocated by Law into the former palace of Cardinal Mazarin around Hôtel Tubeuf, and its failure freed significant space in which the Library would expand (even though the Hotel Tubeuf itself would remain occupied by French East India Company and later by France's financial bureaucracy until the 1820s. Bignon also instituted a complete reform of the library's system. Catalogues were made which appeared from 1739 to 1753 in 11 volumes. The collections increased steadily by purchase and gift to the outbreak of the French Revolution, at which time it was in grave danger of partial or total destruction, but owing to the activities of Antoine-Augustin Renouard and Joseph Van Praet it suffered no injury.[4]
The library's collections swelled to over 300,000 volumes during the radical phase of the French Revolution when the private libraries of aristocrats and clergy were seized. After the establishment of the French First Republic in September 1792, "the Assembly declared the Bibliothèque du Roi to be national property and the institution was renamed the Bibliothèque Nationale. After four centuries of control by the Crown, this great library now became the property of the French people."[3]

A new administrative organization was established. Napoleon took great interest in the library and among other things issued an order that all books in provincial libraries not possessed by the Bibliothèque Nationale should be forwarded to it, subject to replacement by exchanges of equal value from the duplicate collections, making it possible, as Napoleon said, to find a copy of any book in France in the National Library. Napoleon furthermore increased the collections by spoil from his conquests. A considerable number of these books were restored after his downfall. During the period from 1800 to 1836, the library was virtually under the control of Joseph Van Praet. At his death it contained more than 650,000 printed books and some 80,000 manuscripts.[4]
Following a series of regime changes in France, it became the Imperial National Library and in 1868 was moved to newly constructed buildings on the Rue de Richelieu designed by Henri Labrouste. Upon Labrouste's death in 1875 the library was further expanded, including the grand staircase and the Oval Room, by academic architect Jean-Louis Pascal. In 1896, the library was still the largest repository of books in the world, although it has since been surpassed by other libraries for that title.[6] By 1920, the library's collection had grown to 4,050,000 volumes and 11,000 manuscripts.[4]
M. Henri Lemaître, a vice-president of the French Library Association and formerly librarian of the Bibliothèque Nationale ... outlined the story of French libraries and librarians during the German occupation, a record of destruction and racial discrimination. During 1940–1945, more than two million books were lost through the ravages of war, many of them forming the irreplaceable local collections in which France abounded. Many thousands of books, including complete libraries, were seized by the Germans. Yet French librarians stood firm against all threats, and continued to serve their readers to the best of their abilities. In their private lives and in their professional occupations they were in the van of the struggle against the Nazis, and many suffered imprisonment and death for their devotion. Despite Nazi opposition they maintained a supply of books to French prisoners of war. They continued to supply books on various proscribed lists to trustworthy readers; and when liberation came, they were ready with their plans for rehabilitation with the creation of new book centres for the French people on lines of the English county library system.[7]
New buildings

On 14 July 1988, President François Mitterrand announced "the construction and the expansion of one of the largest and most modern libraries in the world, intended to cover all fields of knowledge, and designed to be accessible to all, using the most modern data transfer technologies, which could be consulted from a distance, and which would collaborate with other European libraries". Due to initial trade union opposition, a wireless network was fully installed only in August 2016.
In July 1989, the services of the architectural firm of Dominique Perrault were retained. The design was recognized with the European Union Prize for Contemporary Architecture in 1996. The construction was carried out by Bouygues.[8] Construction of the library ran into huge cost overruns and technical difficulties related to its high-rise design, so much so that it was referred to as the "TGB" or "Très Grande Bibliothèque" (i.e. "Very Large Library", a sarcastic allusion to France's successful high-speed rail system, the TGV).[9] After the move of the major collections from the Rue de Richelieu, the National Library of France was inaugurated on 15 December 1996.[10]
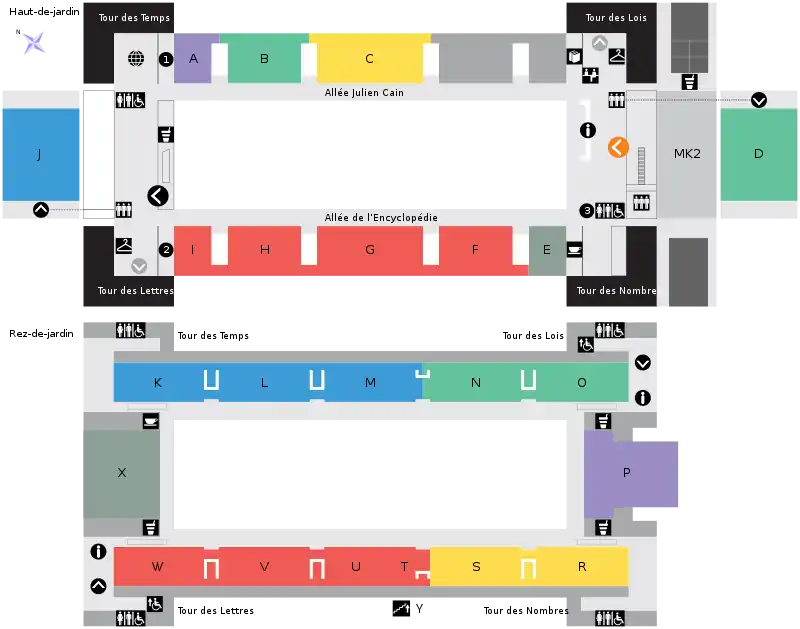
As of 2016, the BnF contained roughly 14 million books at its four Parisian sites (Tolbiac, i.e. Bibliothèque François-Mitterrand, and Richelieu, Arsenal and Opéra) as well as printed documents, manuscripts, prints, photographs, maps and plans, scores, coins, medals, sound documents, video and multimedia documents, scenery elements..."[11] The library retains the use of the Rue de Richelieu complex for some of its collections.
| Located near the Métro station: Bibliothèque François Mitterrand. |
Mission
The National Library of France is a public establishment under the supervision of the Ministry of Culture. Its mission is to constitute collections, especially the copies of works published in France that must, by law, be deposited there, conserve them, and make them available to the public. It produces a reference catalogue, cooperates with other national and international establishments, and participates in research programs.
Manuscript collection
The Manuscripts department houses the largest collection of medieval and modern manuscripts worldwide. The collection includes medieval chansons de geste and chivalric romances, eastern literature, eastern and western religions, ancient history, scientific history, and literary manuscripts by Pascal, Diderot, Apollinaire, Proust, Colette, Sartre, etc. The collection is organised:
- according to language (Ancient Greek, Latin, French and other European languages, Arabic, Coptic, Ethiopian, Hebrew, Persian, Turkish, Near- and Middle-Eastern languages, Chinese, Japanese, Tibetan, Sanskrit,Tamil,Indian languages, Vietnamese, etc.)
- The library holds about 5,000 Ancient Greek manuscripts, which are divided into three fonds: Ancien fonds grec, fonds Coislin, and Fonds du Supplément grec.[12]
- according to content: learned and bibliophilic, collections of learned materials, Library Archives, genealogical collections, French provinces, Masonic collection, etc.
Digital library
Gallica[13] is the digital library for online users of the Bibliothèque nationale de France and its partners. It was established in October 1997. Today it has more than 6 million digitized materials of various types: books, magazines, newspapers, photographs, cartoons, drawings, prints, posters, maps, manuscripts, antique coins, scores, theater costumes and sets, audio and video materials. All library materials are freely available.
On February 10, 2010, a digitized copy of Scenes of Bohemian Life by Henri Murger (1913) became Gallica's millionth document. And in February 2019, the five millionth document was a copy of the manuscript "Record of an Unsuccessful Trip to the West Indies" stored in the Bibliothèque Inguimbertine.
As of 1 January 2020, Gallica had made available on the Web about:
- 6 million documents
- 690,311 books
- 176,341 maps
- 144,859 manuscripts
- 1,468,952 images
- 3,968,841 newspapers and magazines
- 51,055 sheets of music
- 51,170 audio recordings
- 510,807 objects
- 1,705 video recordings
Most of Gallica's collections have been converted into text format using optical character recognition (OCR-processing), which allows full-text search in the library materials.
Each document has a digital identifier, the so-called ARK (Archival Resource Key) of the National Library of France and is accompanied by a bibliographic description.
List of directors
1369–1792
- 1369–1411: Gilles Mallet (fr)
- 1522–1540: Guillaume Budé
- 1540–1552: Pierre Duchâtel
- 1552–1567: Pierre de Montdoré
- 1567–1593: Jacques Amyot
- 1593–1617: Jacques-Auguste de Thou
- 1617–1642: François Auguste de Thou
- 1642–1656: Jérôme Bignon
- 1656–1684: Jérôme II Bignon
- 1560–1604: Jean Gosselin
- 1604–1614: Isaac Casaubon
- 1614–1645: Nicolas Rigault
- 1645–1651: Pierre Dupuy
- 1651–1656: Jacques Dupuy
- 1656–1676: Nicolas Colbert; Pierre de Carcavi (1663-1683)
- 1676–1684: Louis Colbert; Melchisédech Thévenot (1684-1691)
- 1684–1718: Camille Le Tellier de Louvois; Nicolas Clément (1691-1712)
- 1719–1741: Jean-Paul Bignon
- 1741–1743: Jérôme Bignon de Blanzy
- 1743–1772: Armand-Jérôme Bignon
- 1770–1784: Jérôme-Frédéric Bignon; Grégoire Desaunays (from 1775 to 1793)
- 1784–1789: Jean-Charles-Pierre Le Noir (démission)
- 1789–1792: Louis Le Fèvre d'Ormesson de Noyseau
1792–present
- 1792–1793: Jean-Louis Carra and Sébastien-Roch Nicolas de Chamfort (fr)
- 1793: Jean-Baptiste Cœuilhe (interim)
- 1793–1795: Jean Baptiste Lefebvre de Villebrune
- 1795–1796: André Barthélemy de Courcay
- 1796–1798: Jean-Augustin Capperonnier
- 1798–1799: Adrien-Jacques Joly
- 1799–1800: Aubin-Louis Millin de Grandmaison
- 1800–1803: Jean-Augustin Capperonnier
- 1803–1806: Pascal-François-Joseph Gossellin
- 1806–1829: Bon-Joseph Dacier
- 1830–1831: Joseph Van Praet
- 1832: Joseph Van Praet
- 1832: Jean-Pierre Abel-Rémusat
- 1832–1837: Jean-Antoine Letronne
- 1838–1839: Edmé François Jomard
- 1839: Charles Dunoyer
- 1839–1840: Antoine Jean Letronne
- 1840–1858: Joseph Naudet
- 1858–1874: Jules-Antoine Taschereau; the Paris Commune appointed Élie Reclus (29 April to 24 May 1871)
- 1874–1905: Léopold Delisle
- 1905–1913: Henry Marcel
- 1913–1923: Théophile Homolle
- 1923–1930: Pierre-René Roland-Marcel
- 1930–1940: Julien Cain
- 1940–1944: Bernard Faÿ
- 1944–1945: Jean Laran (interim)
- 1945–1964: Julien Cain
- 1964–1975: Étienne Dennery
- 1975–1981: Georges Le Rider
- 1981–1984: Alain Gourdon
- 1984–1987: André Miquel
- 1987–1993: Emmanuel Le Roy Ladurie
- 1989–1994: Dominique Jamet
- 1994–1997: Jean Favier
- 1997–2002: Jean-Pierre Angremy
- 2002–2007: Jean-Noël Jeanneney
- 2007–2016: Bruno Racine
- 2016–present: Laurence Engel
Films about the library
Alain Resnais directed Toute la mémoire du monde, a 1956 short film about the library and its collections.
Famous patrons
Raoul Rigault, leader during the Paris Commune, was known for habitually occupying the library and reading endless copies of the newspaper Le Père Duchesne.[14]
See also
- Arcade (blinkenlights)
- Bibliothèque de l'Arsenal
- Bibliothèque-Musée de l'Opéra National de Paris
- Books in France
- Cabinet des Médailles
- Dossiers Secrets d'Henri Lobineau
- Les Enfers, a department within the Bibliothèque nationale
- Legal deposit
- National electronic library
- Charlemagne chessmen
References
- Jack A. Clarke. "French Libraries in Transition, 1789–95." The Library Quarterly, Vol. 37, No. 4 (Oct., 1967)
- "La BnF en chiffres". Archived from the original on 2007-11-28.
- Priebe, Paul M. (1982). "From Bibliothèque du Roi to Bibliothèque Nationale: The Creation of a State Library, 1789–1793". The Journal of Library History. 17 (4): 389–408. JSTOR 25541320.
- This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Rines, George Edwin, ed. (1920). . Encyclopedia Americana.
- Konstantinos Staikos (2012), History of the Library in Western Civilization: From Petrarch to Michelangelo, New Castle, DE: Oak Knoll Press, ISBN 978-1-58456-182-8
- Dunton, Larkin (1896). The World and Its People. Silver, Burdett. p. 38.
- "University and Research Libraries". Nature. 156 (3962): 417. 6 October 1945. Bibcode:1945Natur.156Q.417.. doi:10.1038/156417a0.
- Bouygues website: Bibliothèque nationale de France Archived November 27, 2006, at the Wayback Machine
- Fitchett, Joseph (30 March 1995). "New Paris Library: Visionary or Outdated?". The New York Times. Retrieved 10 April 2013.
- Ramsay, Raylene L. (2003). French women in politics: writing power, paternal legitimization, and maternal legacies. Berghahn Books. p. 17. ISBN 978-1-57181-082-3. Retrieved 21 May 2011.
- "Welcome to the BnF". BnF (Bibliothèque nationale de France). Archived from the original on 25 January 2016. Retrieved 17 January 2016.
- See the Tome III-1 link: http://editions.bnf.fr/catalogue-des-manuscrits-grecs-iii-1-supplément-grec-n°-1-à-150. The Tome III-2 is not listed on the site. The Tome III-3 link: http://editions.bnf.fr/catalogue-des-manuscrits-grecs-iii-3-supplément-grec-n°-901-1371
- Website link is https://gallica.bnf.fr/accueil/en/content/accueil-en
- Horne, Alistair (1965). The Fall of Paris: The Siege and the Commune 1870-1. St. Martin's Press, New York. pp. 29–30.
Further reading
- Bibliothèque nationale (France), Département de la Phonothèque nationale et de l'Audiovisuel. The National [Sound] Record[ings] and Audiovisual Department of the National Library [of France]. [Paris]: Bibliothèque nationale, [1986]. 9 p.
- David H. Stam, ed. (2001). International Dictionary of Library Histories. Fitzroy Dearborn. ISBN 1-57958-244-3.
- Riding, Alan. "France Detects a Cultural Threat in Google," The New York Times. April 11, 2005.
.jpg.webp)